JDK8新特性7——收集Stream流中的结果到数组和集合
目录
1. 收集Stream流中的结果到集合
1.1 收集到List集合——toList
1.2 收集到Set集合——toSet
1.3 收集到指定集合
2. 收集集合中的数据到数组中
2.1 转成Object数组——toArray
2.2 转成指定类型的数组——toArray
3. 对流中的数据的操作
3.1 对流中的数据进行聚合计算
3.1.1 获取最大值——Collectors.maxBy
3.1.2 获取最小值——Collectors.minBy
3.1.3 求和——Collectors.summingDouble
3.1.4 求平均值——Collectors.averagingDouble
3.1.5 统计数量——Collectors.counting()
3.2 对流中的数据进行分组
3.2.1 简单的分组——Collectors.groupingBy
3.2.1 多级分组——Collectors.groupingBy
3.3 对流中的数据进行分区——Collectors.partitioningBy
3.4 对流中的数据进行拼接——Collertors.joining
1. 收集Stream流中的结果到集合
Stream流提供collect方法,其参数需要一个java.util.stream.Collector
1.1 收集到List集合——toList
例如:
public static void testList(){
Stream stream = Stream.of("张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六");
List list = stream.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
} 1.2 收集到Set集合——toSet
例如:
public static void testSet(){
Stream stream = Stream.of("张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六");
Set set = stream.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(set);
} 1.3 收集到指定集合
例如:收集到ArrayList集合中
public static void testArrayList(){
Stream stream = Stream.of("张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六");
ArrayList arrayList = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
System.out.println(arrayList);
} 2. 收集集合中的数据到数组中
2.1 转成Object数组——toArray
例如:
public static void test2Array(){
Stream stream = Stream.of("张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六");
Object[] array = stream.toArray();
for(Object o : array){
System.out.println(o);
}
} 该方式转成Object类型的数组,我们操作起来不是很方便
2.2 转成指定类型的数组——toArray
例如:将String流转成String数组
public static void test2Array1(){
Stream stream = Stream.of("张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六");
String[] array = stream.toArray(String[]::new);
for(String str : array){
System.out.println("元素是:" + str + " 元素长度是:" + str.length());
}
} 3. 对流中的数据的操作
3.1 对流中的数据进行聚合计算
当我们使用Stream流处理数据后,可以像数据库聚合函数一样,对某个字段进行处理,比如,获取最大值,获取最小值,求总和,平均值,统计数量等。
3.1.1 获取最大值——Collectors.maxBy
例如:
public class StreamCollectTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream stream = Stream.of(
new Student("张三", 21, 97D),
new Student("李四", 23, 88D),
new Student("王五", 20, 62D),
new Student("赵六", 18, 59D),
new Student("钱七", 24, 100D)
);
// 查找分数最大的student
Optional optionalStudent = stream.collect(Collectors.maxBy((s1, s2) -> {
return s1.getScore() - s2.getScore() > 0 ? 1 : -1;
}));
Student student = optionalStudent.get();
System.out.println(student);
}
}
3.1.2 获取最小值——Collectors.minBy
public class StreamCollectTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream stream = Stream.of(
new Student("张三", 21, 97D),
new Student("李四", 23, 88D),
new Student("王五", 20, 62D),
new Student("赵六", 18, 59D),
new Student("钱七", 24, 100D)
);
// 查找分数最小的student
Optional optionalStudent = stream.collect(Collectors.minBy((s1, s2) -> {
return s1.getScore() - s2.getScore() > 0 ? 1 : -1;
}));
Student student = optionalStudent.get();
System.out.println(student);
}
}
3.1.3 求和——Collectors.summingDouble
// 求所有分数之和
Double aDouble = stream.collect(Collectors.summingDouble(Student::getScore));3.1.4 求平均值——Collectors.averagingDouble
// 求分数的平均值
Double aDouble = stream.collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Student::getScore));
System.out.println(aDouble);3.1.5 统计数量——Collectors.counting()
// 求流中一共有多少个数据
Long aLong = stream.collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println(aLong);3.2 对流中的数据进行分组
当我们使用Stream流处理数据后,可以根据某个属性将数据分组
3.2.1 简单的分组——Collectors.groupingBy
方法定义:
public static Collector>> groupingBy(Function classifier) {
return groupingBy(classifier, toList());
} 例1:按年龄分组
package com.bjc.jdk8.col;
import com.bjc.jdk8.pojo.Student;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class StreamCollectTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream stream = Stream.of(
new Student("张三", 21, 97D),
new Student("李四", 21, 88D),
new Student("王五", 24, 62D),
new Student("赵六", 18, 59D),
new Student("钱七", 24, 100D)
);
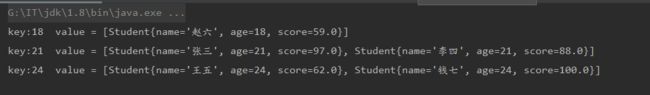
// 根据年龄将数据分组
Map> collect = stream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge));
collect.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println("key:" + k + " value = " + v);
});
}
}
运行结果如图:
例2:按分数区间分组
package com.bjc.jdk8.col;
import com.bjc.jdk8.pojo.Student;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class StreamCollectTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream stream = Stream.of(
new Student("张三", 21, 97D),
new Student("李四", 21, 88D),
new Student("王五", 24, 62D),
new Student("赵六", 18, 59D),
new Student("钱七", 24, 100D)
);
Map> map = stream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(student -> {
if (student.getScore() > 80) {
return "优秀";
} else {
return "良";
}
}));
map.forEach((k,v) -> {
System.out.println("k:" + k + " v:" + v);
});
}
}
运行结果:
3.2.1 多级分组——Collectors.groupingBy
使用Collectors.groupingBy的重载函数,方法定义
public static Collector> groupingBy(Function classifier,Collector downstream) {
return groupingBy(classifier, HashMap::new, downstream);
} 例如:
package com.bjc.jdk8.col;
import com.bjc.jdk8.pojo.Student;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class StreamCollectTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream stream = Stream.of(
new Student("张三", 21, 97D),
new Student("李四", 21, 88D),
new Student("王五", 24, 62D),
new Student("赵六", 18, 59D),
new Student("钱七", 24, 100D)
);
// 先根据年龄分组,在根据分数分组
Map>> collect = stream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge, Collectors.groupingBy(s -> {
if (s.getScore() > 80) {
return "优秀";
} else {
return "一般";
}
})));
collect.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println("age:" + k);
v.forEach((k1,v1)->{
System.out.println("\t" + "k1:" + k1 + " v1:" + v1);
});
});
}
}
运行结果:
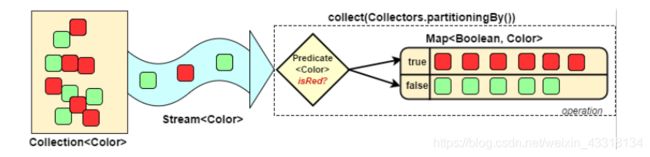
3.3 对流中的数据进行分区——Collectors.partitioningBy
Collectors.partitioningBy会根据值是否为true,把集合分割为两个列表,一个true列表,一个false列表。
如图所示:
例如:
package com.bjc.jdk8.col;
import com.bjc.jdk8.pojo.Student;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class StreamCollectTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream stream = Stream.of(
new Student("张三", 21, 97D),
new Student("李四", 21, 88D),
new Student("王五", 24, 62D),
new Student("赵六", 18, 59D),
new Student("钱七", 24, 100D)
);
Map> map = stream.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> {
return s.getScore() > 80;
}));
map.forEach((k,v) -> {
System.out.println("k:" + k + " v:" + v);
});
}
}
运行结果:
从中我们可以发现,分区其实就是一种特殊发分组。
3.4 对流中的数据进行拼接——Collertors.joining
Collertors.joining会根据指定的连接符,将所有的元素连接成一个字符串。
例如:
package com.bjc.jdk8.col;
import com.bjc.jdk8.pojo.Student;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class StreamCollectTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream stream = Stream.of(
new Student("张三", 21, 97D),
new Student("李四", 21, 88D),
new Student("王五", 24, 62D),
new Student("赵六", 18, 59D),
new Student("钱七", 24, 100D)
);
String collect = stream.map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
System.out.println(collect);
}
}
运行结果: