linux驱动开发之i2c从设备驱动at24c02的编程
编译从设备驱动编程的前奏:
1, 将i2c core层和i2c adapter控制器层编译进内核
make menuconfig
Device Drivers —>
<*> I2C support —> // i2c-core.c
I2C Hardware Bus support —>
<*> S3C2410 I2C Driver // i2c-adatper的驱动–i2c-s3c2410.c
2, 为创建i2c client提供信息,内核就会根据信息自动创建i2c client
在ubuntu中进入linux内核文件路径(/home/ubuntu/s5pv210/kernel/linux-3.0.8),vim arch/arm/mach-s5pv210/mach-smdkv210.c ,修改里面内容
//根据硬件原理图,将i2c client的信息填入到对应的数组
// 硬件连接在第几个总线上,就填入对应的数组
static struct i2c_board_info smdkv210_i2c_devs0[] __initdata = {
{ I2C_BOARD_INFO("at240c2", 0x50), // 参数1--表示用于和i2c driver进行匹配的名字--自定义--需要记住
//参数2--从设备地址--7bit--从芯片手册查询得到
// .type = "24c08", .addr = 0x50
}, /* Samsung S524AD0XD1 */
{ I2C_BOARD_INFO("wm8580", 0x1b), },
};
static struct i2c_board_info smdkv210_i2c_devs1[] __initdata = {
/* To Be Updated */
};
static struct i2c_board_info smdkv210_i2c_devs2[] __initdata = {
/* To Be Updated */
{ I2C_BOARD_INFO("test", 0x2b), }, //这个用于测试---实际没有这个硬件
};
smdkv210_machine_init(void)//该函数在开机就自动执行
|
i2c_register_board_info(0, smdkv210_i2c_devs0,ARRAY_SIZE(smdkv210_i2c_devs0));
i2c_register_board_info(1, smdkv210_i2c_devs1,ARRAY_SIZE(smdkv210_i2c_devs1));
i2c_register_board_info(2, smdkv210_i2c_devs2,ARRAY_SIZE(smdkv210_i2c_devs2));
3.重新编译内核:make zImage
4.更新内核:cp -raf arch/arm/boot/zImage /tftpboot/
5.重启开发板,
[root@farsight devices]# pwd
/sys/bus/i2c/devices
[root@farsight devices]# ls
0-001b 0-0050 i2c-0 i2c-1 i2c-2
[root@farsight 0-0050]# pwd
/sys/bus/i2c/devices/0-0050
[root@farsight 0-0050]# cat name
at240c2
接下来编写i2c driver的驱动代码—at24c02驱动
构建i2c_driver,注册到总线中:
|
—probe(*i2c_client)
|
0, 记录匹配之后的i2c client
1,申请主设备号
2,创建设备节点
3,实现fops
4,根据实际情况去初始化从设备硬件
驱动中涉及到的各种结构体:
//描述了一个从设备的操作方法
struct i2c_driver
{
/* Standard driver model interfaces */
int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *);
int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *);
struct device_driver driver; //父类
const struct i2c_device_id *id_table; //用于和i2c client进行匹配的名字列表
}
//描述了一个从设备的信息---从设备地址,名字
struct i2c_client {
unsigned short addr; //7bit--从设备地址
char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE]; //名字
struct i2c_adapter *adapter; // 指向创建自己的adapter
struct i2c_driver *driver; //指向匹配成功之后的i2c driver
struct device dev; //父类
};
//描述控制器, 比如编号,算法
struct i2c_adapter {
const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; /* the algorithm to access the bus */
|
int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs,int num);
struct device dev; //父类
int nr; //编号
char name[48];
};
//传输的数据包
struct i2c_msg {
__u16 addr; //数据包传输給那个从设备
__u16 flags;//读还是写-- 1读,0写
__u16 len; /* msg length */
__u8 *buf; /* pointer to msg data */
};
i2c 子系统提供读写从设备的接口:
i2c_master_recv(const struct i2c_client * client, char * buf, int count)
i2c_master_send(const struct i2c_client * client, const char * buf, int count)
|
//重点学会用i2c_transfer
int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
从设备驱动at24c02的程序:at24_e2prom_i2c_drv.c
#include 应用程序:at24_app.c
#include 在s5pv210开发板上运行的
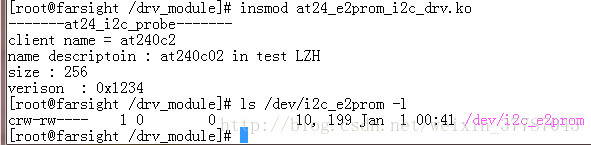

并且写入的数据,掉电不丢失。(因为存储到e2prom里面)
程序文件夹:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1mjFLjoW 密码:5kzf