JZ2440:busybox构建根文件系统
busybox版本是:1.24.2
此文章的链接:http://blog.csdn.net/qqliyunpeng/article/details/52163265
我的nfs的目录是 /source
设置的uboot的启动参数是:
| LIP2440 # baudrate=115200 bootargs=noinitrd boot=/dev/nfs rw nfsroot=10.100.151.215:/source/fs_mini,tcp ip=10.100.151.222:10.100.151.215:10.100.151.2:255.255.255.0:jz2440::off console=ttySAC0,115200 mem=64M init=/linuxrc user_debug=31 bootcmd=tftp 31000000 uImage;bootm 31000000 bootdelay=3 ethact=dm9000 gatewayip=10.100.151.1 ipaddr=10.100.151.222 netmask=255.255.255.0 serverip=10.100.151.215 stderr=serial stdin=serial stdout=serial |
其中:user_debug=31 是多打印一些错误的信息。
1. 从make defconfig开始:
make defconfig
2. 启动图形界面进一步配置:
make menuconfig
Busybox Settings --->
Build Options --->
[*] Build BusyBox as a static binary (no shared libs)
(arm-none-linux-gnueabi-) Cross Compiler prefix(静态编译和交叉编译工具的前缀)
(-march=armv4t) Additional CFLAGS
Installation Options ("make install" behavior) --->
(/source/fs_mini) BusyBox installation prefix(重定向生成的文件存放的位置)
Busybox Library Tuning--->
[*]Username completion(自动补全功能)
[*]Fancy shell prompts
[*]Query cursor position from termina
make busybox(编译buxybox)
make install(将生成的文件放到 /source/fs_mini)
3. 注意事项:
3.1 在busybox中有一个选项:
Busybox Settings --->
General Configuration --->
[ ] Don't use /usr
这一选项并没有选上,考虑到生成的文件中的 /usr 中都是软连接,并不会占用太大的空间,我的空间足够,选择默认,不选。
3.2 上边的编译选项 CFLAGS 的原因:
我用的交叉编译器是 arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc ,是网上提供的通用版本的工具,当我用默认来编译busybox时,
用 arm-none-linux-gnueabi-readelf -A busybox 去查看busybox的 elf 时,打印如下:
zyl@vmpc:/source/fs_mini/bin$ arm-linux-gnueabi-readelf -A busybox
File Attributes
Tag_CPU_name: "5TE"
Tag_CPU_arch: v5TE
Tag_ARM_ISA_use: Yes
Tag_THUMB_ISA_use: Thumb-1
Tag_ABI_PCS_wchar_t: 4
Tag_ABI_FP_rounding: Needed
Tag_ABI_FP_denormal: Needed
Tag_ABI_FP_exceptions: Needed
Tag_ABI_FP_number_model: IEEE 754
Tag_ABI_align_needed: 8-byte
Tag_ABI_align_preserved: 8-byte, except leaf SP
Tag_ABI_enum_size: int
也以这个工具去打印内核的vmlinux:
zyl@vmpc:~/wor_lip/linux-3.4.112$ arm-linux-gnueabi-readelf -A vmlinux
Attribute Section: aeabi
File Attributes
Tag_CPU_name: "4T"
Tag_CPU_arch: v4T
Tag_ARM_ISA_use: Yes
Tag_THUMB_ISA_use: Thumb-1
Tag_ABI_PCS_wchar_t: 4
Tag_ABI_FP_denormal: Needed
Tag_ABI_FP_exceptions: Needed
Tag_ABI_FP_number_model: IEEE 754
Tag_ABI_align_needed: 8-byte
Tag_ABI_enum_size: int
我们看到前两项是不同的,这直接导致如下的错误:
VFS: Mounted root (nfs filesystem) on device 0:12.
Freeing init memory: 140K
linuxrc (1): undefined instruction: pc=000eea38
Code: e12fff1e 03a00001 13a00000 e12fff1e (e16f2f11)
Kernel panic - not syncing: Attempted to kill init! exitcode=0x00000004
[
[
[
[
[
[
[
这个错误表示的是 busybox 的配置和生成的内核有些配置不一样,
不一样还有可能是linux内核在编译的时候没有选上而导致。
当然加了CFLAGS=-march=armv4t (这个选项从linux内核或者uboot源码的 arch/arm 下的Makefile中可以查到)
之后读取elf如下:
zyl@vmpc:/source/fs_mini/bin$ arm-none-linux-gnueabi-readelf -A busybox
Attribute Section: aeabi
File Attributes
Tag_CPU_name: "4T"
Tag_CPU_arch: v4T
Tag_ARM_ISA_use: Yes
Tag_THUMB_ISA_use: Thumb-1
Tag_ABI_PCS_wchar_t: 4
Tag_ABI_FP_rounding: Needed
Tag_ABI_FP_denormal: Needed
Tag_ABI_FP_exceptions: Needed
Tag_ABI_FP_number_model: IEEE 754
Tag_ABI_align_needed: 8-byte
Tag_ABI_align_preserved: 8-byte, except leaf SP
Tag_ABI_enum_size: int
这个问题的原因是我采用的工具链是 arm-none-linux-gnueabi 的工具链,它是一个复合的工具链,可以供很多的版本去编译,因此,需要加上选项去告诉它,你现在编译的是那个系列。
3.3 纠正一个错误:
有的人可能会在自己的虚拟机种的ubuntu中实验 busybox ls 来试验busybox是不是用交叉编译工具编译出来的,实验证明,即使是交叉编译工具生成的也可以在Ubuntu中运行
4. 将根文件系统中其他的文件和lib补充完整:
由于多次敲命令,很有可能中间遇到问题,因此将过程写成了一个脚本:
文件的名字: xx_busybox.sh
本文件也可以到仓库中 去取:
http://git.oschina.net/qqliyunpeng/fs_for_jz2440
| #!/bin/bash
mkdir dev etc lib mnt opt proc srv sys tmp var mkdir -p etc/init.d etc/network etc/mdev.conf mkdir -p var/run touch etc/network/if-down.d etc/network/if-post-down.d \ etc/network/if-pre-up.d etc/network/if-up.d cd dev sudo mknod -m 600 console c 5 1 sudo mknod -m 666 null c 1 3 cd ../etc echo "root::0:0:root:/:/bin/sh" > passwd echo "root::0:" > group
# etc/init.d/rcS cd init.d echo "#!/bin/sh" > rcS echo "" >> rcS echo "mount -a" >> rcS echo "echo /sbin/mdev > /proc/sys/kernel/hotplug" >> rcS echo "mdev -s" >> rcS chmod a+x rcS
# etc/inittab cd ../ echo "# this is run first except when booting in single-user mode." > inittab echo "::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS" >> inittab echo "# /bin/sh invocations on selected ttys" >> inittab echo "# start an "askfirst" shell on the console (whatever that may be)" \ >> inittab echo "::askfirst:-/bin/sh" >> inittab echo "# stuff to do when restarting the init process" >> inittab echo "::restart:/sbin/init" >> inittab echo "# stuff to do before rebooting" >> inittab echo "::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/reboot" >> inittab
# etc/profile echo "#!/bin/sh" >> profile echo "" >> profile echo "export HOSTNAME=lip" >> profile echo "export USER=root" >> profile echo "export HOME=root" >> profile echo 'export PS1='$USER@$HOSTNAME:\w\$ ' >> profile echo "PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin" >> profile echo 'LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/lib:/usr/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH' >> profile echo "export PATH LD_LIBRARY_PATH" >> profile echo "source /etc/bash.bashrc" >> profile echo "export TZ="CST-8" >> profile echo "hwclock -w" >> profile
# etc/fstab echo "#device mount-point type options dump fsck order" > fstab echo "proc /proc proc defaults 0 0" >> fstab echo "devpts /dev/pts devpts defaults 0 0" >> fstab echo "usbfs /proc/bus/usb usbfs defaults 0 0" >> fstab echo "tmpfs /tmp tmpfs defaults 0 0" >> fstab echo "sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0" >> fstab echo "tmpfs /dev/shm tmpfs defaults 0 0" >> fstab
# etc/bash.bashrc echo "#.bashrc" > bash.bashrc echo "" >> bash.bashrc echo "# User specific aliases and function" >> bash.bashrc echo "" >> bash.bashrc echo "alias ll='ls -l'" >> bash.bashrc echo "" >> bash.bashrc echo "# Source global definitions" >> bash.bashrc echo "" >> bash.bashrc echo "if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then" >> bash.bashrc echo " ./etc/bashrc" >> bash.bashrc echo "fi" >> bash.bashrc
# lib cd ../lib echo "#!/bin/bash" > xx_lib.sh echo "" >> xx_lib.sh echo "CROSSTOOL_PREFIX=arm-none-linux-gnueabi" >> xx_lib.sh echo "CROSSTOOL_LIB_PATH=~/arm-2014.05/arm-none-linux-gnueabi/libc/armv4t/lib"\ >> xx_lib.sh echo 'cp $CROSSTOOL_LIB_PATH/* . -a' >> xx_lib.sh echo 'echo "cp $CROSSTOOL_LIB_PATH . -a"' >> xx_lib.sh echo "rm *.a" >> xx_lib.sh echo '$CROSSTOOL_PREFIX-strip *' >> xx_lib.sh echo 'echo "$CROSSTOOL_PREFIX-strip *"' >> xx_lib.sh chmod a+x xx_lib.sh
|
将这个文件加上可执行权限(chmod a+x xx_busybox.sh),
将这个脚本放到刚生成的根文件系统的文件夹下,我的是/source/fs_mini ,
然后执行 ./xx_busybox.sh
之后进入到lib目录下看到 xx_lib.sh 脚本,打开脚本,将CROSSTOOL_PREFIX和CROSSTOOL_LIB_PATH
变量分别改成自己的交叉工具的前缀和要搬移到此lib目录下的文件的路径更改,
然后执行 ./xx_lib.sh 即可,然后查看 这个lib 文件夹的大小,保证小于5M 。
5. 对于这个脚本创建的几个文件的说明如下:
5.1 etc下的几个文件:
etc/inittab -- init初始化解析的配置文件
etc/profile -- shell配置
etc/init.d/rcS -- sysint初始的脚本 ,开机后自动运行的程序可以在这里设置
etc/fstab -- rcS脚本中的 mount -a命令
①etc/inittab
| #this is run first except when booting in single-user mode. ::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS (初始化脚本设置成rcS) # /bin/sh invocations on selected ttys # start an "askfirst" shell on the console (whatever that may be) ::askfirst:-/bin/sh (询问是不是进入console) # stuff to do when restarting the init process ::restart:/sbin/init (重启调用的是 init ) # stuff to do before rebooting ::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/reboot (定义 ctrl+alt+del 为重启) |
该文件中每个条目用来定义一个子进程,并确定它的启动方法,格式如下:
id:表示这个系统要使用的控制台(即标准输入、标准输出、标准错误设备)。如果省略,则使用与 init 进程一样的控制台。
runlevels:对于 BusyBox init程序,这个字段没有意义,可以省略。
action:表示 init 程序如何控制这个子进程。
process:要执行的程序,它可以是可执行程序,也可以是脚本。
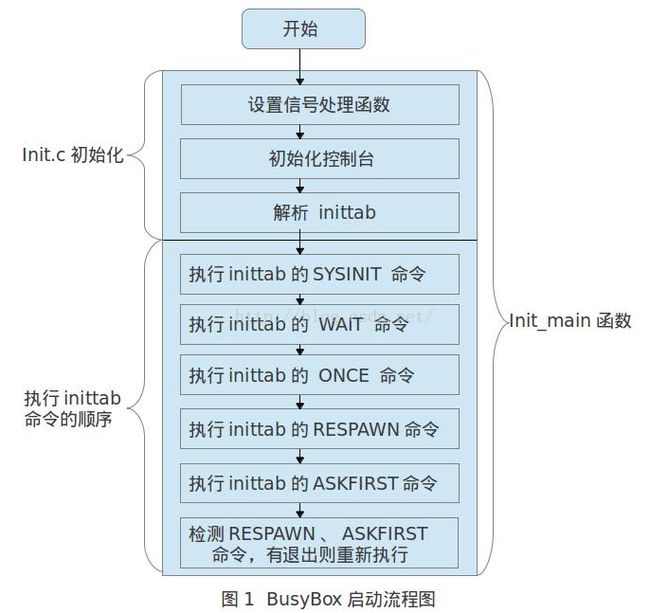
其中,action 字段的意义如下图:
如果想让系统起来后一直重复的执行hello程序可以在inittab中添加如下一句:
::respawn:/home/hello
此部分参照:http://www.programgo.com/article/92903254449/
②etc/profile
| #!/bin/sh export HOSTNAME=lip export USER=root (进入命令行后显示的是 root@lip) export HOME=root export PS1='$USER@$HOSTNAME:\w\$ ' PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/lib:/usr/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH export PATH LD_LIBRARY_PATH source /etc/bash.bashrc (执行初始化文件,此处是添加了一个ll命令) |
这里PS1中 \W 是显示一个目录,这里要用 \w 显示完整路径
有一种写法如下,并不是本文件系统中采用的 .bash_profile
| $ cat .bash_profile |
③etc/init.d/rcS: --还要添加执行权限chmod a+x init.d/rcS
| #!/bin/sh # This is the first script called by init process mkdir -p /dev/pts mkdir -p /dev/shm /bin/mount -a (-a 加载文件/etc/fstab中设置的所有设备) echo /sbin/mdev > /proc/sys/kernel/hotplug /sbin/mdev -s (自动装载 /dev 目录下的设备文件) |
④etc/fstab:
| #device mount-point type options dump fsck order proc /proc proc defaults 0 0 tmpfs /tmp tmpfs defaults 0 0 sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0 tmpfs /dev/shm tmpfs defaults 0 0 |
- proc 是一个伪文件系统,它只存在内存当中,而不占用外存空间。它以文件系统的方式为访问系统内核数据的操作提供接口。用户和应用程序可以通过proc得到系统的信息,并可以改变内核的某些参数。由于系统的信息,如进程,是动态改变的,所以用户或应用程序读取proc文件时,proc文件系统是动态从系统内核读出所需信息并提交的。
- tmpfs 是虚拟的文件系统,在内存中,可以提高linux读写速度
- sysfs 文件系统用来表示设备的结构.将设备的层次结构形象的反应到用户空间中.用户空间可以修改sysfs中的文件属性来修改设备的属性值,
第一列:需要挂在的文件系统后者存储设备
第二列:挂在点
第三列:指定文件系统或分区类型
第四列:挂在选项,
auto: 系统自动挂载,fstab默认就是这个选项
ro: read-only
rw: read-write
defaults: rw, suid, dev, exec, auto, nouser, and async.
第五列:dump,设置是否让备份程序dump备份文件系统,0为忽略,1为备份。
第六列:fsk选项,告诉fsck程序以什么顺序检查文件系统,0为忽略。
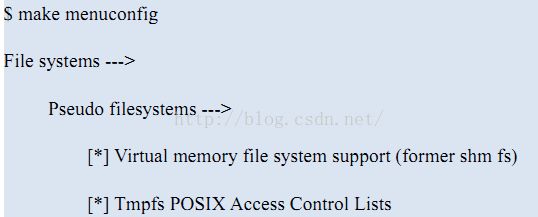
配置内核让其支持 tmpfs:(此项只需要确认就好)
5.2 lib目录下边的文件:
lib目录下的文件要有两类文件:
- 加载器(ld-2.18.so和ld-linux.so.3 -> ld-2.18.so)
- 动态库文件(.so、,so.[0-9]*)
6. 整个执行过程:
linux开机运行后先运行 /linuxrc,linuxrc 调用BusyBox的init 程序,执行:
- 设置 init 信号句柄
- 初始化 console(s)
- 解析inittab文件,/etc/inittab
- 运行系统初始化脚本 -> /etc/init.d/rcS
- 运行inittab中所有action为wait的命令
- 运行inittab中所有action为once的命令
- 循环运行:
- 运行 inittab 中所有action为 respawn 的命令
- 运行 inittab 中所有action为 askfirst 的命令
busybox -> init (init.c)
-解析->/etc/inittab(这里有inittab语法)
-在inittab中设置 sysinit 动作->etc/init.d/tcS
-mount -a->/etc/fstab
补充:
在busybox中添加开机设定网络的文件
Busybox Settings --->
Busybox Library Tuning --->
Support for /etc/networks
在busybox中添加usb/sd自动识别的问题 -- 相当于添加了mdev.conf -- 在busybox中支持
Linux System Utilities --->
[*] mdev
[*] Support /etc/mdev.conf