Spring源码分析,资源文件Rsource,工厂BeanFactory,读取器BeanDefinitionReader 执行流程解读
目录
- Spring 解析
-
- 示例
- 执行流程
- Spring对应Bean管理的核心组件:
- IOC和DI概念
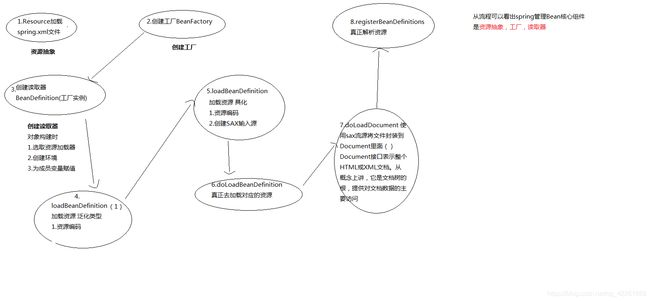
- 1.类路径下的资源 将其具体抽象成资源对象
- 2.创建Bean工厂实例
- 3.创建bean读取器实例
-
- 环境Environment
- 总结:
- 将读取的资源放到defaultListableBeanFactory工厂当中
-
- loadBeanDefinitions
- doLoadBeanDefinitions
- registerBeanDefinitions
- 总结
-
- 4.解析XML文件,将Bean注册到容器当中
-
- BeanDefinitionDocumentReader
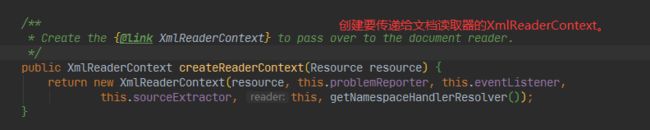
- createReaderContext(resource)
- DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(重要)
-
- doc
- doregisterBeanDefinitions
- BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
- parseBeanDefinitions
- parseDefaultElement
- processBeanDefinition 完成解析和注册
- 1处理给定的bean元素,解析bean定义 将其封装到BeanDefinitionHolder持有对象当中
-
- parseBeanDefinitionElement
- parseBeanDefinitionElement方法
- 2.将其注册到工厂当中
-
- BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
- registerBeanDefinition
- 总结:关于springbean实例的注册流程(重要)
Spring 解析
示例
新增一个Student类
/**
* POJO: Plain Old Java Object
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
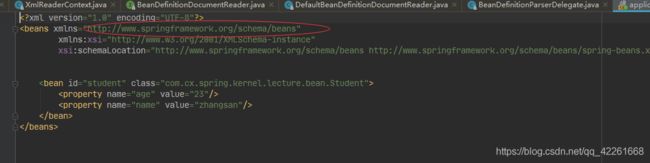
编写Spring.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="student" class="com.cx.spring.kernel.lecture.bean.Student">
<property name="age" value="23"/>
<property name="name" value="zhangsan"/>
</bean>
</beans>
定义一个main方法
/*
IOC(Inverse of Control,控制反转) 本该由使用者来创建对象我们将指定资源交给工厂 此时由工厂进行创建其对应对象 将其加载到内存当中
DI (Dependency Injection,依赖注入) A中依赖B此时将A加载到IOC 此时B也得被加载到IOC 此时A才能被调用。 此时就称为依赖注入
1.需要将bean的定义信息声明在Spring的配置文件当中
2.需要通过Spring抽象出的各种Resource来指定对应的配置文件。
3.需要显示的声明一个Spring工厂,该工厂用来掌控我们在配置文件中所声明的各种bean以及bean之间的依赖关系与注入关系
4.需要定义一个配置信息读取器,该读取器用来读取之前所定义的bean配置文件信息
5.读取器的作用是读取我们所声明的配置文件信息,并且将读取后的信息装配到之前所声明的工厂当中
6.需要将读取器与工厂以及资源对象进行相应的关联处理。
7.工厂所管理的全部对象装配完毕,可以供客户端直接调用,获取客户端想要使用的各种bean对象。
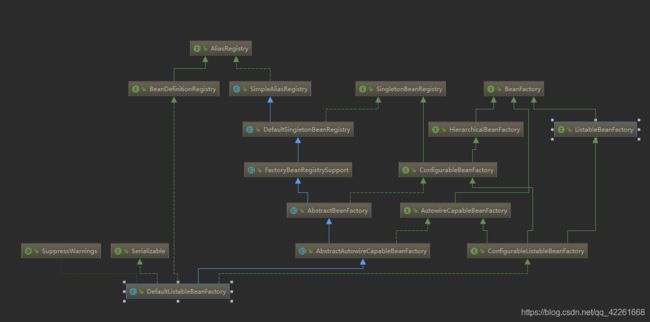
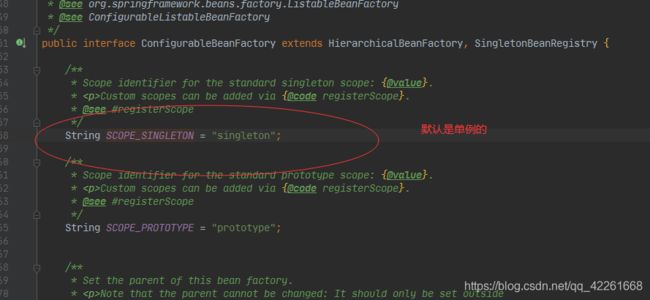
Spring对应Bean管理的核心组件:
1.资源抽象ClassPathResource
2.工厂DefaultListableBeanFactory
3.配置信息读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader (当读取器将资源读取到工厂当中 此时我们只需要跟工厂打交道)
BeanFactory 是Spring工厂 最顶层的抽象(类似Object类) 我们使用的抽象bean工厂都是直接或间接的衍生至BeanFactory
*/
public class SpringClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//类路径下的资源 将其具体抽象成资源对象
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
//创建Bean工厂
DefaultListableBeanFactory defaultListableBeanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
//创建bean读取器
BeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(defaultListableBeanFactory);
//将读取的资源放到defaultListableBeanFactory工厂当中
beanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
//读取完我们需要哪个对象找工厂要
Student student = (Student) defaultListableBeanFactory.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.getAge());
System.out.println(student.getName());
}
}
执行流程
-
1.需要将bean的定义信息声明在Spring的配置文件当中
-
2.需要通过Spring抽象出的各种Resource来指定对应的配置文件。
-
3.需要显示的声明一个Spring工厂,该工厂用来掌控我们在配置文件中所声明的各种bean以及bean之间的依赖关系与注入关系
-
4.需要定义一个配置信息读取器,该读取器用来读取之前所定义的bean配置文件信息
-
5.读取器的作用是读取我们所声明的配置文件信息,并且将读取后的信息装配到之前所声明的工厂当中
-
6.需要将读取器与工厂以及资源对象进行相应的关联处理。
-
7.工厂所管理的全部对象装配完毕,可以供客户端直接调用,获取客户端想要使用的各种bean对象。
Spring对应Bean管理的核心组件:
-
1.资源抽象ClassPathResource
-
2.工厂DefaultListableBeanFactory
-
3.配置信息读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader (当读取器将资源读取到工厂当中 此时我们只需要跟工厂打交道)
IOC和DI概念
IOC(Inverse of Control,控制反转) 本 该由使用者来创建对象我们将指定资源交给工厂 此时由工厂进行创建其对应对象 将其加载到内存当中=
DI (Dependency Injection,依赖注入) A中依赖B此时将A加载到IOC 此时B也得被加载到IOC 此时A才能被调用。 此时就称为依赖注入
1.类路径下的资源 将其具体抽象成资源对象
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
/**
*
为类加载器的使用创建一个新的类路径资源。前导斜杠将被删除,
因为类加载器资源访问方法将不接受它。
*
*/
public ClassPathResource(String path) {
this(path, (ClassLoader) null);
}
/**
* 为类使用创建新的ClassPathResource。路径可以是相对于给定类的,
* 也可以是通过正斜杠在类路径中的绝对路径
*/
public ClassPathResource(String path, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
//底层将传过来的路径进行校正得到合法的路径
String pathToUse = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
if (pathToUse.startsWith("/")) {
pathToUse = pathToUse.substring(1);
}
//得到正常使用的路径 给成员变量赋值
this.path = pathToUse;
this.classLoader = (classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
构建Resource 对象 为成员变量赋值
2.创建Bean工厂实例
DefaultListableBeanFactory defaultListableBeanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
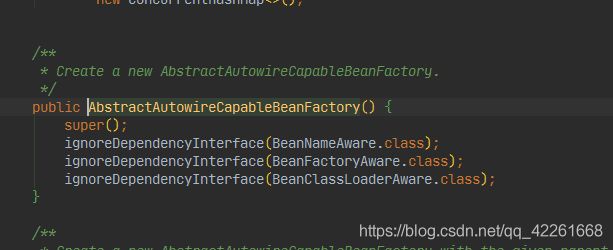
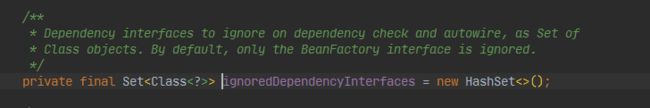
程序在实例化时。将spring提供的三个接口忽略掉,防止他们被解析,也就是说spring不希望当前工厂解析时加载到对应的接口
3.创建bean读取器实例
BeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(defaultListableBeanFactory);
doc
bean定义读取器的简单接口。使用资源和字符串位置参数指定加载方法。
具体的bean定义阅读器当然可以为bean定义添加额外的load和register方法,具体到bean定义格式。
请注意,bean定义读取器不必实现此接口。它只为希望遵循标准命名约定的bean定义读者提供建议。
简单来说就是读取bean的定义通过loadBeanDefinitions这个读取器最终的目的是为构建resource里的bean实例,而该实例是通过传入的BeanFactory来创建
/**
* 为新的XmlBean读取器创建新的XmlBean工厂。
*/
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry);//调用父类的AbstractBeanDefinitionReaher
}
/**
为给定的bean工厂创建一个新的AbstractBeanDefinitionReader。如果传入的BeanFactory不仅实现了
BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,而且实现了ResourceLoader接口,那么它也将用作默认的ResourceLoader。
通常情况下org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext实现。
如果给定一个纯BeanDefinitionRegistry,则默认的ResourceLoader将是
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver。
如果传入的bean factory也实现EnvironmentCapable,则此读取器将使用它的环境。
否则,读取器将初始化并使用标准环境。所有ApplicationContext实现都支持环境,
而普通的BeanFactory实现则不支持。
*/
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
//工厂赋值
this.registry = registry;
// 确定要使用的ResourceLoader。
if (this.registry instanceof ResourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = (ResourceLoader) this.registry;
}
else {
//如果没有定义资源加载器自定义一个类加载器加载资源
this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
}
// Inherit Environment if possible
if (this.registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
//如果传入的bean factory也实现EnvironmentCapable,则此读取器将使用它的环境(概要文件和属性信息)。
this.environment = ((EnvironmentCapable) this.registry).getEnvironment();
}
else {
//否则,读取器将初始化并使用标准环境
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
环境Environment

多种配置信息来源的一种抽象和提取。Environment定义了Profiles的方法处理。PropertyResolver定义了Property属性相关的处理
- 接口,表示当前应用程序正在其中运行的环境。为应用程序环境的两个关键方面建模:概要文件和属性。与属性访问相关的方法通过PropertyResolver(专注于属性的处理)上接口公开
- 概要文件是一个命名的、逻辑的bean定义组,只有在给定的概要文件处于活动状态时才会注册到容器中。bean可以被分配给一个概要文件,不管是用XML定义的还是通过注释定义的;语法细节请参见springbeans3.1模式或@profile注释。与概要文件相关的环境对象的角色是确定哪些概要文件(如果有的话)当前处于活动状态,以及哪些概要文件(如果有的话)在默认情况下应该处于活动状态。
- 属性在几乎所有的应用程序中都扮演着重要的角色,并且可能来自各种来源:属性文件、JVM系统属性、系统环境变量、JNDI、servlet上下文参数、特殊属性对象、映射等等。与属性相关的环境对象的作用是为用户提供一个方便的服务接口,用于配置属性源并从中解析属性。
- 在ApplicationContext中管理的bean可以注册为环境感知的,或者@injecttheenvironment,以便直接查询概要文件状态或解析属性。
- 但是,在大多数情况下,应用程序级bean不需要直接与环境交互,而是可能需要将${…}属性值替换为属性占位符配置器,例如PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer,它本身是环境感知的,从spring3.1开始,默认情况下在使用context:property-placeholder/
- 环境对象的配置必须通过ConfigurableEnvironment接口完成,该接口从所有AbstractApplicationContext子类getEnvironment()方法返回。请参阅ConfigurableEnvironment Javadoc,以获取在应用程序上下文refresh()之前操作属性源的用法示例。
总结:
创建读取器 spring还是会在底层判断创建资源加载器和对应的环境
将读取的资源放到defaultListableBeanFactory工厂当中
beanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
loadBeanDefinitions 做了两件事
1.对xml信息的整体解析
2,将解析完的信息放在一个bean中由工厂来进行统一管理

loadBeanDefinitions
/**
*从指定的XML文件加载bean定义。
*/
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//将资源编码整合成一个bean实例
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
/**
* 从指定的XML文件加载bean定义。
* @param encodedResource 编码后的资源文件
* @return 找到的bean定义数
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
//是否启用跟踪
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
//获取当前线程安全的EncodedResource集合
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
//现有资源存在的话抛异常
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
//防止资源导入中AB互相依赖 循环导入 陷入死循环
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
//读取配置文件信息 jdk1.7提供的获取流无需关闭
try (InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream()) {
//SAX流读取的方式将流包装
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
//如果编码不为空
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
//采用encodedResource的编码格式 解析xml
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
/*
准备工作完成
1.SAX流包装
2.SAX流编码
将SAX流和xml资源 doLoadBeanDefinitions
SAX流解析xml资源
*/
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
//threadLocal 是弱引用 使用完需要主动关闭 防止内存泄露
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
doLoadBeanDefinitions
/**
*真正从指定的XML文件加载bean定义。
* @param inputSource 要从中读取的SAX输入源
* @param resource the XML文件的资源描述符
* @return 找到的bean定义数
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
* @see #doLoadDocument
* @see #registerBeanDefinitions
*/
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
/*
Document接口表示整个HTML或XML文档。
从概念上讲,它是文档树的根,提供对文档数据的主要访问。
将XML数据封装成一个Document 他表示整个HTML或XML文档
*/
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
/*
解析Document 文档数据 返回解析bean数量
*/
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
registerBeanDefinitions
1.创建解析器类的新实例,并对其调用registerBeanDefinitions
2.注册给定DOM文档中包含的bean定义 到容器上面。由loadBeanDefinitions调用。
/**
1.创建解析器类的新实例,并对其调用registerBeanDefinitions
* 2.注册给定DOM文档中包含的bean定义 到容器上面。由loadBeanDefinitions调用。
* @param doc document对象
* @param 资源文件
* @return 找到的bean定义数
*/
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//创建资源读取器
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
//获取工厂解析之前解析的数量(其实就是看ConcurrentHashMap的size)
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
//通过解析器正式开始解析
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
//可能存在注解解析导致之前解析有数据 解析后解析数-解析前解析数
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
总结
4.解析XML文件,将Bean注册到容器当中
在spring当中 Default开头基本都是某个接口的具体实现类 do开头为真正执行的逻辑代码
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
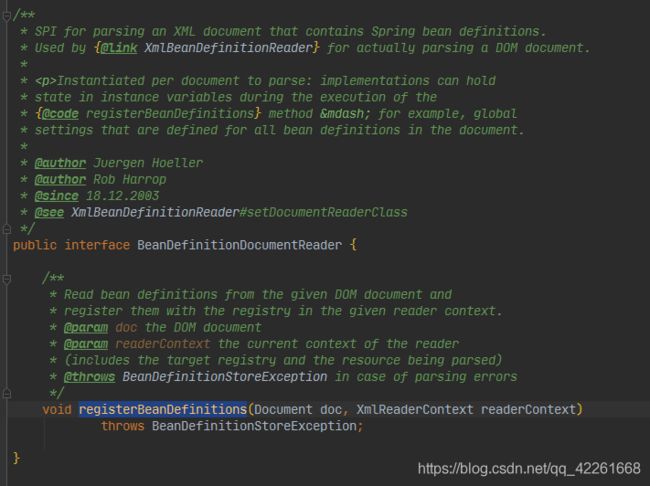
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader
doc
- 用于解析包含springbean定义的XML文档的SPI(接口规范,子类必须遵守规范)。由XmlBeanDefinitionReader用于实际分析DOM文档。
- 实例化每个要解析的文档:在执行registerBeanDefinitions方法期间,实现可以在实例变量中保存状态—例如,为文档中所有bean定义定义的全局设置。
他有个很重要的唯一方法用来想容器注册Bean
/**
*从给定的DOM文档中读取bean定义,并在给定的reader上下文中向注册表注册它们。
* @param doc the DOM document
* @param readerContext 读取器的当前上下文(包括目标注册表和正在解析的资源)
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors
*/
void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
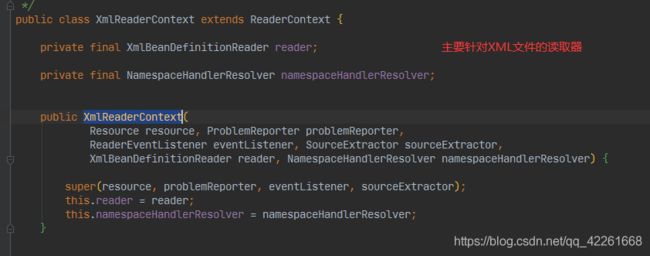
createReaderContext(resource)
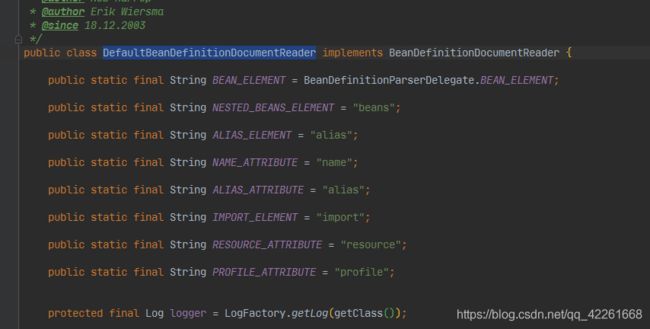
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(重要)
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的实现类主要用来解析spring.xml里的数据,该类封装xml里所有的标签属性(一级标签)
doc
- BeanDefinitionDocumentReader接口的默认实现,该接口根据“Spring-Beans”DTD和XSD格式(spring的默认XMLBean定义格式)读取bean定义。
- 所需XML文档的结构、元素和属性名称都是在此类中硬编码的。(当然,如果需要生成这种格式,可以运行一个转换)。不需要是XML文档的根元素:这个类将解析XML文件中的所有bean定义元素,而不管实际的根元素是什么。
doregisterBeanDefinitions
使用委托模式和来处理 xml数据模板模式来扩展执行前后的逻辑
/**
* This implementation parses bean definitions according to the "spring-beans" XSD
* (or DTD, historically).
* Opens a DOM Document; then initializes the default settings
* specified at the {@code
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
//获取文档元素
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
//开始解析元素都将导致此方法中的递归。在为了正确地传播和保存default-*属性,
跟踪当前(父)委托,该委托可能为空。创建新(子)委托,其中引用了用于回退目的的父级,
然后最终复位这个。委托人返回其原始(父)引用。这种行为模拟了一堆委托,实际上并不需要一个。
*/
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
//采用委托模式解析BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
封装一级标签下对应的子标签属性和对应的解析方法 将解析的数据放在holder持有类当中,该类是一个委托类
parseBeanDefinitions
解析文档中根级别的元素:“import”、“alias”、“bean”。
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// 判断是否是命名空间之内的
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
//包含此节点的所有子节点的节点列表。如果没有子节点,则这是一个不包含节点的NodeList。
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
//获取子节点
Node node = nl.item(i);
//判断是否是Element元素 可能存在注释 注释标签不属于Element
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
//判断是否是命名空间之内的
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
//真正完成对元素解析 由委托对象进行解析
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
parseDefaultElement
因为“import”、“alias”、“bean”。 存在子节点 所以要用于区分 每个子节点下的数据分别进行解析
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
//import标记 加载导入的另一个bean文件
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
//import 解析子节点数据 其他同理
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
//alias标签 处理别名的注册
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
//bean标签 处理bean标签的注册
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
//beans 如果嵌套Beans 重新走一遍流程
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// 重新走一遍流程 执行递归
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
我们具体看bean的处理方案
processBeanDefinition 完成解析和注册
完成两件事
1处理给定的bean元素,解析bean定义 将其封装到BeanDefinitionHolder持有对象当中
/**
完成两件事情
* 1.处理给定的bean元素,解析bean定义
* 2.并将其注册到工厂中。
*/
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
/*获取持有对象 里面封装了《Bean》BeanDefinition(标签节点)
,bean的id值,以及对应的别名数组
一个BeanDefinition 对应一个bean标签
*/
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
//注册到工厂当中
if (bdHolder != null) {
// 加工包装 解析自定的标签属性 持有对象 返回最终的持有对象
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// 最终将加工的持有对象注册到Bean工厂当中
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// 发送注册事件
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
parseBeanDefinitionElement
解析XMLBean定义的节点
/**
* Parses the supplied {@code } element. May return {@code null}
* if there were errors during parse. Errors are reported to the
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ProblemReporter}.
*/
@Nullable
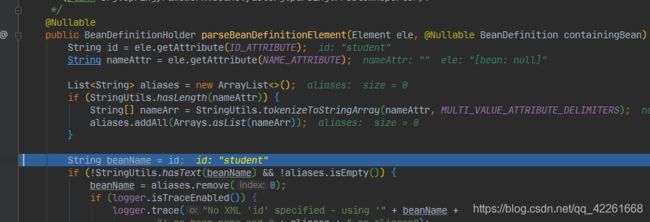
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
//获取id 和name属性值
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
//获取别名
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
//beanName =id值
String beanName = id;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
//获取beanDefinition 对象 里面封装了当前bean的所有信息
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try {
if (containingBean != null) {
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
// Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible,
// if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix.
// This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility.
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
//beanDefinition 解析的标签下所有标签数据,id对应的name 别名数组
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
parseBeanDefinitionElement方法
/**
* Parse the bean definition itself, without regard to name or aliases. May return
* {@code null} if problems occurred during the parsing of the bean definition.
*/
@Nullable
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
String parent = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
/*
解析bean的一些属性标签的一些信息和bean节点之下的标签对应属性的解析
*/
try {
///获取beanDefinition 对象 里面只封装了class对象或者 当前bean的二进制名称
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
//解析各种属性
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//构造器注入bean的解析
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
//Property属性注入解析
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
//setter注入解析
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
//返回装配了xmlBeans标签配置信息的持有对象
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}
/**
* Create a new GenericBeanDefinition for the given parent name and class name,
* eagerly loading the bean class if a ClassLoader has been specified.
* @param parentName the name of the parent bean, if any
* @param className the name of the bean class, if any
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading bean classes
* (can be {@code null} to just register bean classes by name)
* @return the bean definition
* @throws ClassNotFoundException if the bean class could not be loaded
*/
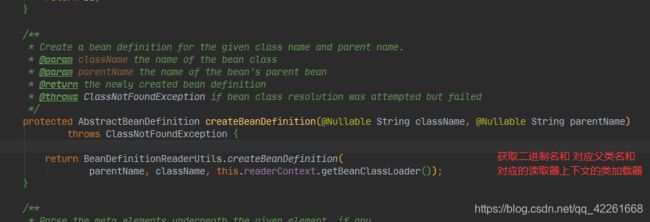
public static AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(
@Nullable String parentName, @Nullable String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//GenericBeanDefinition 描述bean定义的一些信息
GenericBeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition();
bd.setParentName(parentName);
if (className != null) {
if (classLoader != null) {
//如果类加载器存在 就直接加载对应二进制name 获取当前beanclass对象
bd.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader));
}
else {
//指定bean的二进制名 与class对象公用一个字段
bd.setBeanClassName(className);
}
}
return bd;
}
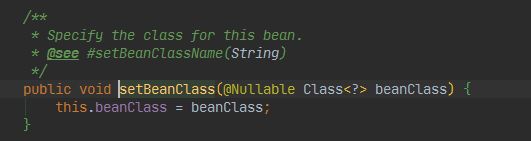

不管是name全称还是对应的class对象 都能唯一确定实例化对象 所有在使用的时候一定会根据这个字段做判断判断他是字符串还是class对象
2.将其注册到工厂当中
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
将持有对象和 当前读取器对应的工厂传入
/**
* 向给定的bean工厂注册给定的bean定义。
* @param definitionHolder bean定义,包括名称和别名
* @param registry 要注册的bean工厂
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if registration failed
*/
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
//获取bean的名字
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
// 将对应的bean注册到工厂上
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
//注册bean名称的别名(如果有的话)。
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
registerBeanDefinition

如上图可知在加载到bean工厂之前持有对象已经封装了装载《beans》标签的所有子标签的配置类,得到了beans的唯一id 的name值,以及对应的别名集合
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of BeanDefinitionRegistry interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
//bean的验证
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
/**
ConcurrentHashMap中获取持有对象
spring是拿beanname 做key 持有对象做value将数据存在 ConcurrentHashMap中
jdk1.5之前使用的hashMap
*/
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
//判断是否存在同id的BeanDefinition
if (existingDefinition != null) {
//判断相同beanId值(默认是覆盖对应bean 如果未开启复写则抛异常)
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
//若已存在的和需要装配的bean不同
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
//如果不存在上述情况 加载到工厂当中(id做key,beanDefinition做value)
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
//检查这个工厂的bean创建阶段是否已经开始,即是否有任何bean同时被标记为已创建。
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
//已经开始创建 先同步并且加载到工厂当中
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
}
else {
//反之
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
//重置当前的bean定义
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
else if (isConfigurationFrozen()) {
clearByTypeCache();
}
}
该map是DefaultListbleBeanFactory工厂的一个属性。此时将bean的唯一id做key ,解析bean BeanDefinition 做value 存储的工厂当中当中

此时我们spring将读取的资源放到defaultListableBeanFactory工厂当中底层源码流程解析完毕
总结:关于springbean实例的注册流程(重要)
- 定义好Spring的配置文件。
- 通过Resource对象将Spring配置文件进行抽象,抽象成一个具体的Resource对象(如ClassPathResoure)。
- 定义好将要使用的Bean工厂(各种BeanFactory)。
- 定义好XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象。并将工厂对象作为参数传递进去,从而构建好二者之间的关联关系转备好环境。
- 通过XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象读取之前所抽取出的Resource对象。
- 流程开始解析。
- 针对XML文件进行各种元素以及元素属性进行解析,这里面。真正解析的是通过。BeanDefinitionParserDalegate对象来完成的(委托模式)。
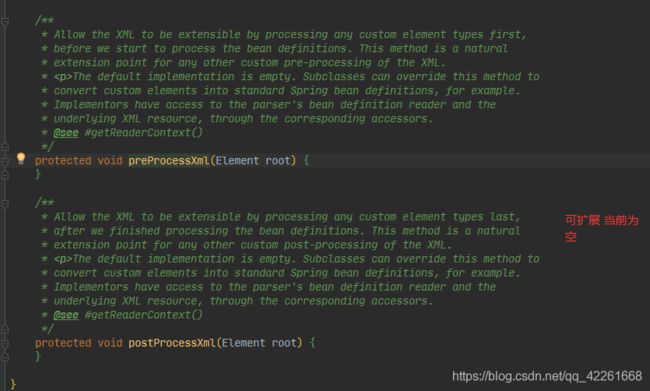
- 通过BeanDefinition对象解析XML文件时,又使用到了(模板方法设计模式pre,process,post)
- 当所有的bean标签元素都解析完毕,会将解析数据放到一个BeanDefinition对象当中,改对象非常重要,里面容纳了一个bean的所有属性。
- BeanDefinition对象创建完毕后,Spring会构建一个DeanDefinitionHolder持有对象来持有这个BeanDefinition对象。
- BeanDefinition对象主要包含三部分 beanName BeanDefinition 和别名
- 当解析完毕,hander会使用构造进来的工厂将解析的bean存放到内部一个ConcurrentHashMap当中,该Map的键是beanName(唯一),值是BeanDefinition对象。
- 调用Bean解析完毕的触发动作,从而触发相应的监听器方法的执行(观察者模式)