在Android中,非主线程不能更新UI
上一篇文章《Anroid异步消息机制(Handler、Looper、Message、MessageQueue)以及ThreadLocal运用》提到,在Android中,非主线程不能更新UI(ViewRootImpl在主线程中创建,所以我们要在主线程中更新UI。同理,如果ViewRootImpl在子线程中创建的话,那么也可以在子线程中更新UI,也就是说在哪里更新UI和ViewRootImpl在哪里创建是关联的。默认ViewRootImpl在主线程中创建),这时候我们可以借助Handler来实现(Activiy.runOnUiThread()也可以实现,但原理也是Handler,调用的post(Runnable))“。
一、我们做个测试
1、activity_main.xml
2、MainActivity.java
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.PixelFormat;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private TextView main_thread = null;
private TextView sub_thread = null;
private TextView sub_thread_thread = null;
private TextView click_thread = null;
private TextView click_subclass_thread = null;
private TextView click_window = null;
private TextView click_subclass_window = null;
private Button click_thread_button = null;
private Button click_subclass_thread_button = null;
private Button click_button = null;
private Button click_windowManager_button = null;
private Button click_subclass_button = null;
private static String TAG = "com.example.test";
private Thread main;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
main_thread = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.main_thread);
sub_thread = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sub_thread);
sub_thread_thread = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sub_thread_thread);
click_thread = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.click_thread);
click_subclass_thread = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.click_subclass_thread);
click_window = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.click_window);
click_subclass_window = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.click_subclass_window);
main_thread.setText("MainActivity." + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "-" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
main = Thread.currentThread();
click_thread_button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.click_thread_button);
click_subclass_thread_button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.click_subclass_thread_button);
click_button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.click_button);
click_windowManager_button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.click_windowManager_button);
click_subclass_button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.click_subclass_button);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (main != Thread.currentThread()) {
Log.d(TAG, "MainActivity.sub_thread not equals main thread");
} else {
Log.d(TAG, "MainActivity.sub_thread equals main thread");
}
sub_thread.setText("MainActivity.sub_thread."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-"
+ Thread.currentThread().getId());
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (main != Thread.currentThread()) {
Log.d(TAG,
"MainActivity.sub_thread_thread not equals main thread");
} else {
Log.d(TAG,
"MainActivity.sub_thread_thread equals main thread");
}
sub_thread_thread
.setText("MainActivity.sub_thread_thread."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "-" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
}).start();
}
}).start();
click_thread_button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (main != Thread.currentThread()) {
Log.d(TAG,
"MainActivity.click_thread not equals main thread");
} else {
Log.d(TAG,
"MainActivity.click_thread equals main thread");
}
Log.d(TAG, "MainActivity.click_thread."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-"
+ Thread.currentThread().getId());
click_thread.setText("MainActivity.click_thread."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-"
+ Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
}).start();
}
});
click_subclass_thread_button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
new SubClass().start();
}
});
click_button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
Log.d(TAG, "MainActivity.click_window."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-"
+ Thread.currentThread().getId());
click_window.setText("MainActivity.click_window."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-"
+ Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
});
click_windowManager_button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
new SubWindow().start();
}
});
click_subclass_button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
new SubClassUpdate().updateMainUI();
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
class SubClass extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
if (main != Thread.currentThread()) {
Log.d(TAG,
"MainActivity.click_subclass_thread not equals main thread");
} else {
Log.d(TAG,
"MainActivity.click_subclass_thread equals main thread");
}
Log.d(TAG, "MainActivity.click_subclass_thread."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-"
+ Thread.currentThread().getId());
click_subclass_thread.setText("MainActivity.click_subclass_thread."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-"
+ Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
}
class SubWindow extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
// Looper.prepare();
TextView tx = new TextView(MainActivity.this);
tx.setText("创建子窗口");
WindowManager wm = MainActivity.this.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams params = new WindowManager.LayoutParams(
250, 150, 200, 200,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FIRST_SUB_WINDOW,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_TOAST, PixelFormat.OPAQUE);
wm.addView(tx, params);
// Looper.loop();
}
}
class SubClassUpdate {
public void updateMainUI() {
Log.d(TAG, "MainActivity.click_subclass_window."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-"
+ Thread.currentThread().getId());
click_subclass_window.setText("MainActivity.click_subclass_window."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-"
+ Thread.currentThread().getId());
TextView tx = new TextView(MainActivity.this);
tx.setText("创建子窗口-非线程创建");
WindowManager wm = MainActivity.this.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams params = new WindowManager.LayoutParams(
250, 150, 200, 200,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FIRST_SUB_WINDOW,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_TOAST, PixelFormat.OPAQUE);
//params.gravity = Gravity.RIGHT | Gravity.BOTTOM;
//params.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
wm.addView(tx, params);
}
}
}点击“点击,直接更新UI进程”,结果图如下:
点击“点击,直接建立子类更新UI线程并且跳出子窗口”,如下图所示:
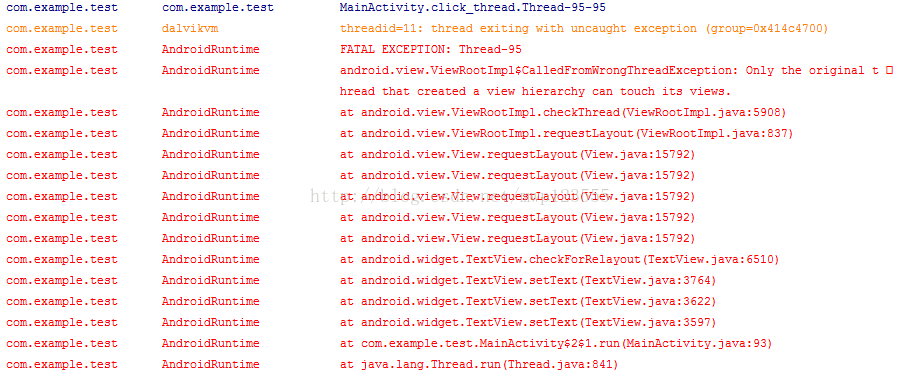
当点击“点击,直接建立子线程”和“点击,建立子类,子类中建立子线程”按钮,应用崩溃报错,如下:
从结果中可以看出,sub_thread、sub_thread_thread、click_window、click_subclass_window对应的操作可以正常更新UI;但点击按钮“点击,直接建立子线程”和“点击,建立子类,子类中建立子线程”按钮的时候,应用崩溃报错(内部类中调用)。从错误日志,可以看出调用顺序
TextView.setText()->TextView.checkForRelayout()->View.requestLayout()->ViewRootImpl.requestLayout(()->ViewRootImpl.checkThread()。
1、TextView (继承View)
private void checkForRelayout() {
// If we have a fixed width, we can just swap in a new text layout
// if the text height stays the same or if the view height is fixed.
if ((mLayoutParams.width != LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT ||
(mMaxWidthMode == mMinWidthMode && mMaxWidth == mMinWidth)) &&
(mHint == null || mHintLayout != null) &&
(mRight - mLeft - getCompoundPaddingLeft() - getCompoundPaddingRight() > 0)) {
// Static width, so try making a new text layout.
int oldht = mLayout.getHeight();
int want = mLayout.getWidth();
int hintWant = mHintLayout == null ? 0 : mHintLayout.getWidth();
/*
* No need to bring the text into view, since the size is not
* changing (unless we do the requestLayout(), in which case it
* will happen at measure).
*/
makeNewLayout(want, hintWant, UNKNOWN_BORING, UNKNOWN_BORING,
mRight - mLeft - getCompoundPaddingLeft() - getCompoundPaddingRight(),
false);
if (mEllipsize != TextUtils.TruncateAt.MARQUEE) {
// In a fixed-height view, so use our new text layout.
if (mLayoutParams.height != LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT &&
mLayoutParams.height != LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
invalidate();
return;
}
// Dynamic height, but height has stayed the same,
// so use our new text layout.
if (mLayout.getHeight() == oldht &&
(mHintLayout == null || mHintLayout.getHeight() == oldht)) {
invalidate();
return;
}
}
// We lose: the height has changed and we have a dynamic height.
// Request a new view layout using our new text layout.
requestLayout();
invalidate();
} else {
// Dynamic width, so we have no choice but to request a new
// view layout with a new text layout.
nullLayouts();
requestLayout();
invalidate();
}
} protected ViewParent mParent;
.........
@CallSuper
public void requestLayout() {
if (mMeasureCache != null) mMeasureCache.clear();
if (mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout == null) {
// Only trigger request-during-layout logic if this is the view requesting it,
// not the views in its parent hierarchy
ViewRootImpl viewRoot = getViewRootImpl();
if (viewRoot != null && viewRoot.isInLayout()) {
if (!viewRoot.requestLayoutDuringLayout(this)) {
return;
}
}
mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout = this;
}
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
if (mParent != null && !mParent.isLayoutRequested()) {
mParent.requestLayout();
}
if (mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout == this) {
mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout = null;
}
} final Thread mThread;
final ViewRootHandler mHandler = new ViewRootHandler();
.........
public ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {
mContext = context;
mWindowSession = WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession();
mDisplay = display;
mBasePackageName = context.getBasePackageName();
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
.........
}
@Override
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
checkThread();
mLayoutRequested = true;
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
void checkThread() {
if (mThread != Thread.currentThread()) {
throw new CalledFromWrongThreadException(
"Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.");
}
}
final class ViewRootHandler extends Handler {
.......
}二、非UI线程中更新UI线程
1、Handler异步消息模式
2、创建新的ViewRootImpl
比如WindowManager
在我们的测试中,点击“点击,建立子窗口”就是实现子线程中利用WindowManager建立新的ViewRootImpl,点击按钮,出现应用崩溃,报错如下图:
根据报错跟踪具体代码,分析如下:
1、WindowManager接口(实现接口ViewManager)
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params);2、WindowManagerImpl(实现接口WindowManager)
private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();
private final Context mContext;
private final Window mParentWindow;
......
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplay(), mParentWindow);
} public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null");
}
if (display == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("display must not be null");
}
if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams");
}
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
if (parentWindow != null) {
parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams);
} else {
// If there's no parent, then hardware acceleration for this view is
// set from the application's hardware acceleration setting.
final Context context = view.getContext();
if (context != null
&& (context.getApplicationInfo().flags
& ApplicationInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0) {
wparams.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED;
}
}
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
// Start watching for system property changes.
if (mSystemPropertyUpdater == null) {
mSystemPropertyUpdater = new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
synchronized (mLock) {
for (int i = mRoots.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
mRoots.get(i).loadSystemProperties();
}
}
}
};
SystemProperties.addChangeCallback(mSystemPropertyUpdater);
}
int index = findViewLocked(view, false);
if (index >= 0) {
if (mDyingViews.contains(view)) {
// Don't wait for MSG_DIE to make it's way through root's queue.
mRoots.get(index).doDie();
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("View " + view
+ " has already been added to the window manager.");
}
// The previous removeView() had not completed executing. Now it has.
}
// If this is a panel window, then find the window it is being
// attached to for future reference.
if (wparams.type >= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FIRST_SUB_WINDOW &&
wparams.type <= WindowManager.LayoutParams.LAST_SUB_WINDOW) {
final int count = mViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (mRoots.get(i).mWindow.asBinder() == wparams.token) {
panelParentView = mViews.get(i);
}
}
}
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
}从上面内容与ViewRootImpl源代码分析,我们知道ViewRootImpl会创建变量ViewRootHandler mHandler,这是Handler对象;从文章《Anroid异步消息机制(Handler、Looper、Message、MessageQueue)以及ThreadLocal运用》,我们知道新建Handler,需要调用Looper.myLooper(),它会检查当前线程是否有Looper存在,如果没有,就报错,提示我们需要通过走新建Looper的流程(Looper.prepare()->Looper.loop(),具体可以看文章)。故需要在WindowManager建立前加上Looper.prepare(),建立后加上Looper.loop(),具体看代码中注释部分。
三、Android视图
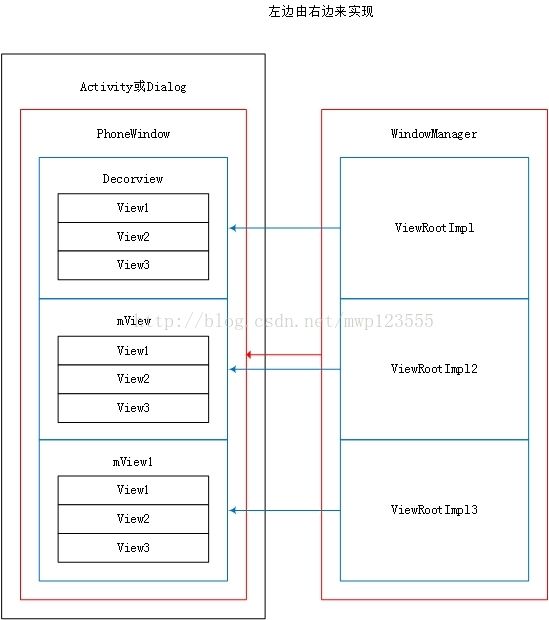
从ViewRootImpl到WindowManger源码分析,可以猜测每个Activity可以有多个ViewRootImpl,通过WindowManager.addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params)将View mView添加到新建的ViewRootImpl中;view的逻辑与事件都会一层层上到ViewRootImpl来处理;各个ViewRootImpl是相互独立的。我们可以推导出WindowManger、ViewRootImpl、View、Activity等之间的关系,如下图所示:
四、遗留问题
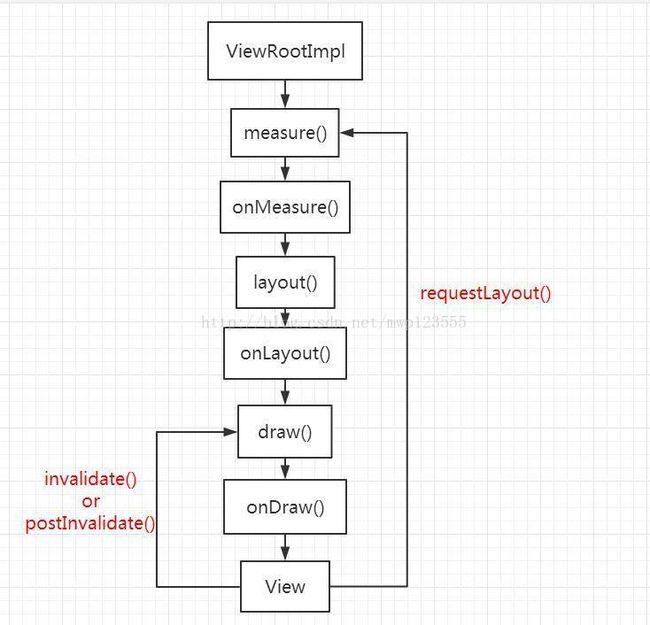
1、requestLayout()、invalidate()有何区别?
requestLayout分为三步:测量(测宽、高),布局(坐标),绘制
invalidate:UI线程,进行绘制
postInvalidate:非UI线程通过Handler更新UI
2、为什么sub_thread、sub_thread_thread对应的操作可以正常更新UI,他们跳过了checkThread()?