redhat linux 7 及之前版本开机启动级别的设置
0:关机。不能将系统缺省运行级别设置为0,否则无法启动。
1:单用户模式,只允许root用户对系统进行维护。
2:多用户模式,但不能使用NFS(相当于Windows下的网上邻居)
3:字符界面的多用户模式。
4:未定义。
5:图形界面的多用户模式。
6:重启。不能将系统缺省运行级别设置为0,否则会一直重启。
init:
以管理员身份进入Linux,修改文件:/etc/inittab
找到“id:5:initdefault:”其中的5就是X-window,为默认的运行级别
systemd:
#
# ADDING CONFIGURATION HERE WILL HAVE NO EFFECT ON YOUR SYSTEM.
#
# Ctrl-Alt-Delete is handled by /usr/lib/systemd/system/ctrl-alt-del.target
#
# systemd uses 'targets' instead of runlevels. By default, there are two main targets:
#
# multi-user.target: analogous to runlevel 3
# graphical.target: analogous to runlevel 5
#
# To view current default target, run:
# systemctl get-default
#
# To set a default target, run:
# systemctl set-default TARGET.target
#
可以通过systemctl get-default查看开机启动级别,
设置开机启动级别default.target
- # This file is part of systemd.
- #
- # systemd is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
- # under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
- # the Free Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or
- # (at your option) any later version.
- [Unit]
- Description=Multi-User System
- Documentation=man:systemd.special(7)
- Requires=basic.target
- Conflicts=rescue.service rescue.target
- After=basic.target rescue.service rescue.target
- AllowIsolate=yes
systemd 使用链接来指向默认的运行级别。在创建新的链接前,你可以通过下面命令删除存在的链接:
rm /etc/systemd/system/default.target
systemctl isolate multi-user.target (or) systemctl isolate runlevel3.target
ln -sf /lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target /etc/systemd/system/default.target
systemctl isolate graphical.target (or) systemctl isolate runlevel5.target
ln -sf /lib/systemd/system/graphical.target /etc/systemd/system/default.target
一、runlevel 到 target的改变
在systemd的管理体系里面,以前的运行级别(runlevel)的概念被新的运行目标(target)所取代。tartget的命名类似于multi-user.target等这种形式,比如原来的运行级别3(runlevel3)就对应新的多用户目标(multi-user.target),run level 5就相当于graphical.target。
由于不再使用runlevle概念,所以/etc/inittab也不再被系统使用 — 无怪乎在新版本ubuntu上找不到inittab文件了。
而在systemd的管理体系里面,默认的target(相当于以前的默认运行级别)是通过软链来实现。如:
ln -s /lib/systemd/system/runlevel3.target /etc/systemd/system/default.target
在/lib/systemd/system/ 下面定义runlevelX.target文件目的主要是为了能够兼容以前的运行级别level的管理方法。 事实上/lib/systemd/system/runlevel3.target,同样是被软连接到multi-user.target。
注:opensuse下是在/usr/lib/systemd/system/目录下。
四、service配置文件
还以上面提到的httpd.service配置为例,httpd.service文件里可以找到如下行:
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
- 1
- 2
- 3
则表明在多用户目标(multi-user.target,相当于level3)时自动启动。如果想在runlevel 5下也自启动,则可以将配置改为如下:
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target graphical.target
- 1
- 2
- 3
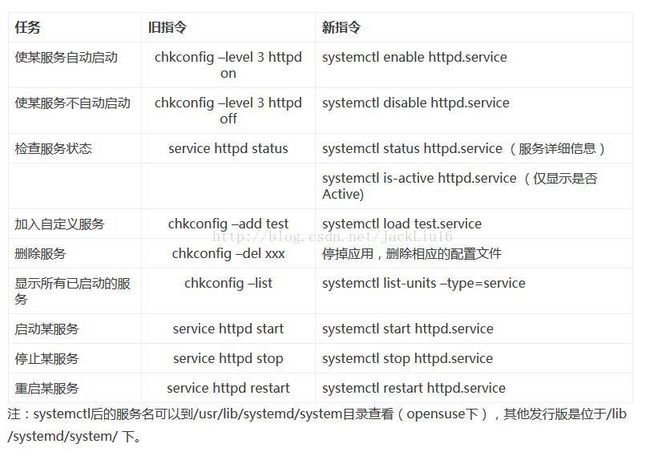
一旦设定了自动启动(enbale),就在/etc/systemd/system/.wants/下面建了一个httpd.service的软连接,连接到/lib/systemd/system/下的相应服务那里 。所以显示自动启动状态的unit (类似于chekconfig –list命令的结果),可以通过下面的方法查看:
#ls /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/systemctl 代替service和chkconfig