深入理解HashTable
说明
本文是基于JDK7对HashTable进行总结。通过阅读源码,对HashTable的底层实现原理,特点等进行理解和掌握。最后,结合前两篇博文《深入理解ConcurrentHashMap》和《深入理解HashMap》,对HashTable,HashMap和ConcurrentHashMap三者的联系与区别进行阐述。
正文
HashTable的特点
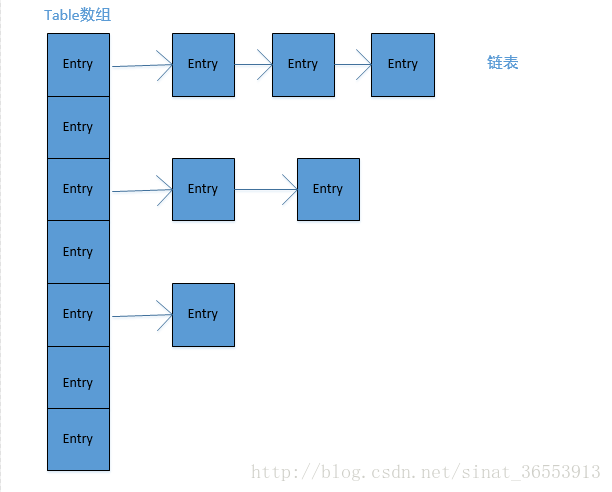
HashTable底层是一个数组链表,其特性与HashMap几乎等价,但是HashTable是线程安全的,并且不允许key或value为null
HashTable的数据结构
HashTable和HashMap底层都是一个数组链表。数组的特性是查找容易增删难,链表的特性是增删容易查找难;两者结合,使得HashTable和HashMap有了两者的特性——查找增删都容易。
HashTable继承了Dictionary类,实现了Map, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable接口
public class Hashtable<K,V>
extends Dictionary<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {HashTable的成员变量
private transient Entry[] table; //Entry类型的数组,每个成员都是一个entry类型的链表
private transient int count;// HashTable中Entry对象的个数
private int threshold;//阈值 是否需要扩容的界限 容量与负载因子的乘积
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;//允许的最大容量
HashTable的构造函数
Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)方法
该方法指定容量和负载因子
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor);
if (initialCapacity==0)
initialCapacity = 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
table = new Entry[initialCapacity];
threshold = (int)(initialCapacity * loadFactor);
}Hashtable(int initialCapacity)方法
该方法指定容量使用默认的负载因子
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0.75f);//默认负载因子为0.75
}Hashtable()方法
该方法使用默认的容量和默认的负载因子
public Hashtable() {
this(11, 0.75f);//默认初始容量为11
}Hashtable(Map< K, V> t)方法
该方法生成一个与指定map有相同映射关系的HashTable
public Hashtable(Map t) {
this(Math.max(2*t.size(), 11), 0.75f);//最小容量为11 采用默认的负载因子
putAll(t);
}HashTable的get(Object key)方法
该方法返回key对应的value值,若key不存在,返回null
public synchronized V get(Object key) {//synchronized修饰 是线程安全的
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();//计算key的hash值
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;//计算桶的位置 (比HashMap计算方式简单)
for (Entry e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return e.value;//存在 返回value
}
}
return null;//不存在 返回null
} HashTable的put(K key, V value)方法
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {//先检查value的值是否为空
throw new NullPointerException();//空 抛出异常
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
//若已存在该映射关系 则更新value值 返回旧值
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
V old = e.value;
e.value = value;
return old;
}
}
modCount++;//结构性修改 modCount值加1
if (count >= threshold) {//插入前先判断是否需要扩容,(HashMap是先插入后判断)
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();//重哈希
tab = table;
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;//计算在新数组桶的位置
}
// Creates the new entry.
Entry e = tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);//创建新的entry 采用头插法插入到链表
count++;//entry数量加1
return null;
} HashTable的rehash()方法
当entry的个数count大于等于阈值threshold时,会自动调用此方法进行扩容
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;//旧容量
Entry[] oldMap = table;//旧数组
// overflow-conscious code
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;//扩容时,变为原来容量的2倍加1
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {//判断新容量是否超出允许最大值
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)//若旧容量为最大值,不再进行重哈希
// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
Entry[] newMap = new Entry[newCapacity];//创建新数组
modCount++;//结构性修改
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);//新阈值
table = newMap;
for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {//从数组尾部开始遍历,将entry赋值到新数组
for (Entry old = oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
Entry e = old;
old = old.next;
//在重新计算桶的位置时,由于容量的变化,会使原来同一个桶中entry分散到不同位置
int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
e.next = newMap[index];//采用头插入法
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
}
HashTable的clear()方法
public synchronized void clear() {
Entry tab[] = table;
modCount++;//结构性修改
for (int index = tab.length; --index >= 0; )
//循环遍历将数组中的每个桶置为null
tab[index] = null;
count = 0;
}HashTable的contains(Object value)方法
该方法与containsKey(Object key)方法一样,都是从数组尾部遍历查找
public synchronized boolean contains(Object value) {
if (value == null) {//先判断value值是否为null
throw new NullPointerException();
}
Entry tab[] = table;
for (int i = tab.length ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if (e.value.equals(value)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} HashTable的遍历
keys()方法
该方法返回key的枚举类型
public synchronized Enumeration keys() {
return this.getEnumeration(KEYS);
} elements()方法
该方法返回value的枚举类型
public synchronized Enumeration elements() {
return this.getEnumeration(VALUES);
} keySet()方法
该方法返回key的set集合,再根据key得到value
public Set keySet() {
if (keySet == null)
//synchronized修饰集合 线程安全
keySet = Collections.synchronizedSet(new KeySet(), this);
return keySet;
} entrySet()方法
该方法返回entry的set集合
public Set> entrySet() {
if (entrySet==null)
entrySet = Collections.synchronizedSet(new EntrySet(), this);
return entrySet;
} values()方法
该方法返回value的Collection视图
public Collection values() {
if (values==null)
values = Collections.synchronizedCollection(new ValueCollection(),
this);
return values;
} HashTable、 HashMap、ConcurrentMap的联系与区别
HashTable与HashMap的联系与区别
实现模板不同
二者都实现了Map接口
HashTable继承自Dictionary类,而HashMap继承自AbstractMap限制不同
HashTable不允许key或value值为null,HashMap允许key和value值为null,且key为null只有一个- 安全性不同
HashTable是线程安全的,类中的方法使用synchronized修饰,HashMap是非线程安全
HashTable与ConcurrentHashMap的联系和区别
安全机制不同
二者都是线程安全的
HashTable是方法使用synchronized保证线程安全,每次只允许一个线程操作,每次操作都要锁整个表
ConcurrentHashMap采用的是分段锁机制,默认情况下允许16个线程同时操作,操作是只锁操作的segment,不锁整个表,并发性能更高限制相同
都不允许key或value值为null
参考的优秀博文
http://blog.csdn.net/justloveyou_/article/details/72862373