SpringMVC源码——doDispatch方法源码分析——一看就会
SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet是负责将请求分发,所有的请求都有经过它来统一分发。其中有一个核心的方法就是doDispatch,了解这个方法的逻辑,对了解mvc的调用流程很有帮助。下面简单的分析一下该方法。
1、源码
下面给出了源码,其实抓住主干部分,下面注释中的7个重要部分,就知道大概的脉络了。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 步骤1,获取执行链,重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 步骤2,获取适配器,重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//步骤3,拦截器pre方法,重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
//步骤4,真正处理逻辑,重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//步骤5,拦截器post方法,重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//步骤6,处理视图,重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
//步骤7,拦截器收尾方法,重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要重要
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
2、分析
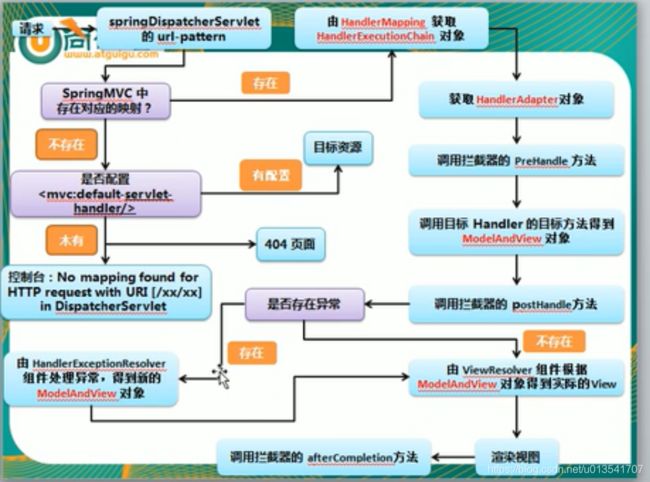
步骤1:mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
该方法得到了一个HandlerExecutionChain处理器执行链,它实际上包含了一个真正的处理器handler和若干个拦截器(若有)。
其中真正的处理器handler是由DispatcherServlet对象中的handlerMapping根据请求路径获取到的,mapping的意思就是路径跟handler的映射。
步骤2:HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());这个根据真正的处理器handler得到一个适配器的类HandlerAdapter ,只不过做了很多的预处理,比如拦截器的pre返回false就返回,等等操作。
步骤3:mappedHandler.applyPreHandle,执行拦截器的pre方法。
步骤4:最最最重要的步骤,就是去正在去执行处理方法,返回一个modelAndView。里面的逻辑较为复杂,可以自行研究。
步骤5:applyPostHandle,拦截器的post方法。
步骤6:processDispatchResult,这是去处理视图的方法,将逻辑视图转为物理视图的过程,所以逻辑视图,比如return了一个index,这仅仅是一个字符串,真正的是图应该是index.jsp页面。所以,首先根据视图解析器获取到view对象,然后使用view对象的render方法去渲染视图。
步骤7:triggerAfterCompletion,拦截器的收尾方法,该方法会在整个请求完成,即视图渲染结束之后执行,主要是做一些资源清理、记录日志信息等工作。
给一个流程图:
以上就是doDispatch方法的逻辑脉络分析,总体而言还是很简单的。喜欢的话,就点个赞吧。
【完】
正在去BAT的路上修行