Time To Get Up
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 524288/524288 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 364 Accepted Submission(s): 288
Problem Description
Little Q's clock is alarming! It's time to get up now! However, after reading the time on the clock, Little Q lies down and starts sleeping again. Well, he has
5 alarms, and it's just the first one, he can continue sleeping for a while.
Little Q's clock uses a standard 7-segment LCD display for all digits, plus two small segments for the '':'', and shows all times in a 24-hour format. The '':'' segments are on at all times.
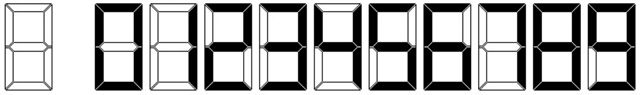
Your job is to help Little Q read the time shown on his clock.
Little Q's clock uses a standard 7-segment LCD display for all digits, plus two small segments for the '':'', and shows all times in a 24-hour format. The '':'' segments are on at all times.
Your job is to help Little Q read the time shown on his clock.
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer
T(1≤T≤1440), denoting the number of test cases.
In each test case, there is an 7×21 ASCII image of the clock screen.
All digit segments are represented by two characters, and each colon segment is represented by one character. The character ''X'' indicates a segment that is on while ''.'' indicates anything else. See the sample input for details.
In each test case, there is an 7×21 ASCII image of the clock screen.
All digit segments are represented by two characters, and each colon segment is represented by one character. The character ''X'' indicates a segment that is on while ''.'' indicates anything else. See the sample input for details.
Output
For each test case, print a single line containing a string
t in the format of
HH:MM, where
t(00:00≤t≤23:59), denoting the time shown on the clock.
Sample Input
1 .XX...XX.....XX...XX. X..X....X......X.X..X X..X....X.X....X.X..X ......XX.....XX...XX. X..X.X....X....X.X..X X..X.X.........X.X..X .XX...XX.....XX...XX.
Sample Output
02:38
Source
2017 Multi-University Training Contest - Team 4
对数字的特征进行一下判断即可。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include