3.CacheManager(shiro缓存管理)
上一章我们讲了SecurityManager,接下来的章节顺序是根据SecurityManager的依次实现类的依赖组件来讲。
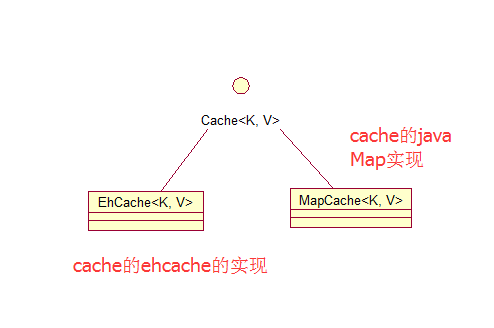
在讲cacheManager前,我们先了解下Cache。
Cache有效的存储临时对象来提升应用的性能。由于Cache不属于安全框架的核心功能,所以shiro本身并没有完全实现Cache机制。Cache接口相当于底层的缓存框架的顶层接口,shiro的一切的缓存操作都与这个Cache顶层接口操作,而底层的实现可以是任何Cache实例(JAche、Ehcache、OSCache、JBossCache..)。
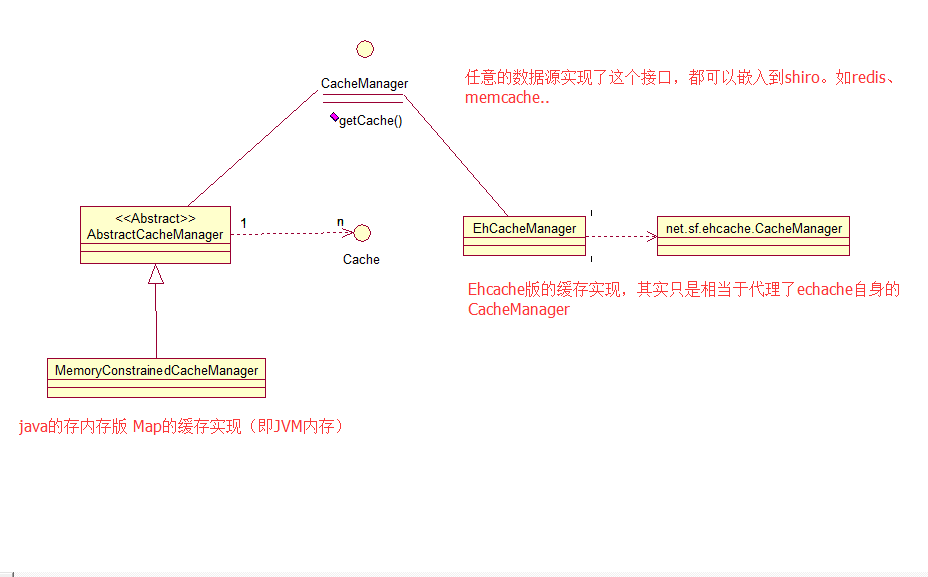
cacheManager维护了Cache实例的生命周期,它和Cache一样,只是shiro的缓存框架的顶层接口,具体底层实现可以是任意的。
1.CacheManager
//CacheManager管理Cache的声明周期
public interface CacheManager {
//根据指定的名字获取Cache(为什么需要根据名字?因为CacheManager就相当于一个大容器,只管理Cache,而这个Cache是个小容器,根据键可以取到对应的值。在shiro里面,AuthenticationInfo(用户登陆信息),AuthorizationInfo(授权信息)生成一个Cache,然后根据唯一的名字存入到CacheManager里),如果不存在,则创建个Cache存入到CacheManager里然后返回。
public Cache getCache(String name) throws CacheException;
}
2.AbstractCacheManager
//CacheManager的简单的抽象实现,该实现把Cache都交由ConcurrentMap来管理。
public abstract class AbstractCacheManager implements CacheManager, Destroyable {
private final ConcurrentMap caches;
public AbstractCacheManager() {
this.caches = new ConcurrentHashMap();
}
//根据名字获取Cache
public Cache getCache(String name) throws IllegalArgumentException, CacheException {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cache name cannot be null or empty.");
}
Cache cache;
//首先根据名字获取从ConcurrentMap里获取cache
cache = caches.get(name);
if (cache == null) {
//如果cache为null的话,则生成个cache存入ConcurrentMap再返回
cache = createCache(name);
//putIfAbsent是ConcurrentMap的一个原子性操作,如果已经存在则不添加。
Cache existing = caches.putIfAbsent(name, cache);
if (existing != null) {
cache = existing;
}
}
//noinspection unchecked
return cache;
}
//创建一个Cache,留待子类实现
protected abstract Cache createCache(String name) throws CacheException;
//销毁CacheManager
public void destroy() throws Exception {
while (!caches.isEmpty()) {
for (Cache cache : caches.values()) {
//LifecycleUtils.destroy()里面,会自动判断该cache是否实现了Destroyable,是的话,执行Destroyable的destroy方法。如果是Collection,迭代元素判断是否实现Destroyable,如果实现,则执行Destroyable的destroy方法
LifecycleUtils.destroy(cache);
}
caches.clear();
}
}
public String toString() {
Collection values = caches.values();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(getClass().getSimpleName())
.append(" with ")
.append(caches.size())
.append(" cache(s)): [");
int i = 0;
for (Cache cache : values) {
if (i > 0) {
sb.append(", ");
}
sb.append(cache.toString());
i++;
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}
3.MemoryConstrainedCacheManager
//继承AbstractCacheManager
public class MemoryConstrainedCacheManager extends AbstractCacheManager {
//该类返回一个MapCache(实现Cache)。
@Override
protected Cache createCache(String name) {
//SoftHashMap实现了Map。该实现Map不会引起内存泄露,因为里面引用了弱引用和强引用。默认的强引用是100个。超出了则为弱引用,垃圾回收器可回收这些弱引用,在需要内存的时候。
return new MapCache(name, new SoftHashMap());
}
} 下面讲的是Ehcache的CacheManager的实现
1.EhCacheManager
//EhCacheManager利用了Ehcache框架来实现所有的缓存功能,可以手动配置net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager和ehcache.xml路径。
public class EhCacheManager implements CacheManager, Initializable, Destroyable {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EhCacheManager.class);
//属于ehcache框架的CacheManager,shiro的EhCacheManager仅仅只是代理它实现缓存功能。
protected net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager manager;
//表面这个manager是由本实例构造的,而非通过外部注入进来的。需要在销毁的时候执行销毁方法
private boolean cacheManagerImplicitlyCreated = false;
// ehcache CacheManager配置文件路径
private String cacheManagerConfigFile = "classpath:org/apache/shiro/cache/ehcache/ehcache.xml";
public EhCacheManager() {
}
public net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager getCacheManager() {
return manager;
}
//设置ehcache的CacheManager
public void setCacheManager(net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager manager) {
this.manager = manager;
}
//如果ehcache的CacheManager没有初始化,则获取 ehcache CacheManager的配置文件路径,来初始化ehcache的CacheManager.路径加载方式可以是:classpath:、url:file:
public String getCacheManagerConfigFile() {
return this.cacheManagerConfigFile;
}
//classpathLocation可以是:classpath:、url:、file:前缀开头的加载方式
public void setCacheManagerConfigFile(String classpathLocation) {
this.cacheManagerConfigFile = classpathLocation;
}
//使用 ResourceUtils.getInputStreamForPath(configFile)来加载配置文件到InputStream
protected InputStream getCacheManagerConfigFileInputStream() {
String configFile = getCacheManagerConfigFile();
try {
return ResourceUtils.getInputStreamForPath(configFile);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ConfigurationException("Unable to obtain input stream for cacheManagerConfigFile [" +
configFile + "]", e);
}
}
//根据名字获取Cache
public final Cache getCache(String name) throws CacheException {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Acquiring EhCache instance named [" + name + "]");
}
try {
//从ehcache框架的CacheManager中根据名字获取ehcache框架的Cache
net.sf.ehcache.Ehcache cache = ensureCacheManager().getEhcache(name);
if (cache == null) {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("Cache with name '{}' does not yet exist. Creating now.", name);
}
//根据名字添加cache
this.manager.addCache(name);
//重新根据名字获取cache
cache = manager.getCache(name);
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("Added EhCache named [" + name + "]");
}
} else {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("Using existing EHCache named [" + cache.getName() + "]");
}
}
//shiro的EhCache包装了ehcache框架的Cache,然后返回
return new EhCache(cache);
} catch (net.sf.ehcache.CacheException e) {
throw new CacheException(e);
}
}
//下面这个我也不是很理解,希望理解的朋友能告知一二。特别是这句(fail-safe expunges cached objects after 2 minutes, something not desirable for Shiro sessions)。大概意思就是讲,如果没有通过setCacheManager 注入CacheManager,那么该方法就会加载ehcache的配置文件路径初始化一个CacheManager
/**
* Initializes this instance.
*
* If a {@link #setCacheManager CacheManager} has been
* explicitly set (e.g. via Dependency Injection or programatically) prior to calling this
* method, this method does nothing.
*
* However, if no {@code CacheManager} has been set, the default Ehcache singleton will be initialized, where
* Ehcache will look for an {@code ehcache.xml} file at the root of the classpath. If one is not found,
* Ehcache will use its own failsafe configuration file.
*
* Because Shiro cannot use the failsafe defaults (fail-safe expunges cached objects after 2 minutes,
* something not desirable for Shiro sessions), this class manages an internal default configuration for
* this case.
*
* @throws org.apache.shiro.cache.CacheException
* if there are any CacheExceptions thrown by EhCache.
* @see net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager#create
*/
public final void init() throws CacheException {
ensureCacheManager();
}
private net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager ensureCacheManager() {
try {
if (this.manager == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("cacheManager property not set. Constructing CacheManager instance... ");
}
//because we need to know if we need to destroy the CacheManager instance - using the static call。
//上面这一句我也不理解。其他几句大概意思就是说,通过CacheManager 的构造方法,得到的实例不是CacheManager里的单例的。我们不知道CacheManager 是否会shutting 它的单例。但是我们通过使用构造EhCacheManager内部的CacheManager,那么EhCacheManager总会shutting EhCacheManager内部的CacheManager。
//using the CacheManager constructor, the resulting instance is _not_ a VM singleton
//(as would be the case by calling CacheManager.getInstance(). We do not use the getInstance here
//because we need to know if we need to destroy the CacheManager instance - using the static call,
//we don't know which component is responsible for shutting it down. By using a single EhCacheManager,
//it will always know to shut down the instance if it was responsible for creating it.
this.manager = new net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager(getCacheManagerConfigFileInputStream());
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("instantiated Ehcache CacheManager instance.");
}
cacheManagerImplicitlyCreated = true;
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("implicit cacheManager created successfully.");
}
}
return this.manager;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException(e);
}
}
//如果CacheManager是由EhCacheManager内部构造的,则会执行CacheManager销毁。如果该CacheManager是通过外部组件注入的,那么该外部组件也应该负责销毁CacheManager。
public void destroy() {
if (cacheManagerImplicitlyCreated) {
try {
net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager cacheMgr = getCacheManager();
cacheMgr.shutdown();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
log.warn("Unable to cleanly shutdown implicitly created CacheManager instance. " +
"Ignoring (shutting down)...");
}
}
cacheManagerImplicitlyCreated = false;
}
}
}