以下部分转载自:Blog
这篇文章讲无权二分图(unweighted bipartite graph)的最大匹配(maximum matching)和完美匹配(perfect matching),以及用于求解匹配的匈牙利算法(Hungarian Algorithm);不讲带权二分图的最佳匹配。
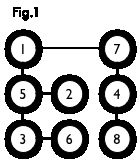
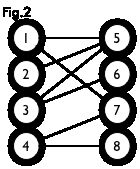
二分图:简单来说,如果图中点可以被分为两组,并且使得所有边都跨越组的边界,则这就是一个二分图。准确地说:把一个图的顶点划分为两个不相交集 U 和 V ,使得每一条边都分别连接 U 、 V 中的顶点。如果存在这样的划分,则此图为一个二分图。二分图的一个等价定义是:不含有「含奇数条边的环」的图。图 1 是一个二分图。为了清晰,我们以后都把它画成图 2 的形式。
匹配:在图论中,一个「匹配」(matching)是一个边的集合,其中任意两条边都没有公共顶点。例如,图 3、图 4 中红色的边就是图 2 的匹配。
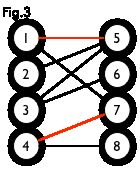
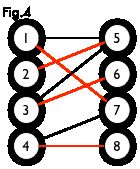
我们定义匹配点、匹配边、未匹配点、非匹配边,它们的含义非常显然。例如图 3 中 1、4、5、7 为匹配点,其他顶点为未匹配点;1-5、4-7为匹配边,其他边为非匹配边。
最大匹配:一个图所有匹配中,所含匹配边数最多的匹配,称为这个图的最大匹配。图 4 是一个最大匹配,它包含 4 条匹配边。
完美匹配:如果一个图的某个匹配中,所有的顶点都是匹配点,那么它就是一个完美匹配。图 4 是一个完美匹配。显然,完美匹配一定是最大匹配(完美匹配的任何一个点都已经匹配,添加一条新的匹配边一定会与已有的匹配边冲突)。但并非每个图都存在完美匹配。
举例来说:如下图所示,如果在某一对男孩和女孩之间存在相连的边,就意味着他们彼此喜欢。是否可能让所有男孩和女孩两两配对,使得每对儿都互相喜欢呢?图论中,这就是完美匹配问题。如果换一个说法:最多有多少互相喜欢的男孩/女孩可以配对儿?这就是最大匹配问题。

基本概念讲完了。求解最大匹配问题的一个算法是匈牙利算法,下面讲的概念都为这个算法服务。
 交替路:从一个未匹配点出发,依次经过非匹配边、匹配边、非匹配边...形成的路径叫交替路。
交替路:从一个未匹配点出发,依次经过非匹配边、匹配边、非匹配边...形成的路径叫交替路。
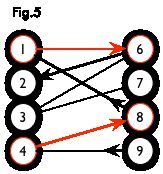
增广路:从一个未匹配点出发,走交替路,如果途径另一个未匹配点(出发的点不算),则这条交替路称为增广路(agumenting path)。例如,图 5 中的一条增广路如图 6 所示(图中的匹配点均用红色标出):
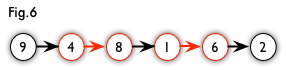
增广路有一个重要特点:非匹配边比匹配边多一条。因此,研究增广路的意义是改进匹配。只要把增广路中的匹配边和非匹配边的身份交换即可。由于中间的匹配节点不存在其他相连的匹配边,所以这样做不会破坏匹配的性质。交换后,图中的匹配边数目比原来多了 1 条。
我们可以通过不停地找增广路来增加匹配中的匹配边和匹配点。找不到增广路时,达到最大匹配(这是增广路定理)。匈牙利算法正是这么做的。在给出匈牙利算法 DFS 和 BFS 版本的代码之前,先讲一下匈牙利树。
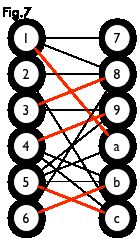
匈牙利树一般由 BFS 构造(类似于 BFS 树)。从一个未匹配点出发运行 BFS(唯一的限制是,必须走交替路),直到不能再扩展为止。例如,由图 7,可以得到如图 8 的一棵 BFS 树:
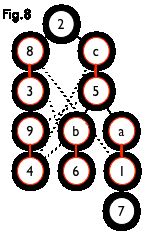
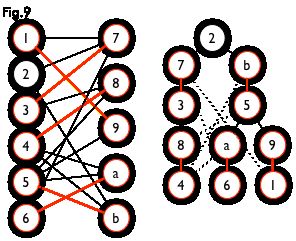
这棵树存在一个叶子节点为非匹配点(7 号),但是匈牙利树要求所有叶子节点均为匹配点,因此这不是一棵匈牙利树。如果原图中根本不含 7 号节点,那么从 2 号节点出发就会得到一棵匈牙利树。这种情况如图 9 所示(顺便说一句,图 8 中根节点 2 到非匹配叶子节点 7 显然是一条增广路,沿这条增广路扩充后将得到一个完美匹配)。
下面给出匈牙利算法的 DFS 和 BFS 版本的代码:
// 顶点、边的编号均从 0 开始
// 邻接表储存
struct Edge
{
int from;
int to;
int weight;
Edge(int f, int t, int w):from(f), to(t), weight(w) {}
};
vector G[__maxNodes]; /* G[i] 存储顶点 i 出发的边的编号 */
vector<Edge> edges;
typedef vector::iterator iterator_t;
int num_nodes;
int num_left;
int num_right;
int num_edges;
int matching[__maxNodes]; /* 存储求解结果 */
int check[__maxNodes];
bool dfs(int u)
{
for (iterator_t i = G[u].begin(); i != G[u].end(); ++i) { // 对 u 的每个邻接点
int v = edges[*i].to;
if (!check[v]) { // 要求不在交替路中
check[v] = true; // 放入交替路
if (matching[v] == -1 || dfs(matching[v])) {
// 如果是未盖点,说明交替路为增广路,则交换路径,并返回成功
matching[v] = u;
matching[u] = v;
return true;
}
}
}
return false; // 不存在增广路,返回失败
}
int hungarian()
{
int ans = 0;
memset(matching, -1, sizeof(matching));
for (int u=0; u < num_left; ++u) {
if (matching[u] == -1) {
memset(check, 0, sizeof(check));
if (dfs(u))
++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
queue Q;
int prev[__maxNodes];
int Hungarian()
{
int ans = 0;
memset(matching, -1, sizeof(matching));
memset(check, -1, sizeof(check));
for (int i=0; i<num_left; ++i) {
if (matching[i] == -1) {
while (!Q.empty()) Q.pop();
Q.push(i);
prev[i] = -1; // 设 i 为路径起点
bool flag = false; // 尚未找到增广路
while (!Q.empty() && !flag) {
int u = Q.front();
for (iterator_t ix = G[u].begin(); ix != G[u].end() && !flag; ++ix) {
int v = edges[*ix].to;
if (check[v] != i) {
check[v] = i;
Q.push(matching[v]);
if (matching[v] >= 0) { // 此点为匹配点
prev[matching[v]] = u;
} else { // 找到未匹配点,交替路变为增广路
flag = true;
int d=u, e=v;
while (d != -1) {
int t = matching[d];
matching[d] = e;
matching[e] = d;
d = prev[d];
e = t;
}
}
}
}
Q.pop();
}
if (matching[i] != -1) ++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
匈牙利算法的要点如下
- 从左边第 1 个顶点开始,挑选未匹配点进行搜索,寻找增广路。
- 如果经过一个未匹配点,说明寻找成功。更新路径信息,匹配边数 +1,停止搜索。
- 如果一直没有找到增广路,则不再从这个点开始搜索。事实上,此时搜索后会形成一棵匈牙利树。我们可以永久性地把它从图中删去,而不影响结果。
- 由于找到增广路之后需要沿着路径更新匹配,所以我们需要一个结构来记录路径上的点。DFS 版本通过函数调用隐式地使用一个栈,而 BFS 版本使用
prev 数组。
性能比较
两个版本的时间复杂度均为 O(V⋅E) 。DFS 的优点是思路清晰、代码量少,但是性能不如 BFS。我测试了两种算法的性能。对于稀疏图,BFS 版本明显快于 DFS 版本;而对于稠密图两者则不相上下。在完全随机数据 9000 个顶点 4,0000 条边时前者领先后者大约 97.6%,9000 个顶点 100,0000 条边时前者领先后者 8.6%, 而达到 500,0000 条边时 BFS 仅领先 0.85%。
补充定义和定理:
最大匹配数:最大匹配的匹配边的数目
最小点覆盖数:选取最少的点,使任意一条边至少有一个端点被选择
最大独立数:选取最多的点,使任意所选两点均不相连
最小路径覆盖数:对于一个 DAG(有向无环图),选取最少条路径,使得每个顶点属于且仅属于一条路径。路径长可以为 0(即单个点)。
定理1:最大匹配数 = 最小点覆盖数(这是 Konig 定理)
定理2:最大匹配数 = 最大独立数
定理3:最小路径覆盖数 = 顶点数 - 最大匹配数
转载部分完。
HDU2063-过山车
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 8503 Accepted Submission(s): 3755
Problem Description
RPG girls今天和大家一起去游乐场玩,终于可以坐上梦寐以求的过山车了。可是,过山车的每一排只有两个座位,而且还有条不成文的规矩,就是每个女生必须找个个男生做partner和她同坐。但是,每个女孩都有各自的想法,举个例子把,Rabbit只愿意和XHD或PQK做partner,Grass只愿意和linle或LL做partner,PrincessSnow愿意和水域浪子或伪酷儿做partner。考虑到经费问题,boss刘决定只让找到partner的人去坐过山车,其他的人,嘿嘿,就站在下面看着吧。聪明的Acmer,你可以帮忙算算最多有多少对组合可以坐上过山车吗?
Input
输入数据的第一行是三个整数K , M , N,分别表示可能的组合数目,女生的人数,男生的人数。0 1<=N 和M<=500.接下来的K行,每行有两个数,分别表示女生Ai愿意和男生Bj做partner。最后一个0结束输入。
Output
对于每组数据,输出一个整数,表示可以坐上过山车的最多组合数。
Sample Input
6 3 3
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
2 3
3 1
0
Sample Output
Author
PrincessSnow
Source
RPG专场练习赛
/*bool 寻找从k出发的对应项出的可增广路
{
while (从邻接表中列举k能关联到顶点j)
{
if (j不在增广路上)
{
把j加入增广路;
if (j是未盖点 或者 从j的对应项出发有可增广路)
{
修改j的对应项为k;
则从k的对应项出有可增广路,返回true;
}
}
}
则从k的对应项出没有可增广路,返回false;
}
void 匈牙利hungary()
{
for i->1 to n
{
if (则从i的对应项出有可增广路)
匹配数++;
}
输出 匹配数;
6 3 3
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
2 3
3 1
0
}*/
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 2000;
bool visited[MAX];
int match[MAX];
int matchNum;
int mapNum;
int BoyNum,GirlNum;
vector map[MAX];
bool isExistCrossPath(int x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < map[x].size(); ++i)
{
int j = map[x][i];
if (!visited[j])
{
visited[j] = true;
if (!match[j] || isExistCrossPath(match[j]))
{
match[j] = x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void hungary()
{
matchNum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= GirlNum; ++i) //要从1开始
{
memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited));
if (isExistCrossPath(i))
++matchNum;
}
}
int main()
{
int T, x, y, i;
// freopen("F:\\2.TXT","r",stdin);
while (cin >> T && T != 0)
{
cin >> GirlNum >> BoyNum;
memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited));
memset(match,0,sizeof(match));
for(i=0; i> x >> y;
map[x].push_back(y);
}
hungary();
cout << matchNum << endl;
}
return 0;
}
HDU1068-Girls and Boys
Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 6411 Accepted Submission(s): 2889
Problem Description
the second year of the university somebody started a study on the romantic relations between the students. The relation “romantically involved” is defined between one girl and one boy. For the study reasons it is necessary to find out the maximum set satisfying the condition: there are no two students in the set who have been “romantically involved”. The result of the program is the number of students in such a set.
The input contains several data sets in text format. Each data set represents one set of subjects of the study, with the following description:
the number of students
the description of each student, in the following format
student_identifier:(number_of_romantic_relations) student_identifier1 student_identifier2 student_identifier3 ...
or
student_identifier:(0)
The student_identifier is an integer number between 0 and n-1, for n subjects.
For each given data set, the program should write to standard output a line containing the result.
Sample Input
7
0: (3) 4 5 6
1: (2) 4 6
2: (0)
3: (0)
4: (2) 0 1
5: (1) 0
6: (2) 0 1
3
0: (2) 1 2
1: (1) 0
2: (1) 0
Sample Output
Source
Southeastern Europe 2000
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1000;
vector map[MAX];
bool visited[MAX];
int match[MAX];
int N;
bool isExistCrossPath(int x)
{
for(int i = 0; i > 1));
}
return 0;
}
HDU1150Machine Schedule
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 4943 Accepted Submission(s): 2450
Problem Description
As we all know, machine scheduling is a very classical problem in computer science and has been studied for a very long history. Scheduling problems differ widely in the nature of the constraints that must be satisfied and the type of schedule desired. Here we consider a 2-machine scheduling problem.
There are two machines A and B. Machine A has n kinds of working modes, which is called mode_0, mode_1, …, mode_n-1, likewise machine B has m kinds of working modes, mode_0, mode_1, … , mode_m-1. At the beginning they are both work at mode_0.
For k jobs given, each of them can be processed in either one of the two machines in particular mode. For example, job 0 can either be processed in machine A at mode_3 or in machine B at mode_4, job 1 can either be processed in machine A at mode_2 or in machine B at mode_4, and so on. Thus, for job i, the constraint can be represent as a triple (i, x, y), which means it can be processed either in machine A at mode_x, or in machine B at mode_y.
Obviously, to accomplish all the jobs, we need to change the machine's working mode from time to time, but unfortunately, the machine's working mode can only be changed by restarting it manually. By changing the sequence of the jobs and assigning each job to a suitable machine, please write a program to minimize the times of restarting machines.
Input
The input file for this program consists of several configurations. The first line of one configuration contains three positive integers: n, m (n, m < 100) and k (k < 1000). The following k lines give the constrains of the k jobs, each line is a triple: i, x, y.
The input will be terminated by a line containing a single zero.
Output
The output should be one integer per line, which means the minimal times of restarting machine.
Sample Input
5 5 10
0 1 1
1 1 2
2 1 3
3 1 4
4 2 1
5 2 2
6 2 3
7 2 4
8 3 3
9 4 3
0
Sample Output
Source
Asia 2002, Beijing (Mainland China)
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1000;
vector map[MAX];
bool visited[MAX];
int match[MAX];
int N, M, T, z, x, y;
bool isCrossPath(int x)
{
for(int i=0; i> N && N != 0 )
{
memset(map,0,sizeof(map));
memset(match,-1,sizeof(match));
cin >> M >> T;
for ( i=0; i< T; ++i )
{
cin >> z >> x >> y;
map[x].push_back(y);
}
cout << Hungary() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
HDU2119http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2119
题意:每次可以删除一行或者一列数,问最少几次可以把所有的1都变成0,也就是都删完。
利用二分图解
行表示二分图的一部分,列表示一部分,为1的点表示连一条边,然后求最小顶点覆盖数。
最小顶点覆盖即表示用最少的顶点把所有的边都关联到。
最小顶点覆盖 = 最大匹配。
//最大匹配
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int n,m;
vector map[101];
int match[101];
bool visited[101];
bool isExistPath(int x)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0; i < map[x].size(); ++i)
{
j = map[x][i];
if (!visited[j])
{
visited[j] = true;
if (match[j]==-1 || isExistPath(match[j]))
{
match[j] = x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int MaxMatch()
{
int i,max = 0;
for (i=0; i < n; ++i)
{
memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited));
if (isExistPath(i))
++max;
}
return max;
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("2.txt","r",stdin);
#endif
int i,j;
bool oz; //one or zero
while (cin >> n && n != 0)
{
cin >> m;
memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited));
memset(match,-1,sizeof(match));
for(i=0; i<101; ++i)
map[i].clear();
for (i=0; i < n; ++i)
{
for (j=0; j < m; ++j)
{
cin >> oz;
if (oz)
map[i].push_back(j);
}
}
cout << MaxMatch() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
// 顶点、边的编号均从 0 开始
// 邻接表储存
struct Edge
{
int from;
int to;
int weight;
Edge(int f, int t, int w):from(f), to(t), weight(w) {}
};
vector G[__maxNodes]; /* G[i] 存储顶点 i 出发的边的编号 */
vector<Edge> edges;
typedef vector::iterator iterator_t;
int num_nodes;
int num_left;
int num_right;
int num_edges;
int matching[__maxNodes]; /* 存储求解结果 */
int check[__maxNodes];
bool dfs(int u)
{
for (iterator_t i = G[u].begin(); i != G[u].end(); ++i) { // 对 u 的每个邻接点
int v = edges[*i].to;
if (!check[v]) { // 要求不在交替路中
check[v] = true; // 放入交替路
if (matching[v] == -1 || dfs(matching[v])) {
// 如果是未盖点,说明交替路为增广路,则交换路径,并返回成功
matching[v] = u;
matching[u] = v;
return true;
}
}
}
return false; // 不存在增广路,返回失败
}
int hungarian()
{
int ans = 0;
memset(matching, -1, sizeof(matching));
for (int u=0; u < num_left; ++u) {
if (matching[u] == -1) {
memset(check, 0, sizeof(check));
if (dfs(u))
++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
queue Q;
int prev[__maxNodes];
int Hungarian()
{
int ans = 0;
memset(matching, -1, sizeof(matching));
memset(check, -1, sizeof(check));
for (int i=0; i<num_left; ++i) {
if (matching[i] == -1) {
while (!Q.empty()) Q.pop();
Q.push(i);
prev[i] = -1; // 设 i 为路径起点
bool flag = false; // 尚未找到增广路
while (!Q.empty() && !flag) {
int u = Q.front();
for (iterator_t ix = G[u].begin(); ix != G[u].end() && !flag; ++ix) {
int v = edges[*ix].to;
if (check[v] != i) {
check[v] = i;
Q.push(matching[v]);
if (matching[v] >= 0) { // 此点为匹配点
prev[matching[v]] = u;
} else { // 找到未匹配点,交替路变为增广路
flag = true;
int d=u, e=v;
while (d != -1) {
int t = matching[d];
matching[d] = e;
matching[e] = d;
d = prev[d];
e = t;
}
}
}
}
Q.pop();
}
if (matching[i] != -1) ++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 交替路:从一个未匹配点出发,依次经过非匹配边、匹配边、非匹配边...形成的路径叫交替路。
交替路:从一个未匹配点出发,依次经过非匹配边、匹配边、非匹配边...形成的路径叫交替路。![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()