【数据结构】二叉树常用操作(Java实现)
文章目录
- 二叉树
-
- 二叉树的定义
- 二叉树的实现
- 二叉树的操作
-
- 遍历
-
- 先根遍历(Pre Order)
- 中根遍历(In Order)
- 后根遍历(Post Order)
- 层次遍历(Level Traverse)
- 常用操作
-
- 创建
- 清空
- 判断是否为空
- 求最大深度(高度)
- 求最小深度
- 求所有节点数
- 求叶子节点个数
- 求第k层节点数
- 返回某节点的父亲节点
- 查找节点
- 判断两棵二叉树是否相等
- 判断两棵二叉树是否镜像
- 判断是否为完全二叉树
- 翻转二叉树(镜像二叉树)
- 判断是否是二叉查找树
- 判断是否是平衡二叉树
二叉树
二叉树的定义
二叉树(Binary Tree)
二叉树(Binary Tree)是有限个节点的集合,这个集合可以是空集,也可以是一个根节点和两颗不相交的子二叉树组成的集合,其中一颗树叫根的左子树,另一颗树叫右子树。所以二叉树是一个递归地概念。
满二叉树(Full Binary Tree)
一棵满二叉树就是高度为k,且拥有(2^k)-1个节点的二叉树,一棵满二叉树每个节点,要么都有两棵子树,要么都没有子树;而且每一层所有的节点之间必须要么都有两棵子树,要么都没子树。
完全二叉树(Complete Binary Tree)
完全二叉树是一颗特殊的二叉树,假设完全二叉树高度为k,则完全二叉树需要符合以下两点:
- 所有叶子节点都出现在k层或k-1层,并且从1~k-1层必须达到最大节点数
- 第k层可以是不满的,但是第k层的所有节点必须集中在最左边
二叉树的实现
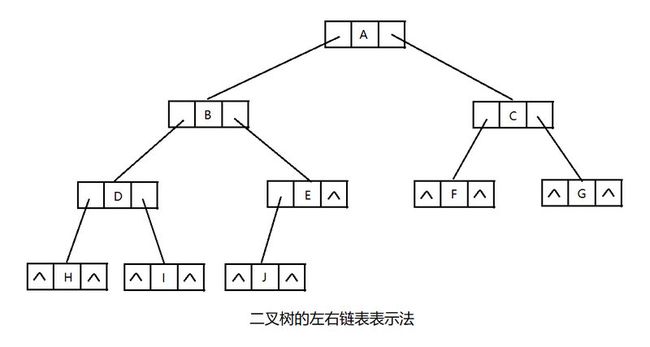
二叉树的左右链表表示法:
public class BinaryTreeNode {
private int data; //数据
private BinaryTreeNode leftChild ; //左孩子
private BinaryTreeNode rightChild ; //右孩子
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public BinaryTreeNode getLeftChild () {
return leftChild ;
}
public void setLeftChild (BinaryTreeNode leftChild ) {
this.leftChild = leftChild ;
}
public BinaryTreeNode getRightChild () {
return rightChild ;
}
public void setRightChild (BinaryTreeNode rightChild ) {
this.rightChild = rightChild ;
}
}
二叉树的操作
遍历
先根遍历(Pre Order)
若二叉树为空,则退出,否则进行下面操作:
- 访问根节点
- 先根遍历左子树
- 先根遍历右子树
- 退出
public void PreOrder(BinaryTreeNode node){
if(node != null){
System.out.println(node.getData()); //先访问根节点
PreOrder(node.getLeftChild ()); //先根遍历左子树
PreOrder(node.getRightChild ()); //先根遍历右子树
}
}
中根遍历(In Order)
若二叉树为空,则退出,否则进行下面操作
- 中根遍历左子树
- 访问根节点
- 中根遍历右子树
- 退出
public void InOrder(BinaryTreeNode node){
if(node != null){
InOrder(node.getLeftChild()); //中根遍历左子树
System.out.println(node.getData()); //访问根节点
InOrder(node.getRightChild()); //中根遍历右子树
}
}
后根遍历(Post Order)
若二叉树为空,则退出,否则进行下面操作
- 后根遍历左子树
- 后根遍历右子树
- 访问根节点
- 退出
public void PostOrder(BinaryTreeNode node){
if(node != null){
PostOrder(node.getLeftChild()); //后根遍历左子树
PostOrder(node.getRightChild()); //后根遍历右子树
System.out.println(node.getData()); //访问根节点
}
}
层次遍历(Level Traverse)
public void levelTraverse(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
LinkedList<BinaryTreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTreeNode node = queue.poll();
System.out.print(node.getData()+" ");
if (node.getLeftChild() != null) {
queue.offer(node.getLeftChild());
}
if (node.getRightChild() != null) {
queue.offer(node.getRightChild());
}
}
}
常用操作
创建
创建二叉树,一般有两种情况:初始化一个根节点或者初始化一棵空二叉树。
public class BinaryTree {
private BinaryTreeNode root;
//初始化二叉树
public BinaryTree(){
}
public BinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode root){
this.root = root;
}
public void setRoot(BinaryTreeNode root){
this.root = root;
}
public BinaryTreeNode getRoot(){
return root;
}
}
清空
对于二叉树的清空,首先提供一个清空某个节点为根节点的子树的方法,即递归的删除每个节点;接着提供删除一个删除树的方法:
//清除某个子树的所有节点
public void clear(BinaryTreeNode node){
if(node!=null){
clear(node.getLeftChild());
clear(node.getRightChild());
node = null; //删除节点
}
}
//清空整个树
public void clear(){
clear(root);
}
判断是否为空
只需判断根节点是否存在即可:
//判断二叉树是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return root == null;
}
求最大深度(高度)
首先需要一种获取以某个节点为子树的高度方法,使用递归实现。如果一个节点为空,那么这个节点肯定是一颗空树,高度为0;如果不为空,则遍历地比较它的左右子树高度,高的一个为这颗子树的最大高度,然后加上自身的高度即可:
//获取二叉树的高度
public int getMaxDepth(){
return getMaxDepth(root);
}
//获取以某节点为子树的高度
public int getMaxDepth(BinaryTreeNode node){
if(node == null){
return 0; //递归结束,空子树高度为0
}else{
//递归获取左子树高度
int l = getMaxDepth(node.getLeftChild());
//递归获取右子树高度
int r = getMaxDepth(node.getRightChild());
//高度应该算更高的一边,(+1是因为要算上自身这一层)
return l > r ? (l+1) : (r+1);
}
}
求最小深度
根节点到最近叶子结点的距离
public int getMinDepth(){
return getMinDepth (root);
}
public int getMinDepth(BinaryTreeNode node) {
if(null == node) {
return 0;
}
if(null == node.getLeftChild()) {
return getMinDepth(node.getRightChild()) + 1;
}
if(null == root.getRightChild()) {
return getMinDepth(node.getLeftChild()) + 1;
}
//递归获取左子树高度
int l = getMaxDepth(node.getLeftChild());
//递归获取右子树高度
int r = getMaxDepth(node.getRightChild());
//高度应该算更低的一边,(+1是因为要算上自身这一层)
return l < r ? (l+1) : (r+1);
}
求所有节点数
获取二叉树节点数,需要获取以某个节点为根的子树的节点数实现。如果节点为空,则个数肯定为0;如果不为空,则算上这个节点之后,继续递归计算所有子树的节点数,全部相加即可:
public int size(){
return size(root);
}
public int size(BinaryTreeNode node){
if(node == null){
return 0; //如果节点为空,则返回节点数为0
}else{
//计算本节点 所以要+1
//递归获取左子树节点数和右子树节点数,最终相加
return 1 + size(node.getLeftChild ()) + size(node.getRightChild ());
}
}
求叶子节点个数
int getNumOfChildNode(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if(null == root) {
return 0;
}
if(null == root.getLeftChild() && null == root.RightChild()) {
return 1;
}
return getNumOfChildNode(root.getLeftChild())+getNumOfChildNode(root.getLeftChild());
}
求第k层节点数
int getNumOfLevelNode(BinaryTreeNode root, int k) {
if(null == root || k < 1) {
return 0;
}
if(1 == k) {
return 1;
}
int numleft = getNumOfLevelNode(root.getLeftChild(), k - 1);
int numright = getNumOfLevelNode(root.RightChild,k - 1);
return numleft + numright;
}
返回某节点的父亲节点
首先,同样需要通过一种方法来获取某个节点在某个子树中的父节点,这里使用递归实现,接着通过这种方法获取这个节点在二叉树中的父节点。
事实上,以现有的这种二叉树的形式,我们并没有办法直接获取一个节点的父节点, 这里只能通过从根节点遍历来比较获取。
//node节点在subTree子树中的父节点
public BinaryTreeNode getParent(BinaryTreeNode subTree, BinaryTreeNode node){
//如果是空子树,则没有父节点
if(subTree == null){
return null;
}
//如果子树的根节点的左右孩子之一是待查节点,则返回子树的根节点
if(subTree.getLeftChild () == node || subTree.getRightChild () == node){
return subTree;
}
BinaryTreeNode parent = null;
//递归左右子树
if(getParent(subTree.getLeftChild (), node) != null){
parent = getParent(subTree.getLeftChild (), node);
return parent;
}else{
return getParent(subTree.getRightChild (), node);
}
}
//查找node节点在二叉树中的父节点
public BinaryTreeNode getParent(BinaryTreeNode node){
return (root == null || root == node) ? null : getParent(root, node);
}
查找节点
public BinaryTreeNode findNode(BinaryTreeNode root, int x){
if(root == null){
return null;
}
else if(root.getData() == x){
return root;
}
//递归搜索左子树
BinaryTreeNode leftNode = findNode(root.getLeftChild(), x);
if(null != leftNode)
return leftNode;
//递归搜索右子树
BinaryTreeNode rightNode = findNode(root.getRightChild(), x);
if(null != rightNode)
return rightNode;
//没找到,返回null
return null;
}
判断两棵二叉树是否相等
public boolean isEquals(BinaryTreeNode root1, BinaryTreeNode root2){
//当前节点均为空或者相等,返回true
if((root1 == null && root2 == null) ||root1.getData() == root2.getData()){
return true;
}
//递归判断所有左右子树,均相等返回true
if(isEquals(root1.getLeftChild(), root2.getLeftChild())
&& isEquals(root1.getRightChild(), root2.getRightChild())){
return true;
}
//否则返回false
return false;
}
判断两棵二叉树是否镜像
boolean isMirrorBTree(BinaryTreeNode root1, BinaryTreeNode root2) {
if(null == root1 && null == root2) {
return true;
}else if(null == root1 || null == root2) {
return false;
}
if(root1.getData() != root2.getData()) {
return false;
}
//此处注意相反比较
return isMirrorBTree(root1.getLeftChild(),root2.getRightChild())
&& isMirrorBTree(root1.getRightChild(),root2.getLeftChild());
}
判断是否为完全二叉树
我们可以根据题意做题即可,我们可以采用分层遍历的方式,在判断一个具体的节点的时候,我们可以有如下的判断依据:
- 如果这个节点的左子树为null,右子树不为null,则一定不是完全二叉树
- 如果这个节点的左右子树均为null,或者这个节点的左子树不为null但是右子树为null,则当前层或者下一层不能再出现含有左右子树的节点
- 如果当前节点的左右子树均不为null,则观察下一个节点
public boolean isCompleteBTree(BinaryTreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
boolean hasLeaf = false;
List<BinaryTreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTreeNode tmp = queue.poll();
if (tmp.getLeftChild() == null) {
if (tmp.getRightChild() != null) {
//情况1,左子树为null,右子树不为null,则一定不是完全二叉树
return false;
}
if (tmp.getRightChild() == null) {
//情况2,左右子树均为null
//则当前层或者下一层不能再出现含有左右子树的节点
hasLeaf = true;
}
} else {
if (hasLeaf) {
//出现了含有左子树的节点,直接返回false
return false;
}
if (tmp.getRightChild() == null) {
//情况2,左子树不为null,右子树为null
//则当前层或者下一层不能再出现含有左右子树的节点
hasLeaf = true;
queue.add(tmp.getLeftChild());
}
if (tmp.getRight() != null) {
//情况3,左右子树均不为null,则观察下一个节点
queue.add(tmp.getLeftChild());
queue.add(tmp.getRightChild());
}
}
}
return true;
}
翻转二叉树(镜像二叉树)
public BinaryTreeNode invertTree(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
//递归反转左右子树
BinaryTreeNode temp = root.getLeftChild();
root.getLeftChild() = invertTree(root.getRightChild());
root.getRightChild() = invertTree(temp);
return root;
}
判断是否是二叉查找树
一棵BST定义为:
- 节点的左子树中的值要严格小于该节点的值
- 节点的右子树中的值要严格大于该节点的值
- 左右子树也必须是二叉查找树
//根节点的值data必然在(minVal,maxVal)这个范围内
public boolean isValidBST(BinaryTreeNode root, long minVal, long maxVal) {
if(null == root) {
return true;
}
if(root.getData() >= maxVal || root.getData() <= minVal) {
return false;
}
return isValidBST(root.getLeftChild(), minVal, root.data)
&& isValidBST(root.getRightChild(), root.data, maxVal);
}
判断是否是平衡二叉树
public boolean IsBalancedTree(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
//左右子树高度绝对值大于1,返回false
if(Math.abs(getMaxDepth(root.getLeftChild())-getMaxDepth(root.getRightChild()))>1){
return false;
}else{
//递归检查左右子树
return IsBalancedTree(root.getLeftChild())
&& IsBalancedTree(root.getRightChild());
}
}
//求高度
public int getMaxDepth(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int left = getMaxDepth(root.getLeftChild());
int right = getMaxDepth(root.getRightChild());
return left > right ? left + 1 : right + 1;
}