安卓多线程---几种实现方式
Android只会存在两种线程:UI主线程(UI thread)和工作线程(work thread).
我们知道Android的UI主线程主要负责处理用户的按键事件、用户的触屏事件以及屏幕绘图事件等,在子线程中处理耗时的任务,任务完成后通过Handler通知UI主线程更新UI界面
注意:
不能阻塞UI主线程,也就是不能在UI主线程中做耗时的操作,如网络连接,文件的IO;
只能在UI主线程中做更新UI的操作;
ANR:
anr:application not reponse:应用程序无响应
主线程:UI线程
anr产生的原因:主线程需要做很多重要的事情,响应点击事件,更新ui,如果在主线程里面阻塞时间过久,应用程序就会无响应,为了避免应用程序出现anr,所有的耗时的操作,都应该放在子线程中执行。
1、使用线程处理 耗时比较长的“业务”
有以下几种方式:
1)Activity.runOnUiThread(Runnable)
2)View.post(Runnable) ;View.postDelay(Runnable , long)
3)Handler
4)AsyncTask
2、使用方法举例
1)Activity.runOnUiThread(Runnable)
采用runOnUiThread(new Runnable()),这要实现Runnable借口,我们可以直接在这个线程中进行UI的更新。是api提供的方法,较为便捷。
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
final String result = LoginServices.loginByGet(username, password);
if(result != null){
//成功
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, result, 0).show();
}
});
}else{
//请求失败
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "请求失败", 0).show();
}
});
}
};
}.start();handler.post(r)其实这样并不会新起线程,只是执行的runnable里的run()方法,却没有执行start()方法,所以runnable走的还是UI线程。
如果像这样,是可以操作ui,但是run还是走在主线程,见打印出来的Log线程名字是main,说明是主线程。
这就是为什么可以直接在run方法里操作ui,因为它本质还是ui线程
handler.post(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
Log.e("当前线程:",Thread.currrentThread.getName());//这里打印de结果会是main
setTitle("哈哈");
}
});3)Handler
Thread与Handler组合,比较常见
这里在加载100张图片,然后没加载完成一个用handler 返回给UI线程一张图片并显示,最后加载完成返回一个List给UI线程 ,Handler就是一个后台线程与UI线程中间的桥梁
package com.android.wei.thread;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class Activity01 extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
/**读取进度**/
public final static int LOAD_PROGRESS =0;
/**标志读取进度结束**/
public final static int LOAD_COMPLETE = 1;
/**开始加载100张图片按钮**/
Button mButton = null;
/**显示内容**/
TextView mTextView = null;
/**加载图片前的时间**/
Long mLoadStart = 0L;
/**加载图片完成的时间**/
Long mLoadEndt = 0L;
Context mContext = null;
/**图片列表**/
private List list;
/**图片容器**/
private ImageView mImageView;
//接受传过来得消息
Handler handler = new Handler(){
public void handleMessage(Message msg){
switch(msg.what){
case LOAD_PROGRESS:
Bitmap bitmap = (Bitmap)msg.obj;
mTextView.setText("当前读取到第"+msg.arg1+"张图片");
mImageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
break;
case LOAD_COMPLETE:
list = (List) msg.obj;
mTextView.setText("读取结束一共加载"+list.size()+"图片");
break;
}
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
};
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
mContext = this;
setContentView(R.layout.main);
mButton =(Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
mTextView=(TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView1);
mImageView =(ImageView) this.findViewById(R.id.imageview);
mTextView.setText("点击按钮加载图片");
mButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v){
//调用方法
LoadImage();
}
});
}
public void LoadImage(){
new Thread(){
public void run(){
mLoadStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
List list = new ArrayList();
for(int i =0;i<100;i++){
Bitmap bitmap=ReadBitmap(mContext,R.drawable.icon);
Message msg = new Message();
msg.what = LOAD_PROGRESS;
msg.arg1 = i+1;
list.add(bitmap);
msg.obj = bitmap;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
mLoadEndt = System.currentTimeMillis();
Message msg = new Message();
msg.what = LOAD_COMPLETE;
msg.obj=list;
msg.arg1 = (int) (mLoadEndt - mLoadStart);
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}.start();
}
public Bitmap ReadBitmap(Context context,int resId){
BitmapFactory.Options opt = new BitmapFactory.Options();
opt.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
opt.inPurgeable = true;
opt.inInputShareable = true;
InputStream is = context.getResources().openRawResource(resId);
return BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is, null, opt);
}
} (1)基本概念
我们如果要定义一个AsyncTask,就需要定义一个类来继承AsyncTask这个抽象类,并实现其唯一的一个 doInBackgroud 抽象方法。要掌握AsyncTask,我们就必须要一个概念,总结起来就是:3个泛型,4个步骤。
AsyncTask 3个泛型:
Progress: 这个泛型指定的是我们的异步任务在执行的时候将执行的 进度返回给UI线程的参数的 类型
Result: 这个泛型指定的异步任务执行完后返回给UI线程的 结果的类型
我们在定义一个类继承AsyncTask类的时候,必须要指定好这三个泛型的类型,如果都不指定的话,则都将其写成Void,例如:
AsyncTask 4个步骤:当我们执行一个异步任务的时候,其需要按照下面的4个步骤分别执行
onPreExecute(): 这个方法是在执行异步任务之前的时候执行,并且是在UI Thread当中执行的,通常我们在这个方法里做一些UI控件的初始化的操作,例如弹出要给ProgressDialog
doInBackground(Params... params): 在onPreExecute()方法执行完之后,会马上执行这个方法,这个方法就是来处理异步任务的方法,Android操作系统会在后台的线程池当中开启一个worker thread来执行我们的这个方法,所以这个方法是在worker thread当中执行的,这个方法执行完之后就可以将我们的执行结果发送给我们的最后一个 onPostExecute 方法,在这个方法里,我们可以从网络当中获取数据等一些耗时的操作
onProgressUpdate(Progess... values): 这个方法也是在UI Thread当中执行的,我们在异步任务执行的时候,有时候需要将执行的进度返回给我们的UI界面,
例如下载一张网络图片,我们需要时刻显示其下载的进度,就可以使用这个方法来更新我们的进度。这个方法在调用之前,我们需要在 doInBackground 方法中调用一个 publishProgress(Progress) 的方法来将我们的进度时时刻刻传递给 onProgressUpdate 方法来更新
onPostExecute(Result... result): 当我们的异步任务执行完之后,就会将结果返回给这个方法,这个方法也是在UI Thread当中调用的,我们可以将返回的结果显示在UI控件上
(2)举例
同样加载100张图片
package com.android.wei.thread;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class Activity02 extends Activity{
/**开始StartAsync按钮**/
Button mButton = null;
Context mContext = null;
//内容显示出来
TextView mTextView = null;
//Timer 对象
Timer mTimer = null;
/** timerTask 对象**/
TimerTask mTimerTask = null;
/**记录TimerId**/
int mTimerId =0;
/**图片列表**/
private List list;
/**图片容器**/
private ImageView mImageView;
public void onCreate(Bundle s){
super.onCreate(s);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
mContext = this;
mButton =(Button) this.findViewById(R.id.button1);
mImageView =(ImageView)this.findViewById(R.id.imageview);
mTextView =(TextView) this.findViewById(R.id.textView1);
mButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v){
StartAsync();
}
});
}
public void StartAsync(){
new AsyncTask(){
protected void onPreExecute(){
//首先执行这个方法,它在UI线程中,可以执行一些异步操作
mTextView.setText("开始加载进度");
super.onPreExecute();
}
@Override
protected Object doInBackground(Object... params) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//异步后台执行,执行完毕可以返回出去一个结果 Object 对象
//得到开始加载得时间
list = new ArrayList();
for(int i =0;i<100;i++){
Bitmap bitmap =ReadBitmap(mContext,R.drawable.icon);
final ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
bitmap.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.PNG, 100, os);
byte[] image = os.toByteArray();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putInt("index", i);
bundle.putByteArray("image", image);
publishProgress(bundle);
list.add(bitmap);
}
return list;
}
protected void onPostExecute(Object result){
//doInBackground 执行之后在这里可以接受到返回结果的对象
List list = (List) result;
mTextView.setText("一共加载了"+list.size()+"张图片");
super.onPostExecute(result);
}
protected void onProgressUpdate(Object... values){
//时时拿到当前的进度更新UI
Bundle bundle = (Bundle)values[0];
byte[] image = bundle.getByteArray("image");
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(image, 0, image.length);
int index = bundle.getInt("index");
mTextView.setText("当前加载进度"+index);
mImageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
super.onProgressUpdate(values);
}
}.execute();
}
public Bitmap ReadBitmap(Context context,int resId){
BitmapFactory.Options opt = new BitmapFactory.Options();
opt.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
opt.inPurgeable = true;
opt.inInputShareable = true;
InputStream is = context.getResources().openRawResource(resId);
return BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is, null, opt);
}
} (3)举一反三
通过AsyncTask来从网络上下载一张图片
下面我们就通过两个代码示例,来看看如何通过AsyncTask来从网络上下载一张图片,并更新到我们的ImageView控件上。
①下载图片时,弹出一个ProgressDialog,但是不显示实时进度
我们来看看布局文件:
就是很简单的一个ImageView控件和一个Button控件,当点击Button控件时,弹出一个ProgressDialog,然后开启一个异步任务,从网络中下载一张图片,并更新到我们的ImageView上。这里还要注意一点,如果我们要使用手机访问网络,必须还要给其授权才行,在后续的学习当中,将会详细讲解Android当中的授权的知识。我们来看看
AndroidManifest.xml文件:
public class MainActivity extends Activity
{
private Button button;
private ImageView imageView;
private ProgressDialog progressDialog;
private final String IMAGE_PATH = "http://developer.android.com/images/home/kk-hero.jpg";
// private final String IMAGE_PATH2 = "http://ww2.sinaimg.cn/mw690/69c7e018jw1e6hd0vm3pej20fa0a674c.jpg";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
button = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
imageView = (ImageView)findViewById(R.id.imageView);
// 弹出要给ProgressDialog
progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(MainActivity.this);
progressDialog.setTitle("提示信息");
progressDialog.setMessage("正在下载中,请稍后......");
// 设置setCancelable(false); 表示我们不能取消这个弹出框,等下载完成之后再让弹出框消失
progressDialog.setCancelable(false);
// 设置ProgressDialog样式为圆圈的形式
progressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_SPINNER);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
// 在UI Thread当中实例化AsyncTask对象,并调用execute方法
new MyAsyncTask().execute(IMAGE_PATH);
}
});
}
/**
* 定义一个类,让其继承AsyncTask这个类
* Params: String类型,表示传递给异步任务的参数类型是String,通常指定的是URL路径
* Progress: Integer类型,进度条的单位通常都是Integer类型
* Result:byte[]类型,表示我们下载好的图片以字节数组返回
* @author xiaoluo
*
*/
public class MyAsyncTask extends AsyncTask
{
@Override
protected void onPreExecute()
{
super.onPreExecute();
// 在onPreExecute()中我们让ProgressDialog显示出来
progressDialog.show();
}
@Override
protected byte[] doInBackground(String... params)
{
// 通过Apache的HttpClient来访问请求网络中的一张图片
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(params[0]);
byte[] image = new byte[]{};
try
{
HttpResponse httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
HttpEntity httpEntity = httpResponse.getEntity();
if(httpEntity != null && httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK)
{
image = EntityUtils.toByteArray(httpEntity);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
httpClient.getConnectionManager().shutdown();
}
return image;
}
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values)
{
super.onProgressUpdate(values);
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(byte[] result)
{
super.onPostExecute(result);
// 将doInBackground方法返回的byte[]解码成要给Bitmap
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(result, 0, result.length);
// 更新我们的ImageView控件
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
// 使ProgressDialog框消失
progressDialog.dismiss();
}
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu)
{
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
} 我们来看看效果图:
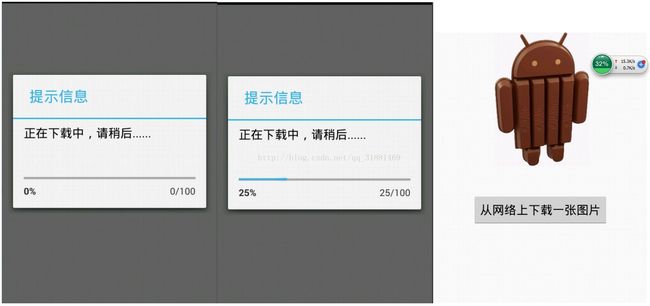
②带有进度条更新的下载一张网络图片
下面这个代码示例,将会在下载图片的时候,显示进度条的更新,配置文件都不变,我们来看看Activity代码:
public class MainActivity extends Activity
{
private Button button;
private ImageView imageView;
private ProgressDialog progressDialog;
private final String IMAGE_PATH = "http://developer.android.com/images/home/kk-hero.jpg";
// private final String IMAGE_PATH2 = "http://ww2.sinaimg.cn/mw690/69c7e018jw1e6hd0vm3pej20fa0a674c.jpg";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
button = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
imageView = (ImageView)findViewById(R.id.imageView);
// 弹出要给ProgressDialog
progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(MainActivity.this);
progressDialog.setTitle("提示信息");
progressDialog.setMessage("正在下载中,请稍后......");
// 设置setCancelable(false); 表示我们不能取消这个弹出框,等下载完成之后再让弹出框消失
progressDialog.setCancelable(false);
// 设置ProgressDialog样式为水平的样式
progressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
new MyAsyncTask().execute(IMAGE_PATH);
}
});
}
/**
* 定义一个类,让其继承AsyncTask这个类
* Params: String类型,表示传递给异步任务的参数类型是String,通常指定的是URL路径
* Progress: Integer类型,进度条的单位通常都是Integer类型
* Result:byte[]类型,表示我们下载好的图片以字节数组返回
* @author xiaoluo
*
*/
public class MyAsyncTask extends AsyncTask
{
@Override
protected void onPreExecute()
{
super.onPreExecute();
// 在onPreExecute()中我们让ProgressDialog显示出来
progressDialog.show();
}
@Override
protected byte[] doInBackground(String... params)
{
// 通过Apache的HttpClient来访问请求网络中的一张图片
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(params[0]);
byte[] image = new byte[]{};
try
{
HttpResponse httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
HttpEntity httpEntity = httpResponse.getEntity();
InputStream inputStream = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
if(httpEntity != null && httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK)
{
// 得到文件的总长度
long file_length = httpEntity.getContentLength();
// 每次读取后累加的长度
long total_length = 0;
int length = 0;
// 每次读取1024个字节
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
inputStream = httpEntity.getContent();
while(-1 != (length = inputStream.read(data)))
{
// 每读一次,就将total_length累加起来
total_length += length;
// 边读边写到ByteArrayOutputStream当中
byteArrayOutputStream.write(data, 0, length);
// 得到当前图片下载的进度
int progress = ((int)(total_length/(float)file_length) * 100);
// 时刻将当前进度更新给onProgressUpdate方法
publishProgress(progress);
}
}
image = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
inputStream.close();
byteArrayOutputStream.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
httpClient.getConnectionManager().shutdown();
}
return image;
}
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values)
{
super.onProgressUpdate(values);
// 更新ProgressDialog的进度条
progressDialog.setProgress(values[0]);
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(byte[] result)
{
super.onPostExecute(result);
// 将doInBackground方法返回的byte[]解码成要给Bitmap
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(result, 0, result.length);
// 更新我们的ImageView控件
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
// 使ProgressDialog框消失
progressDialog.dismiss();
}
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu)
{
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
} 我们来看看效果图:
这样我们就能够通过AsyncTask来实现从网络中下载一张图片,然后将其更新到UI控件中,并时时刻刻的更新当前的进度这个功能了。
(4)AsyncTask的重要知识点
在上面两节已经详细讲解了AsyncTask的工作原理了,这里我们还要补充一下AsyncTask的一些其他知识点:
1.Cancelling a Task
我们可以在任何时刻来取消我们的异步任务的执行,通过调用 cancel(boolean)方法,调用完这个方法后系统会随后调用 isCancelled() 方法并且返回true。如果调用了这个方法,那么在 doInBackgroud() 方法执行完之后,就不会调用 onPostExecute() 方法了,取而代之的是调用 onCancelled() 方法。为了确保Task已经被取消了,我们需要经常调用 isCancelled() 方法来判断,如果有必要的话。
2.在使用AsyncTask做异步任务的时候必须要遵循的原则:
AsyncTask类必须在UI Thread当中加载,在Android Jelly_Bean版本后这些都是自动完成的
AsyncTask的对象必须在UI Thread当中实例化
execute方法必须在UI Thread当中调用
不要手动的去调用AsyncTask的onPreExecute, doInBackground, publishProgress, onProgressUpdate, onPostExecute方法,这些都是由Android系统自动调用的
AsyncTask任务只能被执行一次
TimerTask
可以根据我们的设置来间隔性的运行,可以很好的实现监听功能一般也跟handler一起
package com.android.wei.thread;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class TimerTaskActivity extends Activity{
/**执行Timer进度**/
public final static int LOAD_PROGRESS =0;
/**关闭TImer进度**/
public final static int CLOSE_PROGRESS =1;
/**开始TIMERTASK按钮**/
Button mButton0 = null;
/**关闭TIMERTASK按钮**/
Button mButton1 =null;
/**显示内容**/
TextView mTextView = null;
Context mContext = null;
/**timer对象**/
Timer mTimer = null;
/**TimerTask对象**/
TimerTask mTimerTask = null;
/**记录TimerID**/
int mTimerID =0;
Handler handler = new Handler(){
public void handleMessage(Message msg){
switch(msg.what){
case LOAD_PROGRESS:
mTextView.setText("当前得TimerID为:"+msg.arg1);
break;
case CLOSE_PROGRESS:
mTextView.setText("当前Timer已经关闭请重新启动");
break;
}
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
};
protected void onCreate(Bundle s){
setContentView(R.layout.timer);
mContext = this;
mButton0 = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.button1);
mButton1 = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.button2);
mTextView = (TextView) this.findViewById(R.id.textView1);
mTextView.setText("点击按钮开始更新时间");
mButton0.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v){
StartTimer();
}
});
mButton1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v){
CloseTimer();
}
});
super.onCreate(s);
}
public void StartTimer(){
if(mTimer == null){
mTimerTask = new TimerTask(){
@Override
public void run() {
mTimerID ++;
Message msg = new Message();
msg.what = LOAD_PROGRESS;
msg.arg1 =(int) (mTimerID);
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
};
mTimer = new Timer();
//第一个参数为执行的mTimerTask
//第二个参数为延迟得事件,这里写1000得意思是 mTimerTask将延迟1秒执行
//第三个参数为多久执行一次,这里写1000 表示没1秒执行一次mTimerTask的Run方法
mTimer.schedule(mTimerTask, 1000,1000);
}
}
public void CloseTimer(){
if(mTimer !=null){
mTimer.cancel();
mTimer = null;
}
if(mTimerTask!= null){
mTimerTask = null;
}
mTimerID =0;
handler.sendEmptyMessage(CLOSE_PROGRESS);
}
}参考文章:
http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoluo501395377/p/3430542.html
http://blog.csdn.net/tody_guo/article/details/7363969
http://blog.csdn.net/javazejian/article/details/52464139
http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/47079737/
http://www.cnblogs.com/jinghua1425/p/3825871.html