SpringBoot与缓存使用与原理并debug源码讲解
下面我就开始介绍springboot中的缓存:
首先了解下JSR107、Spring缓存抽象等等概念。
一 、JSR107(下面会有具体Springboot代码演示)
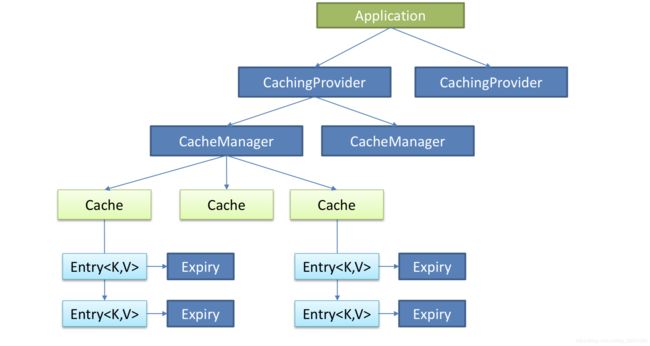
Java Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry 和 Expiry。
1 CachingProvider定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
2 CacheManager定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
3 Cache是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有。
4 Entry是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对.
5 Expiry 每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
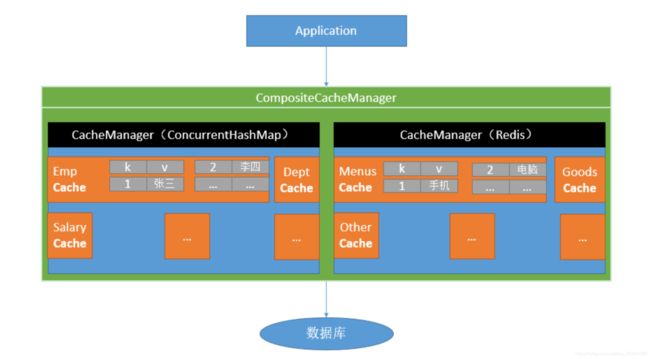
二、 Spring缓存抽象
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术;并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发;
- Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
- Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现,如RedisCache,EhCacheCache , ConcurrentMapCache等;每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果返回给用户。下次直接从缓存中获取。
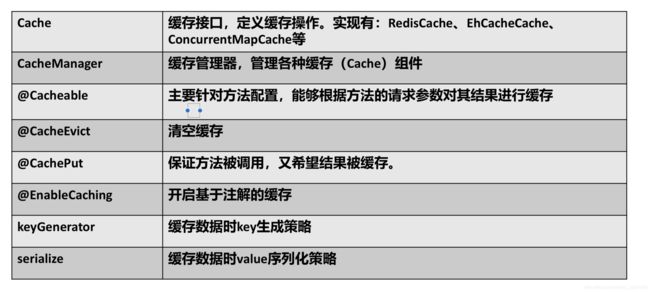
三、几个重要概念&缓存注解
四 、缓存使用
前提条件:创建一个springboot web工程导入mybatis与数据源的整合,因为使用缓存所以需要对库的操作,这里不做详细介绍,主要介绍缓存。我会做一个整合各种资源的工程,后期会上传
1. 要在Springboot中使用缓存需要以下几步:
1.1 导入spring-boot-starter-cache模块
1.2 @EnableCaching开启缓存
1.3 使用缓存注解
1.4切换为其他缓存,这个后面会介绍使用redis缓存
2. 下面来介绍缓存的使用,首先需要导入cache依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cacheartifactId>
dependency>
3. 简单环境介绍,并测试缓存结果
beans类
package com.cjy.mq.bean;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String stuName;
private Integer stuAge;
private String stuEmail;
private Double stuHeight;
private Integer classId;
public Student() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getStuName() {
return stuName;
}
public void setStuName(String stuName) {
this.stuName = stuName;
}
public Integer getStuAge() {
return stuAge;
}
public void setStuAge(Integer stuAge) {
this.stuAge = stuAge;
}
public String getStuEmail() {
return stuEmail;
}
public void setStuEmail(String stuEmail) {
this.stuEmail = stuEmail;
}
public Double getStuHeight() {
return stuHeight;
}
public void setStuHeight(Double stuHeight) {
this.stuHeight = stuHeight;
}
public Integer getClassId() {
return classId;
}
public void setClassId(Integer classId) {
this.classId = classId;
}
public Student(Integer id, String stuName, Integer stuAge, String stuEmail, Double stuHeight, Integer classId) {
this.id = id;
this.stuName = stuName;
this.stuAge = stuAge;
this.stuEmail = stuEmail;
this.stuHeight = stuHeight;
this.classId = classId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentController{" +
"id=" + id +
", stuName='" + stuName + '\'' +
", stuAge=" + stuAge +
", stuEmail='" + stuEmail + '\'' +
", stuHeight=" + stuHeight +
", classId=" + classId +
'}';
}
}
controller层接口
@RestController
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
StudentService studentService;
@GetMapping("/stu/{id}")
public Student getStu(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return studentService.getStudentById(id);
}
@PutMapping("/stu")
public Student update(Student student){
Student stu = studentService.updateStu(student);
return stu;
}
@DeleteMapping("/stu/{id}")
public Student deleteStuById(Integer id){
Student student = studentService.deleteStuById(id);
return student;
}
}
service 实现层,接口就不展示了
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
private static final Logger log= LoggerFactory.getLogger(StudentServiceImpl.class);
@Autowired
StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Override
public Student getStudentById(Integer id) {
Student student = studentMapper.getStudentById(id);
log.info("查询"+id+" 号学生信息:" + student);
return student;
}
@Override
public Student updateStu(Student student) {
Student stu = studentMapper.updateStu(student);
log.info("修改"+student.getId()+" 号学生信息:" + student);
return stu;
}
@Override
public Student deleteStuById(Integer id) {
Student stu = studentMapper.deleteStuById(id);
log.info("删除"+stu.getId()+" 号学生信息:" + stu);
return stu;
}
}
mapper层
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
@Select("select * from student where id=#{id}")
public Student getStudentById(Integer id);
@Select("select * from student ")
public List<Student> getAll();
@Update("update student set stu_name=#{stuName},stu_age=#{stuAge},set stu_email=#{stuEmail} where id=#{id}; ")
Student updateStu(Student student);
@Delete("delete from student where id = #{id}")
public Student deleteStuById(Integer id);
}
4. 查询缓存使用
4.1 启动工程postman测试:http://localhost:8080/stu/1, 点击多次看控制台日志结果
2019-03-16 12:30:36.404 INFO 97519 --- [nio-8080-exec-2] c.c.mq.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl : 查询1 号员工信息:StudentController{id=1, stuName='张三', stuAge=16, stuEmail='zhangsan@email', stuHeight=145.0, classId=1}
2019-03-16 12:30:36.445 DEBUG 97519 --- [nio-8080-exec-2] o.s.b.w.f.OrderedRequestContextFilter : Cleared thread-bound request context: org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade@4b1e4a93
2019-03-16 12:30:40.538 DEBUG 97519 --- [nio-8080-exec-3] o.s.b.w.f.OrderedRequestContextFilter : Bound request context to thread: org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade@4b1e4a93
2019-03-16 12:30:40.561 INFO 97519 --- [nio-8080-exec-3] c.c.mq.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl : 查询1 号员工信息:StudentController{id=1, stuName='张三', stuAge=16, stuEmail='zhangsan@email', stuHeight=145.0, classId=1}
2019-03-16 12:30:40.562 DEBUG 97519 --- [nio-8080-exec-3] o.s.b.w.f.OrderedRequestContextFilter : Cleared thread-bound request context: org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade@4b1e4a93
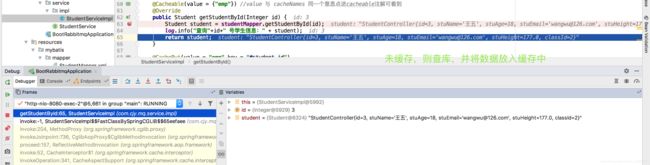
4.2 为查询方法添加缓存注解重启服务,然后再此测试多次发送请求后查看控制台
@Cacheable(value = {"emp"}) //value 与 cacheNames 同一个意思点进cacheable注解可看到
@Override
public Student getStudentById(Integer id) {
Student student = studentMapper.getStudentById(id);
log.info("查询"+id+" 学生信息:" + student);
return student;
}
控制台日志信息,可以看出第一次查库后不在查询,而是去查缓存
2019-03-16 12:33:22.160 INFO 98245 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource : {dataSource-1} inited
2019-03-16 12:33:22.267 INFO 98245 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] c.c.mq.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl : 查询1 号员工信息:StudentController{id=1, stuName='张三', stuAge=16, stuEmail='zhangsan@email', stuHeight=145.0, classId=1}
2019-03-16 12:33:22.308 DEBUG 98245 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.b.w.f.OrderedRequestContextFilter : Cleared thread-bound request context: org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade@68252674
2019-03-16 12:33:22.663 DEBUG 98245 --- [nio-8080-exec-3] o.s.b.w.f.OrderedRequestContextFilter : Bound request context to thread: org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade@68252674
4.3 @Cacheable 注解介绍
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.cache.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Cacheable {
@AliasFor("cacheNames")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String key() default "";
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
String condition() default "";
String unless() default "";
boolean sync() default false;
}
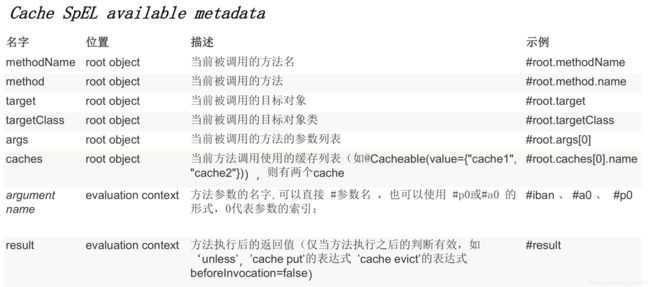
1.@Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先来检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存,如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存;以后再来调用就可以直接使用缓存中的数据;
2.CacheManager:管理多个Cache组件的,对缓存的真正CRUD操作在Cache组件中,每一个缓存组件有自己唯一一个名字;
3.cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字;将方法的返回结果放在哪个缓存中,是数组的方式,可以指定多个缓存;
4.key:缓存数据使用的key;可以用它来指定。默认是使用方法参数的值 1-方法的返回值
5.keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id,key/keyGenerator:二选一使用;
6.condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存;如:condition = "#id>0"表示id大于0的才被缓存
7.unless:否定缓存;当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会被缓存;
可以获取到结果进行判断:unless = "#result == null"
unless = "#a0==2":如果第一个参数的值是2,结果不缓存;
8.sync:是否使用异步模式
5. @CachePut:既调用方法,又更新缓存数据;同步更新缓存
下面测试对一号员工修改然后查询其结果,看看缓存的结果是否是修改后的
5.1 未加缓存更新注解前
1.查询 http://localhost:8080/stu/1
2019-03-16 13:16:56.631 INFO 10391 --- [nio-8080-exec-3] c.c.mq.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl : 查询1 号员工信息:StudentController{id=1, stuName='张三', stuAge=16, stuEmail='zhangsan@email', stuHeight=145.0, classId=1}
2.修改 http://localhost:8080/stu?id=1&stuName=张[email protected]
2019-03-16 13:18:03.895 INFO 10391 --- [nio-8080-exec-6] c.c.mq.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl : 修改1 号员工信息:StudentController{id=1, stuName='张san222', stuAge=null, stuEmail='[email protected]', stuHeight=null, classId=null}
3. 继续查询 http://localhost:8080/stu/1 --未查询数据库,postman中的结果
{
"id": 1,
"stuName": "张三",
"stuAge": 16,
"stuEmail": "zhangsan@email",
"stuHeight": 145,
"classId": 1
}
2019-03-16 13:19:16.870 DEBUG 10391 --- [nio-8080-exec-2] o.s.b.w.f.OrderedRequestContextFilter : Bound request context to thread: org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade@589a1a4e
2019-03-16 13:19:16.872 DEBUG 10391 --- [nio-8080-exec-2] o.s.b.w.f.OrderedRequestContextFilter : Cleared thread-bound request context: org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade@589a1a4e
5.2 下面就来试试神奇的 更新缓存注解
@CachePut
@Override
public Student updateStu(Student student) {
studentMapper.updateStu(student);
log.info("修改"+student.getId()+" 号学生信息:" + student);
return student;
}
//1.注意这时使用更新会报错:http://localhost:8080/stu?id=1&stuName=张[email protected]
java.lang.IllegalStateException: No cache could be resolved for 'Builder[public com.cjy.mq.bean.Student com.cjy.mq.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl.updateStu(com.cjy.mq.bean.Student)] caches=[] | key='' | keyGenerator='' | cacheManager='' | cacheResolver='' | condition='' | unless=''' using resolver 'org.springframework.cache.interceptor.SimpleCacheResolver@169eba48'. At least one cache should be provided per cache operation.
//2. 大概错误意思就是你没有指定我更新那个缓存组件的key是什么的缓存数据
//3.设置注解参数,使用这个才行
@CachePut(value = "emp",key = "#student.id")
@Override
public Student updateStu(Student student) {
studentMapper.updateStu(student);
log.info("修改"+student.getId()+" 学生信息:" + student);
return student;
}
//4. 大概测试就是,先根据id查询一条数据,在根据id修改此条数据,再根据id查询数据结果是修改后的
5.3 @CachePut 介绍
1. @CachePut:既调用方法,又更新缓存数据;同步更新缓存
2. 运行时机:先调用目标方法,将目标方法的结果缓存起来
3. key = "#employee.id":使用传入的参数的员工id
key = "#result.id":使用返回后的id
@Cacheable的key是不能用#result
6. 缓存删除@CacheEvict:缓存清除,这个跟更新差不多也没什么特点就是指定 value,key意思就是那个缓存组件的那条数据即可
注意:缓存清除的时间
/**
* * @CacheEvict:缓存清除
* * key:指定要清除的数据, #id
* * allEntries = true:指定清除这个缓存中所有的数据
* * beforeInvocation = false:缓存的清除是否在方法之前执行
* * 默认代表缓存清除操作是在方法执行之后执行;如果出现异常缓存就不会清除
* *
* * beforeInvocation = true:
* * 代表清除缓存操作是在方法运行之前执行,无论方法是否出现异常,缓存都清除
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Transactional //事物注解,方法执行完毕提交事物,异常则回滚
@CacheEvict(value = "emp",beforeInvocation = true,key = "#id")
@Override
public Integer deleteStuById(Integer id) {
studentMapper.deleteStuById(id);
int i=8/0;
log.info("删除"+id+" 号学生信息:");
return id;
}
//测试流程:1.先查询id=1的数据将其结果缓存起来
//2.移除id=1的数据,方法执行先前移除缓存,但是int i=8/0;导致数据删除失败,但是缓存被清除了
//3.继续查询id=1的数据,发现需要重新向数据库发送sql
7. 其他注解介绍
1. @CacheConfig(cacheNames="emp") //抽取缓存的公共配置,因为不管是存放、修改、清除缓存都需要指定是哪个缓存,如果同一个类操作的缓存模块一样,那么可以抽取出来这个缓存名字配置,表示当前类中的所有缓存操作都是针对类上配置的@CacheConfig(cacheNames="emp") 这个注解的emp缓存
2. 复杂缓存规则定义:将查询的结果用于放入缓存,同时更新缓存
// @Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则
@Caching(
cacheable = {//放入缓存
@Cacheable(/*value="emp",*/key = "#stuName")
},
put = {//更新缓存
@CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.stuEmail")
}
)
五、原理
使用sprinboot应该了解他是自动配置一些相应组件的配置,既然使用cache那么相比应该有一个cacha自动配置的类:CacheAutoConfiguration
- 查找自动配置类
-
自动选择那些组件
-
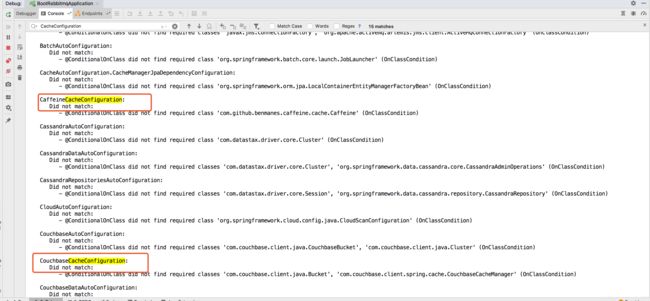
修改配置文件 debug: true 查看启动报告,看默认选择了那个缓存组件
----可以看出选择了这个缓存组件
SimpleCacheConfiguration matched:
- Cache org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration automatic cache type (CacheCondition)
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean (types: org.springframework.cache.CacheManager; SearchStrategy: all) did not find any beans (OnBeanCondition)
--------------------------
CaffeineCacheConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required class 'com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Caffeine' (OnClassCondition)
----------------------------------
CouchbaseCacheConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required classes 'com.couchbase.client.java.Bucket', 'com.couchbase.client.spring.cache.CouchbaseCacheManager' (OnClassCondition)
---------------------------------------
EhCacheCacheConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required class 'net.sf.ehcache.Cache' (OnClassCondition)
重点----------------------------------------------
默认缓存组件:SimpleCacheConfiguration
- 查看默认缓存组件做了什么:SimpleCacheConfiguration 进入这个类
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({CacheManager.class})
@Conditional({CacheCondition.class})
class SimpleCacheConfiguration {
private final CacheProperties cacheProperties;
private final CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker;
SimpleCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties, CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker) {
this.cacheProperties = cacheProperties;
this.customizerInvoker = customizerInvoker;
}
//注意,它向容器中注入了一个ConcurrentMapCacheManager
@Bean
public ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager() {
ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager();
List<String> cacheNames = this.cacheProperties.getCacheNames();
if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {
cacheManager.setCacheNames(cacheNames);
}
return (ConcurrentMapCacheManager)this.customizerInvoker.customize(cacheManager);
}
}
SimpleCacheConfiguration向容器中注入了一个ConcurrentMapCacheManager 缓存管理器,接下来我们就去看看这个缓存管理器做了什么
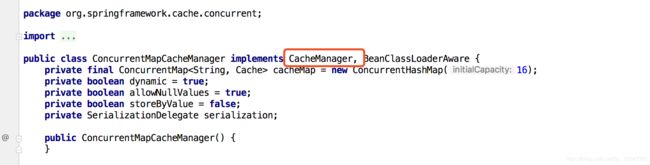
- ConcurrentMapCacheManager 做了什么
5.1 可以看出ConcurrentMapCacheManager实现了CacheManager接口,既然实现了这个接口那么我们就去看看这个接口是干嘛呢。
5.2 CacheManager接口作用
package org.springframework.cache;
import java.util.Collection;
public interface CacheManager {
Cache getCache(String var1);//获取缓存
Collection<String> getCacheNames(); //获取所有缓存
}
5.3 回过来看ConcurrentMapCacheManager 既然它实现了CacheManager那么必然实现它的方法重写,洗面我们就看看怎么重写的,如下代码:
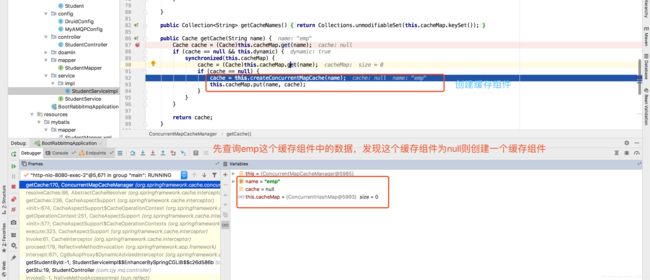
//用于存放所有缓存组件,如上述查询 @Cacheable(value = {"emp"}),这里会存放一个key=emp,value=Cache 的键值对
private final ConcurrentMap<String, Cache> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap(16);
public Collection<String> getCacheNames() {
//cacheMap:可以看出获取的所有缓存实际上是在一个cacheMap集合中,看到这我们应该就大致明白了,创建的缓存组件都存放在这里
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(this.cacheMap.keySet());
}
//根据名称获取缓存组件
public Cache getCache(String name) {
//1.尝试获取
Cache cache = (Cache)this.cacheMap.get(name);
//2.如果当前缓存组件存在则直接返回,若是尚未创建,则调用类中创建方法创建缓存组件
if (cache == null && this.dynamic) {
synchronized(this.cacheMap) {
//3. 再次判断避免重复创建,----单例模式,双重锁机制
cache = (Cache)this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null) {
//4.创建缓存组件。
cache = this.createConcurrentMapCache(name);
this.cacheMap.put(name, cache);
}
}
}
return cache;
}
//下面就来看看缓存组件是怎么创建的,并且缓存组件到底是个什么东西
protected Cache createConcurrentMapCache(String name) {
SerializationDelegate actualSerialization = this.isStoreByValue() ? this.serialization : null;
//这里发现它直接new一个ConcurrentMapCache对象,并且设置了一些参数,那么我么你就去看看这个对象到底是干嘛的。
return new ConcurrentMapCache(name, new ConcurrentHashMap(256), this.isAllowNullValues(), actualSerialization);
}
6. ConcurrentMapCache缓存容器对象里面到底有些什么
//1. 调用了这个构造函数,并且用构造器初始化一些属性
protected ConcurrentMapCache(String name, ConcurrentMap<Object, Object> store, boolean allowNullValues, SerializationDelegate serialization) {
super(allowNullValues);
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
Assert.notNull(store, "Store must not be null");
this.name = name;
this.store = store;
this.serialization = serialization;
}
//2. 变量查看
private final String name; //缓存组件名称
private final ConcurrentMap<Object, Object> store; //缓存组件的容器,存放缓存
private final SerializationDelegate serialization;
//3. 方法查看
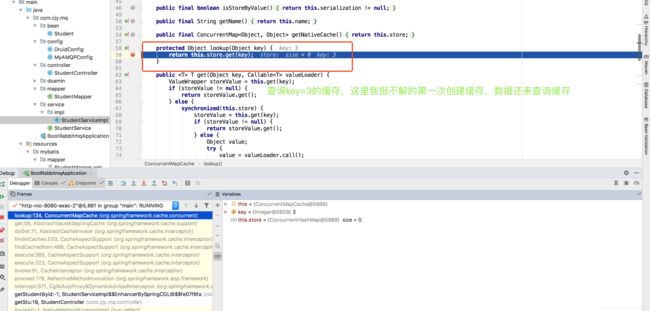
//查询缓存
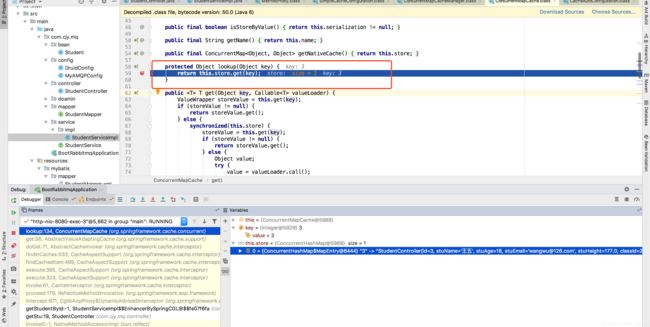
protected Object lookup(Object key) {
return this.store.get(key);
}
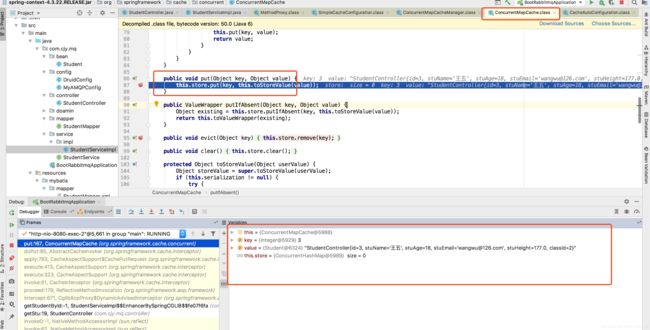
//放入缓存
public void put(Object key, Object value) {
this.store.put(key, this.toStoreValue(value));
}
//根据key删除缓存
public void evict(Object key) {
this.store.remove(key);
}
//清空缓存
public void clear() {
this.store.clear();
}
当然在debug过程中会发现它在执行缓存操作时出现了一些抽象方法,不用管,它的核心实现就是如上面这些,可在我标注的一些地方加上断点,简单走一个debug流程即可明白。都说这么多了那我就在做一个简单的查询数据并放入缓存中的debug流程
六、debug查询数据并放入缓存流程
----------至此结束,半天周末时光又没了,希望对你们有用。