shell执行流程控制及运算符1
目录
- 1. 条件判断
-
- 1.1 判断方式
- 1.2 判断文件类型
- 1.3 判断文件权限
- 1.4 判断文件新旧
- 1.5 判断整数大小
- 1.6 判断字符串
- 1.7 多重条件判断
- 2. if语句
-
- 练习1:根据当前登录用户uid判断是否为超级用户?
- 练习2:用户输入云服务器相关信息(主机名),判断主机名输入是否合法?
- 练习3:判断当前主机是否和远程主机ping通
- 练习4:判断Web服务器中httpd进程是否存在?
- 练习5:判断一个软件包是否安装
- 练习6: 判断当前内核主版本是否为2,且次版本是否大于等于6
- 3. for循环
-
- 3.1 列表循环
- 3.2 不带列表循环
- 3.3 类C语言循环
- 3.4 跳出循环
- 练习 1.计算1-100奇数和
- 练习 2. 判断所输整数是否为质数
- 练习 3. 批量创建用户
- 练习 4. 检测10台与您当前主机直连主机是否网络通常,通则显示主机的ip列表
- 4. while
-
- 练习1:循环打印1-5
- 练习2:循环计算1-50的偶数和
- 练习3:当输入yes/YES才结束程序的执行,否则会告知用户输入字符串
- 5. until
-
- 练习1:当输入yes/YES才结束程序的执行,否则会告知用户输入字符串
- 总结与作业
1. 条件判断
1.1 判断方式
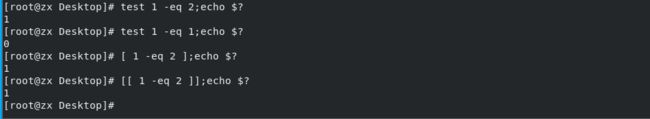
方式1:test
方式2: [ ]
方式3: [[ ]]支持正则
1.2 判断文件类型
判断参数含义
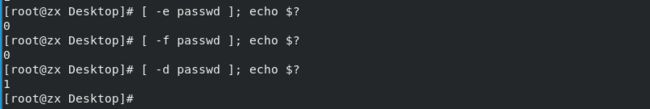
-e ##判断文件是否存在(任何类型文件)
-f ##判断文件是否存在并且是一个普通文件
-d ##判断文件是否存在并且是一个目录
-L ##判断文件是否存在并且是一个软链接文件
-b ##判断文件是否存在并且是一个块设备文件
-S ##判断文件是否存在并且是一个套接字文件
-c ##判断文件是否存在并且是一个字符文件
-p ##判断文件是否存在并且是一个命名管道文件
-s ##判断文件是否存在并且是一个非空文

1.3 判断文件权限
判断 参数含义
-r 当前用户对其是否有读权限
-w 当前用户对其是否有写权限
-x 当前用户对其是否有执行权限
-u 当前用户对其是否有suid特殊权限(高级权限冒险位)
-g 当前用户对其是否有guid特殊权限(高级权限强制位)
-k 当前用户对其是否有o+t特殊权限(高级权限粘滞位)

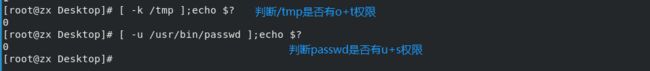
o+t权限:任何用户可以写,但只有文件拥有者和超级用户可以删
u+s权限:针对某个程序任何用户都有读写这个程序的权限
g+s权限:组里的目录下文件编入到此群组中,无论是哪个用户创建的文件
1.4 判断文件新旧
判断参数含义
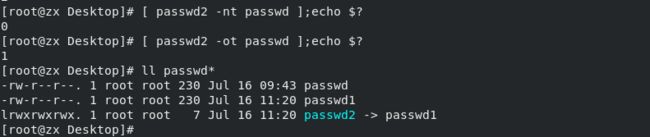
file1 -nt file2 比较file1是否比file2新
file1 -ot file2 比较file1是否比file2旧
file1 -ef file2 比较是否为同一个文件,或者用于判断硬连接,是否指向同一个inode
1.5 判断整数大小
判断参数含义
-eq 相等
-ne 不相等
-gt 大于
-ge 大于等于
-lt 小于
-le 小于等于
1.6 判断字符串
判断参数含义
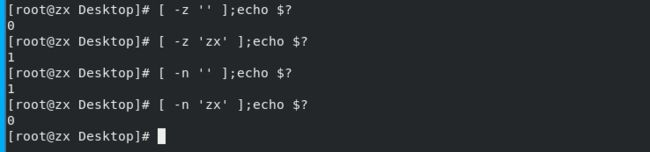
-z 判断是否为空字符串,字符串长度位0
-n 判断是否为非空字符串,字符串长度大于0
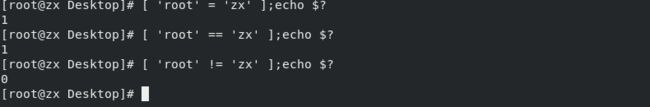
string1 = string2 判断字符串是否相等
string1 != string2 判断字符串是否不相等
1.7 多重条件判断
判断符号含义举例
-a 和 && 逻辑与,全真则真
-o 和 || 逻辑或,全假则假
[ -f /etc/passswd -a -f /etc/group]
[ -f /etc/passwd ] && [ -f /etc/group ]
[ -f /etc/passswd -o -f /etc/group ]
[ -f /etc/passwd ] || [ -f /etc/group ]
2. if语句
流程控制语句
if 条件判断语句;then
command1
elif 条件判断语句;then
command2
else
command3
fi
拓展: 类C风格的数值比较规则
• ((表达式))
• =表示赋值
• ==表示判断数值是否相等
练习1:根据当前登录用户uid判断是否为超级用户?
提示:uid=0代表超级用户
如果是超级用户输出”the user is root”,否则输出”the user is not root”
#!/bin/bash
if [ “id -u” -ne 0 ]; then
echo “the user is not root”
else
echo “the user is root”
fi
练习2:用户输入云服务器相关信息(主机名),判断主机名输入是否合法?
#!/bin/bash
read -p ‘请输入主机名:’ hostname
if [-z "${hostname}" ];then
ehco “please rewrite hostname”
else
echo $hostname
练习3:判断当前主机是否和远程主机ping通
#!/bin/bash
read -p "please input ipaddress:" address
#[ ping -c1 $address &>/dev/null ] && echo “disconnect” || ehco “connect”
#或
ip=$*
if [ -z ip ];then
echo 1
else
ping -c1 $ip &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0];then
ehco “$ip can ping”
else
echo “ip can not ping”
fi
fi
练习4:判断Web服务器中httpd进程是否存在?
#!/bin/bash
name = $*
gprep $name &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo “$name process exists”
else
echo “$name process not exists”
fi
3.输入一个用户,用脚本判断该用户是否存在?
#!/bin/bash
userid = $*
ip $userid &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo “$userid exists”
else
echo “$ userid not exists”
fi
练习5:判断一个软件包是否安装
如果没安装则安装它(假设本地yum源已配好)
#!/bin/bash
read -p "please input package name:" name
rpm -ql $name &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo "software has installed"
else
echo "software uninstall"
dnf install -y $name 1> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0];then
echo "$name install succeed"
else
echo "$name install failed"
fi
fi
练习6: 判断当前内核主版本是否为2,且次版本是否大于等于6
如果都满足则输出当前内核版本,返回内核版本
uname -r 第一列主版本,第二列次版本
#!/bin/bash
versdetail='uname -r'
Mainversion='awk -F . ‘$1’ versdetail'
Salveversion='awk -F . ‘$2’ versdetail'
if [ $Mainversion == 2 -a $Salveversion -ge 6 ];then
echo “$versdetail”
fi
3. for循环
for ## 定义变量
do ## 使用变量,执行动作
done ## 结束标志
3.1 列表循环
格式一:
#!/bin/bash
for n in `seq 2 2 10`
do
echo $n
done
格式二:
for n in 1 2 3
do
echo $n
done
格式三:
for n in {
10..1..2} ##从10到1步长为2
do
echo $n
done
3.2 不带列表循环
for var
do
echo $var
done
echo "脚本后面有$#个参数"
3.3 类C语言循环
for ((WESTOS=0;WESTOS<10;WESTOS++)) ##i+=2
do
echo $WESTOS
done
3.4 跳出循环
循环体: do…done之间的内容
continue:继续;表示循环体内下面的代码不执行,重新开始下一次循环
break:打断;马上停止执行本次循环,执行循环体外的代码
exit:表示直接跳出程序
练习 1.计算1-100奇数和
for num in ‘1..100..2’
sum=0
do
let sum=$sum+$num ##let以数值的方式进行相加
done
echo $sum
练习 2. 判断所输整数是否为质数
num=$*
if [ $num=2 ];then
echo “是质数”
elif [ $num=3 ];then
echo “是质数”
else
for i in {
2..num-1}
do
if [ $num%$i=0 ];then
echo “不是质数”
exit
fi
done
fi
echo "$number是质数" && exit
练习 3. 批量创建用户
- 需求:批量加5个新用户,以u1到u5命名,并统一加一个新组,组名为class,统一改密码为123,
- 要求这几个用户的家目录都在/rhome
- 思路
● 添加用户的命令
● 判断class组是否存在
● 根据题意,判断该脚本循环5次来添加用户
● 给用户设置密码,应该放到循环体里面
#!/bin/bash
echo '1. Create Group'
grep -w class /etc/group &>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo “group [class] has exist”
else
groupadd class
[ $? -eq 0 ]&& echo “group [class] creat ok” || echo “group [class] creat filed”
fi
echo '2. Create User'
for count in {
1..5}
do
username=”u$count”
id $username &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0];then
echo “user $username exist”
else
useradd -G class $username
usermod -d /rhome $username
echo $username
echo 123 | passwd --stdin $username
done
练习 4. 检测10台与您当前主机直连主机是否网络通常,通则显示主机的ip列表
#!/bin/bash
for i in {
1..10}
do
if ping -c1 192.168.43.$i &> /dev/null then
echo 192.168.43.$I is connection
sed -i "/192.168.43.$1" /mnt/list
else
echo 192.168.43.$I is timeout
fi
done
echo "*********ping通ip列表********"
cat /mnt/list
4. while
##不定循环
while [ condition ] <== 中括号内的状态就是判断式
do <== 循环的开始
程序段落
done <== 循环的结束
##while表示当…时,因此是当condition条件成立时进行循环,直到condition的条件不成立才停止
练习1:循环打印1-5
i=1
while [ $i -le 5 ]
do
echo $i
$i=$i+1
done
练习2:循环计算1-50的偶数和
i=2
sum=0
while[ $i -le 50]
do
let $sum=$sum+i
let $i=$i+2
done
练习3:当输入yes/YES才结束程序的执行,否则会告知用户输入字符串
while [ "$I" != "yes" -a "$I" != "YES" ]
do
read -p "Please Input yes/YES to stop program: " I
done
echo "OK,Exit Successfully!"
5. until
不定循环
until [ condition ]
do
程序段落
done
##只有当…时循环才会结束,先做do操作,满足until条件时,done,否则会一直进行循环
练习1:当输入yes/YES才结束程序的执行,否则会告知用户输入字符串
until [ "$I" == "yes" -o "$I" == "YES" ]
do
read -p "Please Input yes/YES to stop program: " I
done
echo "OK,Exit Successfully!"
总结与作业
● 判断/tmp/run目录是否存在,如果不存在就建立,如果存在就删除目录里所有文件
#!/bin/bash
if [ -d tmp/run ];then
echo "dir exist";
rm -fr /tmp/run/*
echo "files have deleted"
else
mkdir /tmp/run
echo "dir has build"
}
● 输入一个路径,判断路径是否存在,输出是文件还是目录,如果是链接文件
#!/bin/bash
read -p "Input a path:" path
if [ -L $path -a -e $path ];then
echo "this is effective link"
elif [ -L $path -a ! -e $path ];then
echo "this is not effective link"
elif [ -d $path ];then
echo "this is a director"
elif [ -f $path ];then
echo "this is file"
else
echo "the file is not exist"
fi
● 交互模式要求输入一个ip,然后脚本判断这个IP对应的主机是否能ping 通,输出结果类似于:
Server 10.1.1.20 is Down! 最后要求把结果邮件到本地管理员root@localhost
mail01@localhost
#!/bin/bash
mailaddr="root@localhost mail@localhost"
read -p "please input ip:" IP
ping -c 1 $IP > /dev/null 2>&1
if [ $? -eq 0 ] ;then
echo "Server $ip if ok" | mail -s 'check server' $mailaddr
else
echo "Server $ip if DOWN" | mail -s 'check server' $mailaddr
fi
● 写一个脚本/home/program,要求当给脚本输入参数hello时,脚本返回world,给脚本输入参数
world时,脚本返回hello。而脚本没有参数或者参数错误时,屏幕上输出
“usage:/home/program hello or world”
#!/bin/bash
while [ "$i" != "exit" ]
do
read -p "please input:" i
if [ "$i" == "hello" ];then
echo "world"
elif [ "$i" == "world" ];then
echo "hello"
else
echo "usage:/home/program hello or world"
fi
done


