VSCode技术揭秘(一)
前言
Visual Studio Code(以下简称VSCode)是一个轻量且强大的跨平台开源代码编辑器(IDE),VSCode 采用了 Electron,使用的代码编辑器名为 Monaco、Monaco 也是 Visual Studio Team Service(Visual Studio Online)使用的代码编辑器,在语言上,VSCode 使用了自家的 TypeScript 语言开发。
VSCode提供了强大的插件拓展机制,并提供 插件市场 供开发者发布、下载插件。VSCode提供了丰富的扩展能力模型,例如基础的语法高亮/API提示、引用跳转(转到定义)、文件搜索、主题定制,高级的debug协议等等。但不允许插件直接访问底层UI DOM(即很难定制VSCode外观),因为VSCode开发团队随着优化VSCode而频繁更改UI Dom,所以将UI定制能力限制起来。
但是当你想要开发一款专用IDE时,不想从零开始撸,而是站在巨人的肩膀上做二次开发的话,那么VSCode将是你不二的选择,像 Weex Studio、白鹭Egret Wing、快应用IDE等IDE,都是基于VSCode扩展增强。
Weex Studio
Egret Wing
快应用
本系列文章将带你了解VSCode源码的整体架构和定制方法,一步一步从源码入手,定制一款专用开发工具。
技术介绍
学习VSCode源码的同学基本上都是做前端工作的,那么node.js和javascript都是基本功了,这里不用过分强调了。但是在阅读VSCode源码之前,还是需要对VSCode使用相关技术框架有所了解。
Electron介绍
众所周知,VSCode是一款桌面编辑器应用,但是前端单纯用js是做不了桌面应用的,所以采用Electron来构建。Electron是基于 Chromium 和 Node.js,使用 JavaScript, HTML 和 CSS 构建跨平台的桌面应用,它兼容 Mac、Windows 和 Linux,可以构建出三个平台的应用程序。

从实现上来看,Electron = Node.js + Chromium + Native API
也就是说Electron拥有Node运行环境,赋予了用户与系统底层进行交互的能力,依靠Chromium提供基于Web技术(HTML、CSS、JS)的界面交互支持,另外还具有一些平台特性,比如桌面通知等。
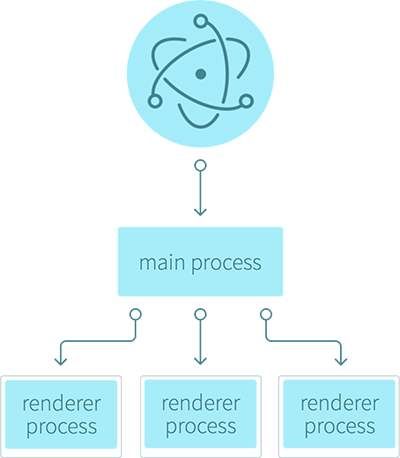
从API设计上来看,Electron App一般都有1个Main Process和多个Renderer Process:
- main process:主进程环境下可以访问Node及Native API
- renderer process:渲染器进程环境下可以访问Browser API和Node API及一部分Native API。
主进程和渲染进程
在Electron应用中,通过执行package.json中的main字段所指向的文件,可以开启electron的主进程(main process)。在主进程中使用BrowserWindow 实例创建web页面,而且一个electron应用有且只能有一个主进程。
主进程一般用于:
- 多窗体管理(创建/切换)
- 应用生命周期管理
- 作为进程通信基站(IPC Server)
- 工具条菜单栏注册
由于electron使用Chromium来展示web页面,Chromium多进程架构也会被用到。每一张web页面都运行在它自己的进程里,该进程称为渲染进程(renderer process)。渲染进程一般负责界面交互相关的,具体的业务功能。
在web页面里,调用系统底层的API是不被允许的,这是因为在web页面上处理底层GUI资源是非常危险的,很容易导致资源泄漏。如果你想要在web页面上执行GUI操作,相应web页面的渲染进程必须与主进程进行通信,向主进程发起请求去执行那些操作.在electron中,有几种主进程与渲染进程通信的方法,比如用ipcRenderer和ipcMain模块来发送信息,还有RPC风格的远程通信模块。关于Electron进程间通讯,这里不做过多的介绍,可以看Electron官网和网上资料来学习主进程和渲染进程间通讯。
更多的了解可以参考Electron应用架构
编辑器Monaco Editor
微软之前有个项目叫做Monaco Workbench,后来这个项目变成了VSCode,而Monaco Editor(下文简称monaco)就是从这个项目中成长出来的一个web编辑器,他们很大一部分的代码(monaco-editor-core)都是共用的,所以monaco和VSCode在编辑代码,交互以及UI上几乎是一摸一样的,有点不同的是,两者的平台不一样,monaco基于浏览器,而VSCode基于electron,所以功能上VSCode更加健全,并且性能比较强大。
TypeScript
TypeScript是JavaScript类型的超集,它可以编译成纯JavaScript。TypeScript可以在任何浏览器、任何计算机和任何操作系统中运行,并且是开源的。TypeScript具有以下特点:
- 类型批注和编译时的类型检查
- 强类型语言
- 面向对象
- 类class
- 接口
- lambda函数
- 泛型
VSCode源码的编写主要用TypeScript,所以学习VSCode源码的时候还是先对TypeScript的基本使用有所了解。
以上内容是学习VSCode源码所要了解的基本内容,可以先学习Electron做个简单的桌面应用,然后学习一下TypeScript的基本语法,就可以开始VSCode源码的学习。
VSCode架构
VSCode中包含主进程,渲染进程,同时因为VSCode提供了插件的扩展能力,又出于安全稳定性的考虑,图中又多了一个Extension Host,其实这个Extension Host也是一个独立的进程,用于运行我们的插件代码。并且同渲染进程一样,彼此都是独立互不影响的。Extension Host Process暴露了一些VSCode的API供插件开发者去使用。
VSCode的进程结构
VSCode采用多进程架构,启动后主要由下面几个进程:
- 后台进程
- 编辑器窗口 - 由后台进程启动,也是多进程架构
- HTML编写的UI
- ActivityBar
- SideBar
- Panel
- Editor
- StatusBar
- Nodejs异步IO
- FileService
- ConfigurationService
- 插件宿主进程
- 插件实例
- 插件子进程 - 如TS语言服务
- 插件实例
- 插件实例
- 插件实例
- Debug进程
- Search进程
- HTML编写的UI
后台进程
后台进程是 VSCode 的入口,主要负责管理编辑器生命周期,进程间通信,自动更新,菜单管理等。
我们启动 VSCode 的时候,后台进程会首先启动,读取各种配置信息和历史记录,然后将这些信息和主窗口 UI 的 HTML 主文件路径整合成一个 URL,启动一个浏览器窗口来显示编辑器的 UI。后台进程会一直关注 UI 进程的状态,当所有 UI 进程被关闭的时候,整个编辑器退出。
此外后台进程还会开启一个本地的 Socket,当有新的 VSCode 进程启动的时候,会尝试连接这个 Socket,并将启动的参数信息传递给它,由已经存在的 VSCode 来执行相关的动作,这样能够保证 VSCode 的唯一性,避免出现多开文件夹带来的问题。
编辑器窗口
编辑器窗口进程负责整个 UI 的展示。也就是我们所见的部分。UI 全部用 HTML 编写没有太多需要介绍的部分。
Nodejs异步IO
项目文件的读取和保存由主进程的 NodeJS API 完成,因为全部是异步操作,即便有比较大的文件,也不会对 UI 造成阻塞。IO 跟 UI 在一个进程,并采用异步操作,在保证 IO 性能的基础上也保证了 UI 的响应速度。
插件进程
每一个 UI 窗口会启动一个 NodeJS 子进程作为插件的宿主进程。所有的插件会共同运行在这个进程中。这样设计最主要的目的就是避免复杂的插件系统阻塞 UI 的响应。但是将插件放在一个单独进程也有很明显的缺点,因为是一个单独的进程,而不是 UI 进程,所以没有办法直接访问 DOM 树,想要实时高效的改变 UI 变得很难,在 VSCode 的扩展体系中几乎没有对 UI 进行扩展的 API。
Debug进程
Debugger 插件跟普通的插件有一点区别,它不运行在插件进程中,而是在每次 debug 的时候由UI单独新开一个进程。
搜索进程
搜索是一个十分耗时的任务,VSCode 也使用的单独的进程来实现这个功能,保证主窗口的效率。将耗时的任务分到多个进程中,有效的保证了主进程的响应速度。
VSCode源码运行
环境安装
- Git
- Node.JS,version >= 10.16.0, < 11.0.0
- Yarn
- Python,版本2.7以上,不支持3.0及其以上版本(mac电脑自带python不需要下载)
以上环境安装相信大家都轻车熟路了,由于我电脑使用的Mac,所以相关的示例都在Mac系统中运行,windows上的大同小异,具体可以参考官网Wiki文档。
源码下载
VSCode的源码每次更新都会优化UI部分,但整体架构是没有差别的,可能网上的关于VSCode的源码教程用的老版本的VSCode,在这里我采用目前最新的版本 - v1.39.2版本来讲解。
源码下载:VSCode Releases
下载后解压用VSCode编辑器打开,在命令行中输入 yarn 命令来安装依赖,中间会很耗时。

中间会安装很多依赖包,如果发现网络不通、下载失败等情况,首先需要检查上述开发环境版本是否正确,必要时需要科学上网。
源码运行
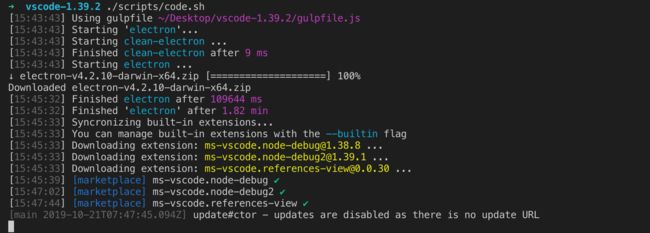
依赖安装完成后,进入到项目中,执行 yarn watch 执行构建工作:
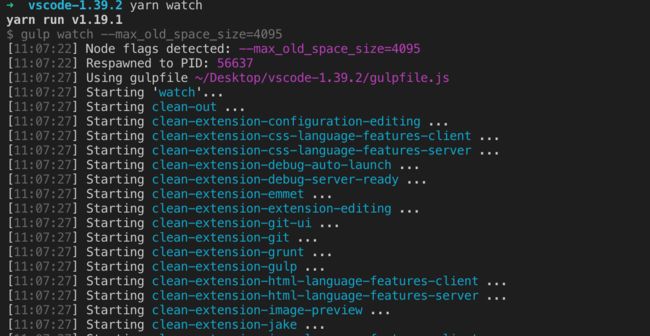
直到你看到 Finished compilation with 0 errors after 108726 ms 输出,说明构建成功了!

这时候不要关闭当前命令行,构建命令没有退出,它会监视vscode源码文件的变化,如果有变化,它会马上执行增量的构建,实时反映源码变化的结果。
新起一个命令行,执行 ./scripts/code.sh ,windows下执行 \scripts\code.bat,此时会下载Electron。
VSCode源码结构
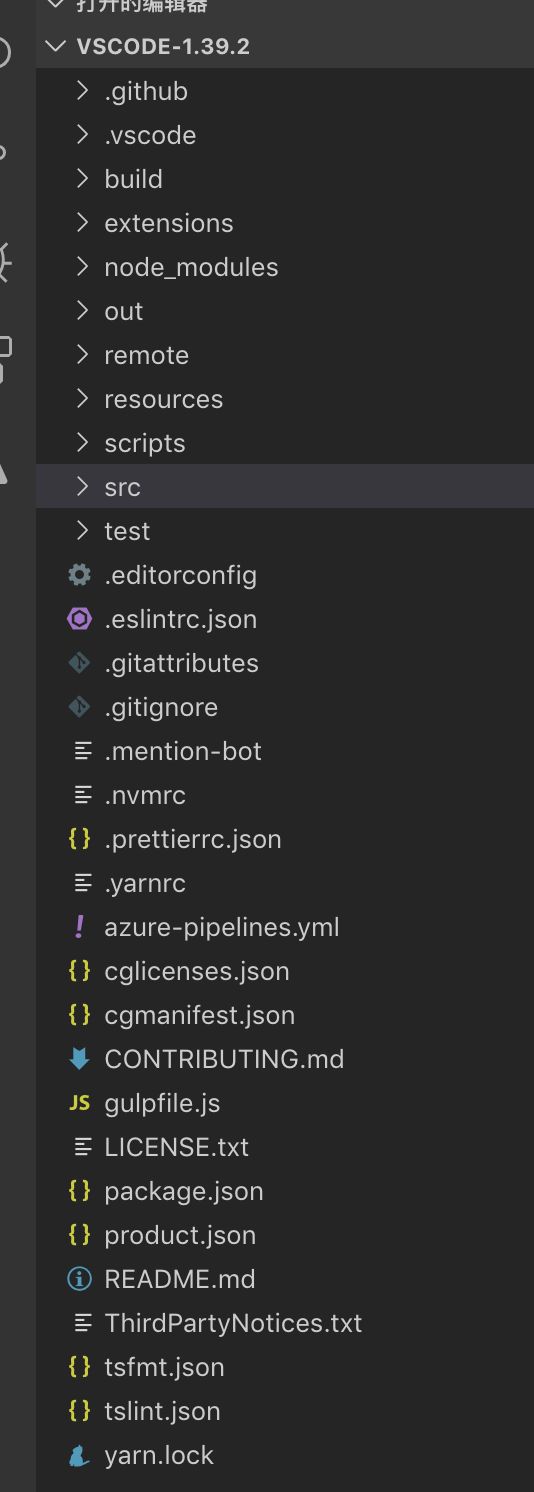
整体文件目录结构如下所示:
├── build # gulp编译构建脚本
├── extensions # 内置插件
├── gulpfile.js # gulp task
├── out # 编译输出目录
├── resources # 平台相关静态资源,图标等
├── scripts # 工具脚本,开发/测试
├── src # 源码目录
├── test # 测试套件
└── product.json # App meta信息
src下文件目录结构,如下图:
├── bootstrap-amd.js # 子进程实际入口
├── bootstrap-fork.js #
├── bootstrap-window.js #
├── bootstrap.js # 子进程环境初始化
├── buildfile.js # 构建config
├── cli.js # CLI入口
├── main.js # 主进程入口
├── paths.js # AppDataPath与DefaultUserDataPath
├── typings
│ └── xxx.d.ts # ts类型声明
└── vs
├── base # 定义基础的工具方法和基础的 DOM UI 控件
│ ├── browser # 基础UI组件,DOM操作、交互事件、DnD等
│ ├── common # diff描述,markdown解析器,worker协议,各种工具函数
│ ├── node # Node工具函数
│ ├── parts # IPC协议(Electron、Node),quickopen、tree组件
│ ├── test # base单测用例
│ └── worker # Worker factory 和 main Worker(运行IDE Core:Monaco)
├── code # VSCode Electron 应用的入口,包括 Electron 的主进程脚本入口
│ ├── electron-browser # 需要 Electron 渲染器处理API的源代码(可以使用 common, browser, node)
│ ├── electron-main # 需要Electron主进程API的源代码(可以使用 common, node)
│ ├── node # 需要Electron主进程API的源代码(可以使用 common, node)
│ ├── test
│ └── code.main.ts
├── editor # Monaco Editor 代码编辑器:其中包含单独打包发布的 Monaco Editor 和只能在 VSCode 的使用的部分
│ ├── browser # 代码编辑器核心
│ ├── common # 代码编辑器核心
│ ├── contrib # vscode 与独立 IDE共享的代码
│ ├── standalone # 独立 IDE 独有的代码
│ ├── test
│ ├── editor.all.ts
│ ├── editor.api.ts
│ ├── editor.main.ts
│ └── editor.worker.ts
├── platform # 依赖注入的实现和 VSCode 使用的基础服务 Services
├── workbench # VSCode 桌面应用程序工作台的实现
├── buildunit.json
├── css.build.js # 用于插件构建的CSS loader
├── css.js # CSS loader
├── loader.js # AMD loader(用于异步加载AMD模块,类似于require.js)
├── nls.build.js # 用于插件构建的 NLS loader
└── nls.js # NLS(National Language Support)多语言loader
首先 VSCode 整体由其核心core和内置的扩展Extensions组成,core是实现了基本的代码编辑器和 VSCode 桌面应用程序,即 VSCode workbench,同时提供扩展 API,允许内置的扩展和第三方开发的扩展程序来扩展 VSCode Core 的能力。
其次,由于 VSCode 依赖 Electron,而 Electron 存在着主进程和渲染进程,它们能使用的 API 有所不到,所以 VSCode Core 中每个目录的组织也按照它们能使用的 API 来组织安排。在 Core 下的每个子目录下,按照代码所运行的目标环境分为以下几类:
- common: 只使用 JavaScript API 的源代码,可能运行在任何环境
- browser: 需要使用浏览器提供的 API 的源代码,如 DOM 操作等
- node: 需要使用Node.js提供的 API 的源代码
- electron-browser: 需要使用 Electron 渲染进程 API 的源代码
- electron-main: 需要使用 Electron 主进程 API 的源代码
按照上述规则,即src/vs/workbench/browser中的源代码只能使用基本的 JavaScript API 和浏览器提供的 API,而src/vs/workbench/electron-browser中的源代码则可以使用 JavaScript API,浏览器提供的 API、Node.js提供的 API、和 Electron 渲染进程中的 API。
在 VSCode 代码仓库中,出了上述的src/vs的Core之外,还有一大块即 VSCode 内置的扩展,它们源代码位于extensions内。
VSCode 作为代码编辑器,与各种代码编辑的功能如语法高亮、补全提示、验证等都有扩展实现的。所以在 VSCode 的内置扩展内,一大部分都是各种编程语言的支持扩展,如:extensions\html、extensions\javascript、extensions\cpp等等,大部分语言扩展中都会出现如.tmTheme、.tmLanguage等 TextMate 的语法定义。还有一类内置的扩展是 VSCode 主体扩展,如 VSCode 默认主体extensions/theme-defaults等。
VSCode启动流程
由于VSCode是基于Electron开发的,Electron的启动入口在package.json中,其中的 main 字段所表示的脚本为应用的启动脚本,它将会在主进程中执行。
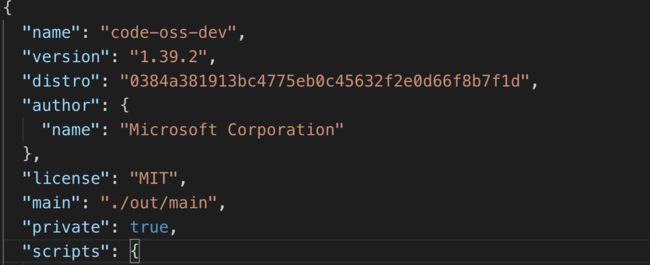
./out/main.js显然这就是主进程的入口程序,但是main.js是在out文件夹下,很明显是编译输出出来的,然后找到src下tsconfig.json文件中有以下配置:
"outDir": "../out",
所以很明显是将src下代码编译后输出到out文件夹中。所以真实入口在src下main.js中,接下来只需从main.js文件分析即可。
在main.js中,我们可以看到下面一行引入
const app = require('electron').app;
electron.app负责管理Electron 应用程序的生命周期,运行在主进程中,然后找到 ready 监听事件
// Load our code once ready
app.once('ready', function () {
if (args['trace']) {
// @ts-ignore
const contentTracing = require('electron').contentTracing;
const traceOptions = {
categoryFilter: args['trace-category-filter'] || '*',
traceOptions: args['trace-options'] || 'record-until-full,enable-sampling'
};
contentTracing.startRecording(traceOptions, () => onReady());
} else {
onReady();
}
});
这个ready监听表示,Electron 会在初始化后并准备,部分 API 在 ready 事件触发后才能使用。创建窗口也需要在ready后创建。最后这个函数中调用 onReady() 函数。
function onReady() {
perf.mark('main:appReady');
Promise.all([nodeCachedDataDir.ensureExists(), userDefinedLocale]).then(([cachedDataDir, locale]) => {
if (locale && !nlsConfiguration) {
nlsConfiguration = lp.getNLSConfiguration(product.commit, userDataPath, metaDataFile, locale);
}
if (!nlsConfiguration) {
nlsConfiguration = Promise.resolve(undefined);
}
// First, we need to test a user defined locale. If it fails we try the app locale.
// If that fails we fall back to English.
nlsConfiguration.then(nlsConfig => {
const startup = nlsConfig => {
nlsConfig._languagePackSupport = true;
process.env['VSCODE_NLS_CONFIG'] = JSON.stringify(nlsConfig);
process.env['VSCODE_NODE_CACHED_DATA_DIR'] = cachedDataDir || '';
// Load main in AMD
perf.mark('willLoadMainBundle');
require('./bootstrap-amd').load('vs/code/electron-main/main', () => {
perf.mark('didLoadMainBundle');
});
};
// We received a valid nlsConfig from a user defined locale
if (nlsConfig) {
startup(nlsConfig);
}
// Try to use the app locale. Please note that the app locale is only
// valid after we have received the app ready event. This is why the
// code is here.
else {
let appLocale = app.getLocale();
if (!appLocale) {
startup({
locale: 'en', availableLanguages: {
} });
} else {
// See above the comment about the loader and case sensitiviness
appLocale = appLocale.toLowerCase();
lp.getNLSConfiguration(product.commit, userDataPath, metaDataFile, appLocale).then(nlsConfig => {
if (!nlsConfig) {
nlsConfig = {
locale: appLocale, availableLanguages: {
} };
}
startup(nlsConfig);
});
}
}
});
}, console.error);
}
整个函数读取了用户语言设置,然后最终调用了 startup()。
const startup = nlsConfig => {
nlsConfig._languagePackSupport = true;
process.env['VSCODE_NLS_CONFIG'] = JSON.stringify(nlsConfig);
process.env['VSCODE_NODE_CACHED_DATA_DIR'] = cachedDataDir || '';
// Load main in AMD
perf.mark('willLoadMainBundle');
require('./bootstrap-amd').load('vs/code/electron-main/main', () => {
perf.mark('didLoadMainBundle');
});
};
startup中主要是引入了 boostrap-amd ,这个bootstrap-amd引入了/vs/loader,并创建了一个loader。
const loader = require('./vs/loader');
loader是微软自家的AMD模块加载开源项目:https://github.com/Microsoft/vscode-loader/
然后通过loader加载 vs/code/electron-main/main 模块,这是 VSCode 真正的入口,然后在 vs/code/electron-main/main.ts 中可以看到定义了一个 CodeMain 类,然后初始化这个CodeMain类,并调用了 main 函数。
// src/vs/code/electron-main/main
class CodeMain {
main(): void {
...
// Launch
this.startup(args);
}
private async startup(args: ParsedArgs): Promise<void> {
// We need to buffer the spdlog logs until we are sure
// we are the only instance running, otherwise we'll have concurrent
// log file access on Windows (https://github.com/Microsoft/vscode/issues/41218)
const bufferLogService = new BufferLogService();
const [instantiationService, instanceEnvironment] = this.createServices(args, bufferLogService);
try {
// Init services
await instantiationService.invokeFunction(async accessor => {
const environmentService = accessor.get(IEnvironmentService);
const configurationService = accessor.get(IConfigurationService);
const stateService = accessor.get(IStateService);
try {
await this.initServices(environmentService, configurationService as ConfigurationService, stateService as StateService);
} catch (error) {
// Show a dialog for errors that can be resolved by the user
this.handleStartupDataDirError(environmentService, error);
throw error;
}
});
// Startup
await instantiationService.invokeFunction(async accessor => {
const environmentService = accessor.get(IEnvironmentService);
const logService = accessor.get(ILogService);
const lifecycleMainService = accessor.get(ILifecycleMainService);
const configurationService = accessor.get(IConfigurationService);
const mainIpcServer = await this.doStartup(logService, environmentService, lifecycleMainService, instantiationService, true);
bufferLogService.logger = new SpdLogService('main', environmentService.logsPath, bufferLogService.getLevel());
once(lifecycleMainService.onWillShutdown)(() => (configurationService as ConfigurationService).dispose());
return instantiationService.createInstance(CodeApplication, mainIpcServer, instanceEnvironment).startup();
});
} catch (error) {
instantiationService.invokeFunction(this.quit, error);
}
}
private createServices(args: ParsedArgs, bufferLogService: BufferLogService): [IInstantiationService, typeof process.env] {
const services = new ServiceCollection();
const environmentService = new EnvironmentService(args, process.execPath);
const instanceEnvironment = this.patchEnvironment(environmentService); // Patch `process.env` with the instance's environment
services.set(IEnvironmentService, environmentService);
const logService = new MultiplexLogService([new ConsoleLogMainService(getLogLevel(environmentService)), bufferLogService]);
process.once('exit', () => logService.dispose());
services.set(ILogService, logService);
services.set(IConfigurationService, new ConfigurationService(environmentService.settingsResource));
services.set(ILifecycleMainService, new SyncDescriptor(LifecycleMainService));
services.set(IStateService, new SyncDescriptor(StateService));
services.set(IRequestService, new SyncDescriptor(RequestMainService));
services.set(IThemeMainService, new SyncDescriptor(ThemeMainService));
services.set(ISignService, new SyncDescriptor(SignService));
return [new InstantiationService(services, true), instanceEnvironment];
}
...
}
// Main Startup
const code = new CodeMain();
code.main();
可以看到 main() 函数最终调用了 startup() 函数。
在 startup() 函数中,先调用了 this.createServices() 函数来创建依赖的Services。
Services(服务) 是 VSCode 中一系列可以被注入的公共模块,这些 Services 分别负责不同的功能,在这里创建了几个基本服务。除了这些基本服务,VSCode 内还包含了大量的服务,如 IModeService、ICodeEditorService、IPanelService 等,通过 VSCode 实现的「依赖注入」模式,可以在需要用到这些服务的地方以 Decorator 的方式做为构造函数参数声明依赖,会被自动注入到类中。关于服务的依赖注入,后面的章节会重点讲解。
private createServices(args: ParsedArgs, bufferLogService: BufferLogService): [IInstantiationService, typeof process.env] {
const services = new ServiceCollection();
const environmentService = new EnvironmentService(args, process.execPath);
const instanceEnvironment = this.patchEnvironment(environmentService); // Patch `process.env` with the instance's environment
// environmentService 一些基本配置,包括运行目录、用户数据目录、工作区缓存目录等
services.set(IEnvironmentService, environmentService);
const logService = new MultiplexLogService([new ConsoleLogMainService(getLogLevel(environmentService)), bufferLogService]);
process.once('exit', () => logService.dispose());
// logService 日志服务
services.set(ILogService, logService);
// ConfigurationService 配置项
services.set(IConfigurationService, new ConfigurationService(environmentService.settingsResource));
// LifecycleService 生命周期相关的一些方法
services.set(ILifecycleMainService, new SyncDescriptor(LifecycleMainService));
// StateService 持久化数据
services.set(IStateService, new SyncDescriptor(StateService));
// RequestService 请求服务
services.set(IRequestService, new SyncDescriptor(RequestMainService));
services.set(IThemeMainService, new SyncDescriptor(ThemeMainService));
services.set(ISignService, new SyncDescriptor(SignService));
return [new InstantiationService(services, true), instanceEnvironment];
}
代码中可以看到 createServices() 最终实例化了一个 InstantiationService 实例并return回去,然后在 startup() 中调用 InstantiationService的createInstance方法并传参数CodeApplication,表示初始化CodeApplication实例,然后调用实例的 startup() 方法。
return instantiationService.createInstance(CodeApplication, mainIpcServer,instanceEnvironment).startup();
接下来我们去看CodeApplication中的startup方法。
//src/vs/code/electron-main/app.ts
export class CodeApplication extends Disposable {
...
async startup(): Promise<void> {
this.logService.debug('Starting VS Code');
this.logService.debug(`from: ${
this.environmentService.appRoot}`);
this.logService.debug('args:', this.environmentService.args);
// Make sure we associate the program with the app user model id
// This will help Windows to associate the running program with
// any shortcut that is pinned to the taskbar and prevent showing
// two icons in the taskbar for the same app.
const win32AppUserModelId = product.win32AppUserModelId;
if (isWindows && win32AppUserModelId) {
app.setAppUserModelId(win32AppUserModelId);
}
// Fix native tabs on macOS 10.13
// macOS enables a compatibility patch for any bundle ID beginning with
// "com.microsoft.", which breaks native tabs for VS Code when using this
// identifier (from the official build).
// Explicitly opt out of the patch here before creating any windows.
// See: https://github.com/Microsoft/vscode/issues/35361#issuecomment-399794085
try {
if (isMacintosh && this.configurationService.getValue<boolean>('window.nativeTabs') === true && !systemPreferences.getUserDefault('NSUseImprovedLayoutPass', 'boolean')) {
systemPreferences.setUserDefault('NSUseImprovedLayoutPass', 'boolean', true as any);
}
} catch (error) {
this.logService.error(error);
}
// Create Electron IPC Server
const electronIpcServer = new ElectronIPCServer();
// Resolve unique machine ID
this.logService.trace('Resolving machine identifier...');
const {
machineId, trueMachineId } = await this.resolveMachineId();
this.logService.trace(`Resolved machine identifier: ${
machineId} (trueMachineId: ${
trueMachineId})`);
// Spawn shared process after the first window has opened and 3s have passed
const sharedProcess = this.instantiationService.createInstance(SharedProcess, machineId, this.userEnv);
const sharedProcessClient = sharedProcess.whenReady().then(() => connect(this.environmentService.sharedIPCHandle, 'main'));
this.lifecycleMainService.when(LifecycleMainPhase.AfterWindowOpen).then(() => {
this._register(new RunOnceScheduler(async () => {
const userEnv = await getShellEnvironment(this.logService, this.environmentService);
sharedProcess.spawn(userEnv);
}, 3000)).schedule();
});
// Services
const appInstantiationService = await this.createServices(machineId, trueMachineId, sharedProcess, sharedProcessClient);
// Create driver
if (this.environmentService.driverHandle) {
const server = await serveDriver(electronIpcServer, this.environmentService.driverHandle!, this.environmentService, appInstantiationService);
this.logService.info('Driver started at:', this.environmentService.driverHandle);
this._register(server);
}
// Setup Auth Handler
this._register(new ProxyAuthHandler());
// Open Windows
const windows = appInstantiationService.invokeFunction(accessor => this.openFirstWindow(accessor, electronIpcServer, sharedProcessClient));
// Post Open Windows Tasks
this.afterWindowOpen();
// Tracing: Stop tracing after windows are ready if enabled
if (this.environmentService.args.trace) {
this.stopTracingEventually(windows);
}
}
...
private openFirstWindow(accessor: ServicesAccessor, electronIpcServer: ElectronIPCServer, sharedProcessClient: Promise<Client<string>>): ICodeWindow[] {
// Register more Main IPC services
const launchMainService = accessor.get(ILaunchMainService);
const launchChannel = createChannelReceiver(launchMainService, {
disableMarshalling: true });
this.mainIpcServer.registerChannel('launch', launchChannel);
// Register more Electron IPC services
const updateService = accessor.get(IUpdateService);
const updateChannel = new UpdateChannel(updateService);
electronIpcServer.registerChannel('update', updateChannel);
const issueService = accessor.get(IIssueService);
const issueChannel = createChannelReceiver(issueService);
electronIpcServer.registerChannel('issue', issueChannel);
const electronService = accessor.get(IElectronService);
const electronChannel = createChannelReceiver(electronService);
electronIpcServer.registerChannel('electron', electronChannel);
sharedProcessClient.then(client => client.registerChannel('electron', electronChannel));
const sharedProcessMainService = accessor.get(ISharedProcessMainService);
const sharedProcessChannel = createChannelReceiver(sharedProcessMainService);
electronIpcServer.registerChannel('sharedProcess', sharedProcessChannel);
const workspacesService = accessor.get(IWorkspacesService);
const workspacesChannel = createChannelReceiver(workspacesService);
electronIpcServer.registerChannel('workspaces', workspacesChannel);
const menubarService = accessor.get(IMenubarService);
const menubarChannel = createChannelReceiver(menubarService);
electronIpcServer.registerChannel('menubar', menubarChannel);
const urlService = accessor.get(IURLService);
const urlChannel = createChannelReceiver(urlService);
electronIpcServer.registerChannel('url', urlChannel);
const storageMainService = accessor.get(IStorageMainService);
const storageChannel = this._register(new GlobalStorageDatabaseChannel(this.logService, storageMainService));
electronIpcServer.registerChannel('storage', storageChannel);
const loggerChannel = new LoggerChannel(accessor.get(ILogService));
electronIpcServer.registerChannel('logger', loggerChannel);
sharedProcessClient.then(client => client.registerChannel('logger', loggerChannel));
// ExtensionHost Debug broadcast service
electronIpcServer.registerChannel(ExtensionHostDebugBroadcastChannel.ChannelName, new ExtensionHostDebugBroadcastChannel());
// Signal phase: ready (services set)
this.lifecycleMainService.phase = LifecycleMainPhase.Ready;
// Propagate to clients
const windowsMainService = this.windowsMainService = accessor.get(IWindowsMainService);
this.dialogMainService = accessor.get(IDialogMainService);
// Create a URL handler to open file URIs in the active window
const environmentService = accessor.get(IEnvironmentService);
urlService.registerHandler({
async handleURL(uri: URI, options?: IOpenURLOptions): Promise<boolean> {
// Catch file URLs
if (uri.authority === Schemas.file && !!uri.path) {
const cli = assign(Object.create(null), environmentService.args);
const urisToOpen = [{
fileUri: URI.file(uri.fsPath) }];
windowsMainService.open({
context: OpenContext.API, cli, urisToOpen, gotoLineMode: true });
return true;
}
return false;
}
});
// Create a URL handler which forwards to the last active window
const activeWindowManager = new ActiveWindowManager(electronService);
const activeWindowRouter = new StaticRouter(ctx => activeWindowManager.getActiveClientId().then(id => ctx === id));
const urlHandlerRouter = new URLHandlerRouter(activeWindowRouter);
const urlHandlerChannel = electronIpcServer.getChannel('urlHandler', urlHandlerRouter);
const multiplexURLHandler = new URLHandlerChannelClient(urlHandlerChannel);
// On Mac, Code can be running without any open windows, so we must create a window to handle urls,
// if there is none
if (isMacintosh) {
urlService.registerHandler({
async handleURL(uri: URI, options?: IOpenURLOptions): Promise<boolean> {
if (windowsMainService.getWindowCount() === 0) {
const cli = {
...environmentService.args };
const [window] = windowsMainService.open({
context: OpenContext.API, cli, forceEmpty: true, gotoLineMode: true });
await window.ready();
return urlService.open(uri);
}
return false;
}
});
}
// Register the multiple URL handler
urlService.registerHandler(multiplexURLHandler);
// Watch Electron URLs and forward them to the UrlService
const args = this.environmentService.args;
const urls = args['open-url'] ? args._urls : [];
const urlListener = new ElectronURLListener(urls || [], urlService, windowsMainService);
this._register(urlListener);
// Open our first window
const macOpenFiles: string[] = (<any>global).macOpenFiles;
const context = !!process.env['VSCODE_CLI'] ? OpenContext.CLI : OpenContext.DESKTOP;
const hasCliArgs = args._.length;
const hasFolderURIs = !!args['folder-uri'];
const hasFileURIs = !!args['file-uri'];
const noRecentEntry = args['skip-add-to-recently-opened'] === true;
const waitMarkerFileURI = args.wait && args.waitMarkerFilePath ? URI.file(args.waitMarkerFilePath) : undefined;
// new window if "-n" was used without paths
if (args['new-window'] && !hasCliArgs && !hasFolderURIs && !hasFileURIs) {
return windowsMainService.open({
context,
cli: args,
forceNewWindow: true,
forceEmpty: true,
noRecentEntry,
waitMarkerFileURI,
initialStartup: true
});
}
// mac: open-file event received on startup
if (macOpenFiles && macOpenFiles.length && !hasCliArgs && !hasFolderURIs && !hasFileURIs) {
return windowsMainService.open({
context: OpenContext.DOCK,
cli: args,
urisToOpen: macOpenFiles.map(file => this.getWindowOpenableFromPathSync(file)),
noRecentEntry,
waitMarkerFileURI,
gotoLineMode: false,
initialStartup: true
});
}
// default: read paths from cli
return windowsMainService.open({
context,
cli: args,
forceNewWindow: args['new-window'] || (!hasCliArgs && args['unity-launch']),
diffMode: args.diff,
noRecentEntry,
waitMarkerFileURI,
gotoLineMode: args.goto,
initialStartup: true
});
}
...
}
在CodeApplication.startup 中首先会启动 SharedProcess 共享进程,同时也创建了一些窗口相关的服务,包括 WindowsManager、WindowsService、MenubarService 等,负责窗口、多窗口管理及菜单等功能。然后调用 openFirstWindow 方法来开启窗口。
在openFirstWindow中,先创建一系列 Electron 的 IPC 频道,用于主进程和渲染进程间通信,其中 window 和 logLevel 频道还会被注册到 sharedProcessClient ,sharedProcessClient 是主进程与共享进程(SharedProcess)进行通信的 client,之后根据 environmentService 提供的相关参数(file_uri、folder_uri)调用了 windowsMainService.open 方法。
windowsMainService是WindowsManager实例化的服务,而WindowsManager是多窗体管理类(src/vs/code/electron-main/windows.ts)。接下来我们看windowsMainService.open 方法,可以看到其调用了doOpen方法。
open(openConfig: IOpenConfiguration): ICodeWindow[] {
...
// Open based on config
const usedWindows = this.doOpen(openConfig, workspacesToOpen, foldersToOpen,
...
}
doOpen方法最终调用了openInBrowserWindow方法。
private doOpen(
openConfig: IOpenConfiguration,
workspacesToOpen: IWorkspacePathToOpen[],
foldersToOpen: IFolderPathToOpen[],
emptyToRestore: IEmptyWindowBackupInfo[],
emptyToOpen: number,
fileInputs: IFileInputs | undefined,
foldersToAdd: IFolderPathToOpen[]
) {
const usedWindows: ICodeWindow[] = [];
...
// Handle empty to open (only if no other window opened)
if (usedWindows.length === 0 || fileInputs) {
if (fileInputs && !emptyToOpen) {
emptyToOpen++;
}
const remoteAuthority = fileInputs ? fileInputs.remoteAuthority : (openConfig.cli && openConfig.cli.remote || undefined);
for (let i = 0; i < emptyToOpen; i++) {
usedWindows.push(this.openInBrowserWindow({
userEnv: openConfig.userEnv,
cli: openConfig.cli,
initialStartup: openConfig.initialStartup,
remoteAuthority,
forceNewWindow: openFolderInNewWindow,
forceNewTabbedWindow: openConfig.forceNewTabbedWindow,
fileInputs
}));
// Reset these because we handled them
fileInputs = undefined;
openFolderInNewWindow = true; // any other window to open must open in new window then
}
}
return arrays.distinct(usedWindows);
}
在openInBrowserWindow中,创建一个CodeWindow实例并返回,并且还调用了doOpenInBrowserWindow这个方法,这个方法看下文介绍。
private openInBrowserWindow(options: IOpenBrowserWindowOptions): ICodeWindow {
...
// Create the window
window = this.instantiationService.createInstance(CodeWindow, {
state,
extensionDevelopmentPath: configuration.extensionDevelopmentPath,
isExtensionTestHost: !!configuration.extensionTestsPath
});
...
// If the window was already loaded, make sure to unload it
// first and only load the new configuration if that was
// not vetoed
if (window.isReady) {
this.lifecycleMainService.unload(window, UnloadReason.LOAD).then(veto => {
if (!veto) {
this.doOpenInBrowserWindow(window!, configuration, options);
}
});
} else {
this.doOpenInBrowserWindow(window, configuration, options);
}
return window;
}
接下来我们找到CodeWindow定义在src/vs/code/electron-main/window.ts中,在CodeWindow的构造函数中调用了createBrowserWindow方法,然后在createBrowserWindow方法中看到实例化了一个BrowserWindow,这是Electron中浏览器窗口的定义。
//src/vs/code/electron-main/window.ts
export class CodeWindow extends Disposable implements ICodeWindow {
...
constructor(
config: IWindowCreationOptions,
@ILogService private readonly logService: ILogService,
@IEnvironmentService private readonly environmentService: IEnvironmentService,
@IFileService private readonly fileService: IFileService,
@IConfigurationService private readonly configurationService: IConfigurationService,
@IThemeMainService private readonly themeMainService: IThemeMainService,
@IWorkspacesMainService private readonly workspacesMainService: IWorkspacesMainService,
@IBackupMainService private readonly backupMainService: IBackupMainService,
) {
super();
this.touchBarGroups = [];
this._lastFocusTime = -1;
this._readyState = ReadyState.NONE;
this.whenReadyCallbacks = [];
// create browser window
this.createBrowserWindow(config);
// respect configured menu bar visibility
this.onConfigurationUpdated();
// macOS: touch bar support
this.createTouchBar();
// Request handling
this.handleMarketplaceRequests();
// Eventing
this.registerListeners();
}
private createBrowserWindow(config: IWindowCreationOptions): void {
...
// Create the browser window.
this._win = new BrowserWindow(options);
...
}
}
现在窗口有了,那么什么时候加载页面呢?刚刚我们在上文提到,在openInBrowserWindow中,创建一个CodeWindow实例并返回,并且还调用了doOpenInBrowserWindow这个方法,那么我们看一下这个方法的定义。
private doOpenInBrowserWindow(window: ICodeWindow, configuration: IWindowConfiguration, options: IOpenBrowserWindowOptions): void {
...
// Load it
window.load(configuration);
...
}
这个方法有调用CodeWindow的load方法,然后看一下load方法的定义。会看到调用了this._win.loadURL,这个this._win就是CodeWindow创建的BrowserWindow窗口,这就找到了窗口加载的URL时机。
load(config: IWindowConfiguration, isReload?: boolean, disableExtensions?: boolean): void {
...
// Load URL
perf.mark('main:loadWindow');
this._win.loadURL(this.getUrl(configuration));
...
}
然后看一下getUrl方法的定义,最终返回的configUrl是调用doGetUrl获取的。
private getUrl(windowConfiguration: IWindowConfiguration): string {
...
let configUrl = this.doGetUrl(config);
...
return configUrl;
}
然后看一下doGetUrl方法,可以看到返回的Url路径为vs/code/electron-browser/workbench/workbench.html。
private doGetUrl(config: object): string {
return `${
require.toUrl('vs/code/electron-browser/workbench/workbench.html')}?config=${
encodeURIComponent(JSON.stringify(config))}`;
}
这是整个 Workbench 的入口,HTML出现了,主进程的使命完成,渲染进程登场。
//src/vs/code/electron-browser/workbench/workbench.html
<!-- Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="default-src 'none'; img-src 'self' https: data: blob: vscode-remote-resource:; media-src 'none'; frame-src 'self' https://*.vscode-webview-test.com; object-src 'self'; script-src 'self'; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; connect-src 'self' https:; font-src 'self' https: vscode-remote-resource:;">
</head>
<body class="vs-dark" aria-label="">
</body>
<!-- Startup via workbench.js -->
<script src="workbench.js"></script>
</html>
workbench.html中加载了workbench.js文件,这个文件负责加载真正的 Workbench 模块并调用其 main 方法初始化主界面。
// src/vs/code/electron-browser/workbench/workbench.js
const bootstrapWindow = require('../../../../bootstrap-window');
// Setup shell environment
process['lazyEnv'] = getLazyEnv();
// Load workbench main JS, CSS and NLS all in parallel. This is an
// optimization to prevent a waterfall of loading to happen, because
// we know for a fact that workbench.desktop.main will depend on
// the related CSS and NLS counterparts.
bootstrapWindow.load([
'vs/workbench/workbench.desktop.main',
'vs/nls!vs/workbench/workbench.desktop.main',
'vs/css!vs/workbench/workbench.desktop.main'
],
function (workbench, configuration) {
perf.mark('didLoadWorkbenchMain');
return process['lazyEnv'].then(function () {
perf.mark('main/startup');
// @ts-ignore
//加载 Workbench 并初始化主界面
return require('vs/workbench/electron-browser/desktop.main').main(configuration);
});
}, {
removeDeveloperKeybindingsAfterLoad: true,
canModifyDOM: function (windowConfig) {
showPartsSplash(windowConfig);
},
beforeLoaderConfig: function (windowConfig, loaderConfig) {
loaderConfig.recordStats = true;
},
beforeRequire: function () {
perf.mark('willLoadWorkbenchMain');
}
});
我们可以看到加载了vs/workbench/electron-browser/desktop.main模块,并调用了模块的main方法。main方法中实例化了一个DesktopMain,并调用了DesktopMain的open方法。
class DesktopMain extends Disposable {
async open(): Promise<void> {
...
// Create Workbench
const workbench = new Workbench(document.body, services.serviceCollection, services.logService);
// Listeners
this.registerListeners(workbench, services.storageService);
// Startup
const instantiationService = workbench.startup();
...
}
...
}
export function main(configuration: IWindowConfiguration): Promise<void> {
const renderer = new DesktopMain(configuration);
return renderer.open();
}
我们看到DesktopMain的open方法中实例化了Workbench类,并调用了Workbench的startup方法。接下来我们看一下这个Workbench类。
export class Workbench extends Layout {
...
startup(): IInstantiationService {
try {
// Configure emitter leak warning threshold
setGlobalLeakWarningThreshold(175);
// ARIA
setARIAContainer(document.body);
// Services
const instantiationService = this.initServices(this.serviceCollection);
instantiationService.invokeFunction(async accessor => {
const lifecycleService = accessor.get(ILifecycleService);
const storageService = accessor.get(IStorageService);
const configurationService = accessor.get(IConfigurationService);
// Layout
this.initLayout(accessor);
// Registries
this.startRegistries(accessor);
// Context Keys
this._register(instantiationService.createInstance(WorkbenchContextKeysHandler));
// Register Listeners
this.registerListeners(lifecycleService, storageService, configurationService);
// Render Workbench
this.renderWorkbench(instantiationService, accessor.get(INotificationService) as NotificationService, storageService, configurationService);
// Workbench Layout
this.createWorkbenchLayout(instantiationService);
// Layout
this.layout();
// Restore
try {
await this.restoreWorkbench(accessor.get(IEditorService), accessor.get(IEditorGroupsService), accessor.get(IViewletService), accessor.get(IPanelService), accessor.get(ILogService), lifecycleService);
} catch (error) {
onUnexpectedError(error);
}
});
return instantiationService;
} catch (error) {
onUnexpectedError(error);
throw error; // rethrow because this is a critical issue we cannot handle properly here
}
}
...
}
我们可以看到Workbench继承Layout布局类,在 workbench.startup 方法中构建主界面布局、创建全局事件监听以及实例化一些依赖的服务,全部完成后会还原之前打开的编辑器,整个 Workbench 加载完成。
所以前文中的大量代码只是为这里最终创建主界面做铺垫,Workbench 模块主要代码都在 vs/workbench 目录下,主要负责界面元素的创建和具体业务功能的实现。
至此,从启动到加载到html,再到构建主界面布局,整个流程很清晰。
应用信息定制
在VSCode源码根目录下有一个product.json文件,此文件用于配置应用的信息。
{
"nameShort": "Code - OSS",
"nameLong": "Code - OSS",
"applicationName": "code-oss",
"dataFolderName": ".vscode-oss",
"win32MutexName": "vscodeoss",
"licenseName": "MIT",
"licenseUrl": "https://github.com/Microsoft/vscode/blob/master/LICENSE.txt",
"win32DirName": "Microsoft Code OSS",
"win32NameVersion": "Microsoft Code OSS",
"win32RegValueName": "CodeOSS",
"win32AppId": "{
{E34003BB-9E10-4501-8C11-BE3FAA83F23F}",
"win32x64AppId": "{
{D77B7E06-80BA-4137-BCF4-654B95CCEBC5}",
"win32UserAppId": "{
{C6065F05-9603-4FC4-8101-B9781A25D88E}",
"win32x64UserAppId": "{
{C6065F05-9603-4FC4-8101-B9781A25D88E}",
"win32AppUserModelId": "Microsoft.CodeOSS",
"win32ShellNameShort": "C&ode - OSS",
"darwinBundleIdentifier": "com.visualstudio.code.oss",
"linuxIconName": "com.visualstudio.code.oss",
"licenseFileName": "LICENSE.txt",
"reportIssueUrl": "https://github.com/Microsoft/vscode/issues/new",
"urlProtocol": "code-oss",
"extensionAllowedProposedApi": [
"ms-vscode.references-view"
]
}
可以修改product.json的信息来更新定制VSCode的名称等信息。如果你在执行了./scripts/code.sh后修改了product.json的信息,比如修改了nameLong的配置,这时候重新运行./scripts/code.sh会报错。
错误信息是 ./scripts/code.sh: line 53: /Users/jiangshuaijie/Desktop/vscode-1.39.2/.build/electron/test.app/Contents/MacOS/Electron: No such file or directory ,可以看出是在code.sh中报错了,看一下code.sh中内容。
...
function code() {
cd "$ROOT"
if [[ "$OSTYPE" == "darwin"* ]]; then
NAME=`node -p "require('./product.json').nameLong"`
CODE="./.build/electron/$NAME.app/Contents/MacOS/Electron"
else
NAME=`node -p "require('./product.json').applicationName"`
CODE=".build/electron/$NAME"
fi
...
# Launch Code
exec "$CODE" . "$@"
}
...
最终根据product.json中的nameLong来运行根目录下.build/electron/下生成的app,这时候的应用是之前生成过的,所以会报错。我们只需删除掉根目录下.build文件夹,重新执行./scripts/code.sh即可。
应用图标定制
在VSCode源码根目录下resources文件夹主要用于存放VSCode平台的静态资源,例如应用图标等。
其中darwin、linux、win32对应三个不同的平台,可以在不同平台文件夹下替换图片资源。
更多精彩请关注 https://codeteenager.github.io/vscode-analysis/ ,后面会更新更多内容。