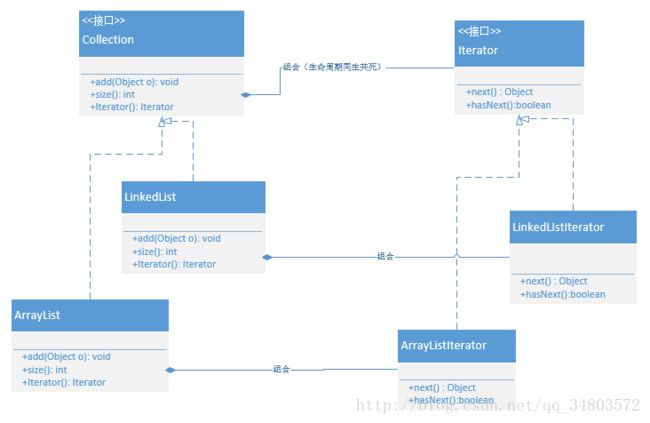
Iterator Pattern (Collection接口&Iterator接口&ArrayList&LinkedList)
容器、泛型、迭代器相关内容可以结合java se分类下的第七章:异常 7.5-7.7容器:持有事务
迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)是 Java 和 .Net 编程环境中非常常用的设计模式。这种模式用于顺序访问集合对象的元素,不需要知道集合对象的底层表示。
迭代器模式属于行为型模式。
主要解决:不同的方式来遍历整个整合对象。
关键代码:定义接口:hasNext, next。
应用实例:JAVA 中的iterator。
使用场景: 1、访问一个聚合对象的内容而无须暴露它的内部表示。 2、需要为聚合对象提供多种遍历方式。 3、为遍历不同的聚合结构提供一个统一的接口。
迭代器模式的结构
抽象容器:一般是一个接口,提供一个iterator()方法,例如java中的Collection接口,List接口,Set接口等。
具体容器:就是抽象容器的具体实现类,比如List接口的有序列表实现ArrayList,List接口的链表实现LinkList,Set接口的哈希列表的实现HashSet等。
抽象迭代器:定义遍历元素所需要的方法,一般来说会有这么三个方法:取得第一个元素的方法first(),取得下一个元素的方法next(),判断是否遍历结束的方法isDone()(或者叫hasNext()),移出当前对象的方法remove(),
迭代器实现:实现迭代器接口中定义的方法,完成集合的迭代。
容器与容器遍历
1. 实现一个可动态添加对象的容器(基于数组、基于链表)
2. 考虑不同容器的可替换性
3. 实现容器内元素的遍历
Test测试类
package com.dp.Iterator.Test;
import com.dp.Iterator.Collection.ArrayList;
import com.dp.Iterator.Collection.Collection;
import com.dp.Iterator.Collection.LinkedList;
import com.dp.Iterator.Entity.Cat;
import com.dp.Iterator.Iterator.Iterator;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Collection c = new ArrayList(); //针对接口编程,父类引用指向子类对象
Collection c = new LinkedList();
for(int i=0; i<15; i++) {
c.add(new Cat(i));
}
System.out.println(c.size());
Iterator it = c.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Object o = it.next();
System.out.print(o+" ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
}
/*
15
Cat [id=0] Cat [id=1] Cat [id=2] Cat [id=3] Cat [id=4] Cat [id=5] Cat [id=6] Cat [id=7]
Cat [id=8] Cat [id=9] Cat [id=10] Cat [id=11] Cat [id=12] Cat [id=13] Cat [id=14]
*/
}
Collection接口
package com.dp.Iterator.Collection;
import com.dp.Iterator.Iterator.Iterator;
/**
* 容器接口
*/
public interface Collection {
void add(Object o);
int size();
Iterator iterator();
}
package com.dp.Iterator.Collection;
import com.dp.Iterator.Iterator.Iterator;
public class ArrayList implements Collection{
Object[] objects = new Object[10];
int index = 0; //个数
public void add(Object o) {
if(index == objects.length) {//原空间不够时copy到新的空间
Object[] newObjects = new Object[objects.length*2];
System.arraycopy(objects, 0, newObjects, 0,objects.length);
objects = newObjects;
}
objects[index] = o;
index++;
}
public int size() {
return index;
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new ArrayListIterator();
}
private class ArrayListIterator implements Iterator {//这里用的内部类
private int currentIndex = 0; //下一个元素的下标
@Override
public Object next() {
Object o = objects[currentIndex];
currentIndex++;
return o;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if(currentIndex >= index) { //下一个元素的下标等于数组个数时表示到头
return false;
}else return true;
}
}
}
package com.dp.Iterator.Collection;
import com.dp.Iterator.Iterator.Iterator;
public class LinkedList implements Collection{
Node head = null;
Node tail = null;
int size = 0;
public void add(Object o) {
Node n = new Node(o,null);
if(head == null) {
head = n;
tail = n; //复制了引用,head、tail和n指向的是同一内存空间,head、tail是n的别名
}
tail.setNext(n); //接入新的节点
tail = n; //tail再次指向链表尾部
size++;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new LinkedListIterator();
}
private class LinkedListIterator implements Iterator{//这里用的内部类
Node current = head;
@Override
public Object next() {
Object o = current.getData();
current = current.getNext();
return o;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if(current == null)
return false ;
else return true;
}
}
}
package com.dp.Iterator.Collection;
public class Node {
private Object data;
private Node next;
public Node(Object data, Node next) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
}迭代器相关类
package com.dp.Iterator.Iterator;
public interface Iterator {
Object next();
boolean hasNext();
}
package com.dp.Iterator.Entity;
public class Cat {
private int id;
public Cat(int id) {
super();
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat [id=" + id + "]";
}
}
package com.dp.Iterator.Generic;
import com.dp.Iterator.Collection.Collection;
/**
* 泛型的使用
* */
public class GenericArrayList {
Object[] objects = new Object[10];
int index = 0; //个数
public void add(E o) {
if(index == objects.length) {//原空间不够时copy到新的空间
Object[] newObjects = new Object[objects.length*2];
System.arraycopy(objects, 0, newObjects, 0,objects.length);
objects = newObjects;
}
objects[index] = o;
index++;
}
public int size() {
return index;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericArrayList g = new GenericArrayList();
g.add("hello");
}
}