线程池及参数 以及 AsyncTask
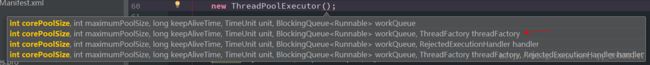
常用方式
一般常用的是第一和第二种,阿里巴巴推荐的是使用带有 ThreadFactory,也就是第二种 或者 第四种
源码参数说明
/** * Creates a new {@code ThreadPoolExecutor} with the given initial * parameters and default rejected execution handler. * * @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even * if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set * @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the * pool * @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than * the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads * will wait for new tasks before terminating. * @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument * @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are * executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable} * tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method. * @param threadFactory the factory to use when the executor * creates a new thread * @throws IllegalArgumentException if one of the following holds:
* {@code corePoolSize < 0}
* {@code keepAliveTime < 0}
* {@code maximumPoolSize <= 0}
* {@code maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize} * @throws NullPointerException if {@code workQueue} * or {@code threadFactory} is null */ public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory) { this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory, defaultHandler); }
corePoolSize:核心线程数
重点:CPU核心数
int i = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
maximumPoolSize:最大线程数
keepAliveTime:存活时间
重点:是个Long值,记得数字加单位 如:60L
unit:时间单位
重点:天、时、分、秒、微妙、毫秒、纳秒
workQueue:任务列队
直接 new 会默认使用 21亿
public LinkedBlockingDeque() { this(Integer.MAX_VALUE); }等同于
new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>(Integer.MAX_VALUE)
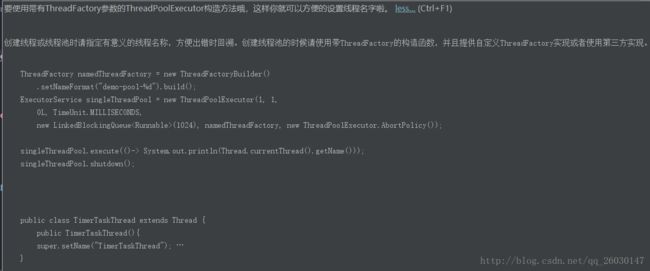
threadFactory:线程工厂
public interface ThreadFactory { /** * Constructs a new {@code Thread}. Implementations may also initialize * priority, name, daemon status, {@code ThreadGroup}, etc. * * @param r a runnable to be executed by new thread instance * @return constructed thread, or {@code null} if the request to * create a thread is rejected */ Thread newThread(Runnable r); }重点:实现类可以使用 new Thread(r,name); 定义线程名称
/** * Allocates a new {@code Thread} object. This constructor has the same * effect as {@linkplain #Thread(ThreadGroup,Runnable,String) Thread} * {@code (null, target, name)}. * * @param target * the object whose {@code run} method is invoked when this thread * is started. If {@code null}, this thread's run method is invoked. * * @param name * the name of the new thread */ public Thread(Runnable target, String name) { init(null, target, name, 0); }
AsyncTask中的线程池
private static final String LOG_TAG = "AsyncTask"; private static final int CPU_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); // We want at least 2 threads and at most 4 threads in the core pool, // preferring to have 1 less than the CPU count to avoid saturating // the CPU with background work private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = Math.max(2, Math.min(CPU_COUNT - 1, 4)); private static final int MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE = CPU_COUNT * 2 + 1; private static final int KEEP_ALIVE_SECONDS = 30; private static final ThreadFactory sThreadFactory = new ThreadFactory() { private final AtomicInteger mCount = new AtomicInteger(1); public Thread newThread(Runnable r) { return new Thread(r, "AsyncTask #" + mCount.getAndIncrement()); } }; private static final BlockingQueue<Runnable> sPoolWorkQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(128); /** * An {@link Executor} that can be used to execute tasks in parallel. */ public static final Executor THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR; static { ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( CORE_POOL_SIZE, MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE, KEEP_ALIVE_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS, sPoolWorkQueue, sThreadFactory); threadPoolExecutor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true); THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR = threadPoolExecutor; }
1、当前CPU核数 CPU_COUNT
2、核心线程数 CORE_POOL_SIZE 看说明
如果你的CPU核数是 1,那么核心线程数就是2,
如果你的CPU核数是 8,那么你的核心线程数是4
数据比较设计的很巧妙,我们可能就 if else 或者 三元计算了
3、最大线程数,核数x2+1
4、线程存活 30 S
5、双端列队 最大容量128
6、线程命名 (重要)
这里很有趣
private static final ThreadFactory sThreadFactory = new ThreadFactory() { private final AtomicInteger mCount = new AtomicInteger(1); public Thread newThread(Runnable r) { return new Thread(r, "AsyncTask #" + mCount.getAndIncrement()); } };
原子对象 mCount,调用增 1 方法,所以 线程名称 不会乱
public final int getAndIncrement() { return U.getAndAddInt(this, VALUE, 1); }