第六章 类变量解析
类变量解析
- Java类变量解析的原理
- 计算机基础——偏移量与内存对齐
- Java类与字段的对齐与补白
- Java字段的继承机制
- 使用HSDB查看运行时的Java类结构
类变量解析
在ClassFileParser::parseClassFile()函数中,解析完常量池、父类和接口后,接着编调用parse_fields()函数解析类变量信息:
// Fields (offsets are filled in later)
FieldAllocationCount fac;
objArrayHandle fields_annotations;
typeArrayHandle fields = parse_fields(class_name, cp, access_flags.is_interface(), &fac, &fields_annotations,
&java_fields_count,
CHECK_(nullHandle));
FieldAllocationCount的声明如下:
class FieldAllocationCount: public ResourceObj {
public:
u2 count[MAX_FIELD_ALLOCATION_TYPE];
FieldAllocationCount() {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_FIELD_ALLOCATION_TYPE; i++) {
count[i] = 0;
}
}
FieldAllocationType update(bool is_static, BasicType type) {
FieldAllocationType atype = basic_type_to_atype(is_static, type);
// Make sure there is no overflow with injected fields.
assert(count[atype] < 0xFFFF, "More than 65535 fields");
count[atype]++;
return atype;
}
};
FieldAllocationCount主要记录了静态类型变量的数量和非静态类型的变量数量,后面JVM为Java类分配内存空间时,会根据这些变量的数量计算所占内存大小。下面我们看JVM对Java类域变量的具体解析逻辑:
typeArrayHandle ClassFileParser::parse_fields(Symbol* class_name,
constantPoolHandle cp, bool is_interface,
FieldAllocationCount *fac,
objArrayHandle* fields_annotations,
u2* java_fields_count_ptr, TRAPS) {
ClassFileStream* cfs = stream();
typeArrayHandle nullHandle;
cfs->guarantee_more(2, CHECK_(nullHandle)); // length,获取Java类域变量的数量
u2 length = cfs->get_u2_fast();
*java_fields_count_ptr = length;
int num_injected = 0;
InjectedField* injected = JavaClasses::get_injected(class_name, &num_injected);
// Tuples of shorts [access, name index, sig index, initial value index, byte offset, generic signature index]
typeArrayOop new_fields = oopFactory::new_permanent_shortArray((length + num_injected) * FieldInfo::field_slots, CHECK_(nullHandle));
typeArrayHandle fields(THREAD, new_fields);
typeArrayHandle field_annotations;
for (int n = 0; n < length; n++) {
cfs->guarantee_more(8, CHECK_(nullHandle)); // access_flags, name_index, descriptor_index, attributes_count
//读取变量访问表示,如private|public等
AccessFlags access_flags;
jint flags = cfs->get_u2_fast() & JVM_RECOGNIZED_FIELD_MODIFIERS;
verify_legal_field_modifiers(flags, is_interface, CHECK_(nullHandle));
access_flags.set_flags(flags);
//读取变量名称索引
u2 name_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
int cp_size = cp->length();
check_property(
valid_cp_range(name_index, cp_size) && cp->tag_at(name_index).is_utf8(),
"Invalid constant pool index %u for field name in class file %s",
name_index, CHECK_(nullHandle));
Symbol* name = cp->symbol_at(name_index);
verify_legal_field_name(name, CHECK_(nullHandle));
//读取类型索引
u2 signature_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
check_property(
valid_cp_range(signature_index, cp_size) &&
cp->tag_at(signature_index).is_utf8(),
"Invalid constant pool index %u for field signature in class file %s",
signature_index, CHECK_(nullHandle));
Symbol* sig = cp->symbol_at(signature_index);
verify_legal_field_signature(name, sig, CHECK_(nullHandle));
u2 constantvalue_index = 0;
bool is_synthetic = false;
u2 generic_signature_index = 0;
bool is_static = access_flags.is_static();
//读取变量属性
u2 attributes_count = cfs->get_u2_fast();
if (attributes_count > 0) {
parse_field_attributes(cp, attributes_count, is_static, signature_index,
&constantvalue_index, &is_synthetic,
&generic_signature_index, &field_annotations,
CHECK_(nullHandle));
if (field_annotations.not_null()) {
if (fields_annotations->is_null()) {
objArrayOop md = oopFactory::new_system_objArray(length, CHECK_(nullHandle));
*fields_annotations = objArrayHandle(THREAD, md);
}
(*fields_annotations)->obj_at_put(n, field_annotations());
}
if (is_synthetic) {
access_flags.set_is_synthetic();
}
}
FieldInfo* field = FieldInfo::from_field_array(fields(), n);
field->initialize(access_flags.as_short(),
name_index,
signature_index,
constantvalue_index,
generic_signature_index,
0);
//判断变量属性
BasicType type = cp->basic_type_for_signature_at(signature_index);
// Remember how many oops we encountered and compute allocation type
FieldAllocationType atype = fac->update(is_static, type);
// The correct offset is computed later (all oop fields will be located together)
// We temporarily store the allocation type in the offset field
field->set_offset(atype);
}
if (num_injected != 0) {
int index = length;
for (int n = 0; n < num_injected; n++) {
// Check for duplicates
if (injected[n].may_be_java) {
Symbol* name = injected[n].name();
Symbol* signature = injected[n].signature();
bool duplicate = false;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
FieldInfo* f = FieldInfo::from_field_array(fields(), i);
if (name == cp->symbol_at(f->name_index()) &&
signature == cp->symbol_at(f->signature_index())) {
// Symbol is desclared in Java so skip this one
duplicate = true;
break;
}
}
if (duplicate) {
// These will be removed from the field array at the end
continue;
}
}
// Injected field
FieldInfo* field = FieldInfo::from_field_array(fields(), index);
field->initialize(JVM_ACC_FIELD_INTERNAL,
injected[n].name_index,
injected[n].signature_index,
0,
0,
0);
BasicType type = FieldType::basic_type(injected[n].signature());
// Remember how many oops we encountered and compute allocation type
FieldAllocationType atype = fac->update(false, type);
// The correct offset is computed later (all oop fields will be located together)
// We temporarily store the allocation type in the offset field
field->set_offset(atype);
index++;
}
if (index < length + num_injected) {
// sometimes injected fields already exist in the Java source so
// the fields array could be too long. In that case trim the
// fields array.
new_fields = oopFactory::new_permanent_shortArray(index * FieldInfo::field_slots, CHECK_(nullHandle));
for (int i = 0; i < index * FieldInfo::field_slots; i++) {
new_fields->short_at_put(i, fields->short_at(i));
}
fields = new_fields;
}
}
if (_need_verify && length > 1) {
// Check duplicated fields
ResourceMark rm(THREAD);
NameSigHash** names_and_sigs = NEW_RESOURCE_ARRAY_IN_THREAD(
THREAD, NameSigHash*, HASH_ROW_SIZE);
initialize_hashtable(names_and_sigs);
bool dup = false;
{
debug_only(No_Safepoint_Verifier nsv;)
for (AllFieldStream fs(fields, cp); !fs.done(); fs.next()) {
Symbol* name = fs.name();
Symbol* sig = fs.signature();
// If no duplicates, add name/signature in hashtable names_and_sigs.
if (!put_after_lookup(name, sig, names_and_sigs)) {
dup = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (dup) {
classfile_parse_error("Duplicate field name&signature in class file %s",
CHECK_(nullHandle));
}
}
return fields;
}
从上面代码中可以看到JVM解析Java类变量的逻辑:
- 获取Java类中的变量数量
- 读取变量的访问标识
- 读取变量名称索引
- 读取变量类型索引
- 读取变量属性
- 判断变量类型
- 统计各类型数量
在Java类所对应的字节码文件中,有专门的一块区域保存Java类的变量信息,字节码文件会一次描述各个变量的访问标识、名称索引、类型索引、和属性,而且都占用2字节,所以只需要依次调用cfs->get_u2_fast()即可。解析完一个变量的属性后,调用fields->short_at_put(),fields是一开始就申请的内存:
typeArrayOop new_fields = oopFactory::new_permanent_shortArray((length + num_injected) * FieldInfo::field_slots, CHECK_(nullHandle));
偏移量
解析完字节码文件中Java类的全部域变量信息后,JVM计算出五种数据类型各自的数量,并据此计算各个变量的偏移量。
静态变量偏移量
instanceKlassHandle ClassFileParser::parseClassFile(Symbol* name,
Handle class_loader,
Handle protection_domain,
KlassHandle host_klass,
GrowableArray* cp_patches,
TempNewSymbol& parsed_name,
bool verify,
TRAPS) {
//省略部分代码
// Field size and offset computation
int nonstatic_field_size = super_klass() == NULL ? 0 : super_klass->nonstatic_field_size();
#ifndef PRODUCT
int orig_nonstatic_field_size = 0;
#endif
int static_field_size = 0;
int next_static_oop_offset;
int next_static_double_offset;
int next_static_word_offset;
int next_static_short_offset;
int next_static_byte_offset;
int next_static_type_offset;
int next_nonstatic_oop_offset;
int next_nonstatic_double_offset;
int next_nonstatic_word_offset;
int next_nonstatic_short_offset;
int next_nonstatic_byte_offset;
int next_nonstatic_type_offset;
int first_nonstatic_oop_offset;
int first_nonstatic_field_offset;
int next_nonstatic_field_offset;
// Calculate the starting byte offsets
next_static_oop_offset = instanceMirrorKlass::offset_of_static_fields();
next_static_double_offset = next_static_oop_offset +
(fac.count[STATIC_OOP] * heapOopSize);
if ( fac.count[STATIC_DOUBLE] &&
(Universe::field_type_should_be_aligned(T_DOUBLE) ||
Universe::field_type_should_be_aligned(T_LONG)) ) {
next_static_double_offset = align_size_up(next_static_double_offset, BytesPerLong);
}
next_static_word_offset = next_static_double_offset +
(fac.count[STATIC_DOUBLE] * BytesPerLong);
next_static_short_offset = next_static_word_offset +
(fac.count[STATIC_WORD] * BytesPerInt);
next_static_byte_offset = next_static_short_offset +
(fac.count[STATIC_SHORT] * BytesPerShort);
next_static_type_offset = align_size_up((next_static_byte_offset +
fac.count[STATIC_BYTE] ), wordSize );
static_field_size = (next_static_type_offset -
next_static_oop_offset) / wordSize;
first_nonstatic_field_offset = instanceOopDesc::base_offset_in_bytes() +
nonstatic_field_size * heapOopSize;
next_nonstatic_field_offset = first_nonstatic_field_offset;
//省略部分代码
}
对于JDK1.6而言,静态变量存储在JVM中所对应的镜像类Mirror中,当Java代码访问静态变量时,最终JVM也是通过设置偏移量进行访问。
非静态变量偏移量
非静态类型变量的偏移量计算逻辑可以分为五个步骤:
- 计算非静态变量起始偏移量
- 计算nonstatic_double_offset和nonestatic_oop_offset这2中非静态类型变量的起始偏移
- 计算剩余三种类型变量的起始偏移量
- 计算对齐补白空间
- 计算补白后非静态变量所需要的内存空间总大小
计算非静态变量起始偏移量
在JVM内部,使用oop-klass模型描述对象,常量池本身就是这种模型,对于Java类,JVM内部也是这样描述,对应的oop类是instanceOopDesc,对应的klass是instanceKlass。
oop模型主要是存储对象实例的实际数据,而klass模型则主要存储对象结构信息和虚函数方法表,就是类的结构和行为。当JVM加载一个Java类时,会首先构建对应的instanceKlass对象,而当new一个Java对象实例时,就会构建出对应的instanceOop对象。
instanceOop对象主要由Java类的成员变量组成,而这些成员变量在instanceOop中的排列,便由各种变量类型的偏移量决定。在Hotspot内部,oop对象都包含对象头,因此实际上非静态变量的偏移量要从对象头末尾开始计算。
first_nonstatic_field_offset = instanceOopDesc::base_offset_in_bytes() +
nonstatic_field_size * heapOopSize;
instanceOopDesc::base_offset_in_bytes()声明如下:
static int base_offset_in_bytes() {
return UseCompressedOops ?
klass_gap_offset_in_bytes() :
sizeof(instanceOopDesc);
}
压缩策略
如果没有启用压缩策略,在64位平台,oopDesc的值是16,如果启用了压缩策略则是12,因为oop._mark是不会被压缩的,任何时候都占8字节,而oop._klass则会受影响,若开启了压缩策略则它仅会占用4字节,所以oop对象头总共占用12字节内存空间。
继承
Java类是面向对象的,除了Object类外,其他类都显示或隐式的继承了某个父类,字段继承和方法继承则构成了继承的全部内容,子类必须将分类中所定义的非静态字段信息全部复制一遍,才能实现字段继承的目标,因此计算子类的非静态字段的起始偏移量时必须将父类可悲继承的字段的内存大小考虑在内。Hotspot将父类可悲继承的字段的内存空间安排在子类所对应的oop对象头后,因此最终一个Java类中非静态字段的起始偏移地址在父类被继承的字段域的末尾。
内存对齐与字段重排
- 什么是内存对齐
内存对齐与数据在内存中的位置有关,如果一个变量的起始地址正好等于其长度的整数倍,则这种内存分配就称作自然对齐。例如一个int型变量的内存地址是0x00000008,则该变量是自然对齐的。
32位平台的内存对齐规则
| 变量类型 | 长度 | 对齐规则 |
|---|---|---|
| char | 1字节 | 按1字节对齐 |
| short | 2字节 | 按2字节对齐 |
| int | 4字节 | 按4字节对齐 |
- 为什么要字节对齐
- 一些平台对某些特定类型的数据只能从某些特定地址开始存取,例如有些架构的CPU在访问一个没有进行对齐的变量时会发生错误。
- 如果不按要求对数据存放进行对齐,在存取效率上会有损失
为了实现内存对齐,JVM不仅使用了补白,还使用了字段重排,将相同类型的字段组合在一起,按照double->word->short->byte-oop的顺序依次分配。
- 计算变量偏移量
Hotspot将相同类型的字段存储在一起,那么便可以先计算出其内部的5大类型字段的起始偏移量,基于该类型的起始偏移量,便可逐个计算出该类型所对应的每一个具体的Java类字段的偏移量:
//Java类字段的起始偏移量
first_nonstatic_field_offset = instanceOopDesc::base_offset_in_bytes() +
nonstatic_field_size * heapOopSize;
next_nonstatic_field_offset = first_nonstatic_field_offset;
//分别获取五种类型字段的数量
unsigned int nonstatic_double_count = fac.count[NONSTATIC_DOUBLE];
unsigned int nonstatic_word_count = fac.count[NONSTATIC_WORD];
unsigned int nonstatic_short_count = fac.count[NONSTATIC_SHORT];
unsigned int nonstatic_byte_count = fac.count[NONSTATIC_BYTE];
unsigned int nonstatic_oop_count = fac.count[NONSTATIC_OOP];
//根据不同的顺序策略,计算起始偏移量
if( allocation_style < 0 || allocation_style > 2 ) { // Out of range?
assert(false, "0 <= FieldsAllocationStyle <= 2");
allocation_style = 1; // Optimistic
}
// The next classes have predefined hard-coded fields offsets
// (see in JavaClasses::compute_hard_coded_offsets()).
// Use default fields allocation order for them.
if( (allocation_style != 0 || compact_fields ) && class_loader.is_null() &&
(class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_AssertionStatusDirectives() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_Class() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_ClassLoader() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_ref_Reference() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_ref_SoftReference() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_StackTraceElement() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_String() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_Throwable() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_Boolean() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_Character() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_Float() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_Double() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_Byte() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_Short() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_Integer() ||
class_name == vmSymbols::java_lang_Long())) {
allocation_style = 0; // Allocate oops first
compact_fields = false; // Don't compact fields
}
if( allocation_style == 0 ) {
// Fields order: oops, longs/doubles, ints, shorts/chars, bytes
next_nonstatic_oop_offset = next_nonstatic_field_offset;
next_nonstatic_double_offset = next_nonstatic_oop_offset +
(nonstatic_oop_count * heapOopSize);
} else if( allocation_style == 1 ) {
// Fields order: longs/doubles, ints, shorts/chars, bytes, oops
next_nonstatic_double_offset = next_nonstatic_field_offset;
} else if( allocation_style == 2 ) {
// Fields allocation: oops fields in super and sub classes are together.
if( nonstatic_field_size > 0 && super_klass() != NULL &&
super_klass->nonstatic_oop_map_size() > 0 ) {
int map_count = super_klass->nonstatic_oop_map_count();
OopMapBlock* first_map = super_klass->start_of_nonstatic_oop_maps();
OopMapBlock* last_map = first_map + map_count - 1;
int next_offset = last_map->offset() + (last_map->count() * heapOopSize);
if (next_offset == next_nonstatic_field_offset) {
allocation_style = 0; // allocate oops first
next_nonstatic_oop_offset = next_nonstatic_field_offset;
next_nonstatic_double_offset = next_nonstatic_oop_offset +
(nonstatic_oop_count * heapOopSize);
}
}
if( allocation_style == 2 ) {
allocation_style = 1; // allocate oops last
next_nonstatic_double_offset = next_nonstatic_field_offset;
}
} else {
ShouldNotReachHere();
}
//计算出实际起始偏移量
next_nonstatic_word_offset = next_nonstatic_double_offset +
(nonstatic_double_count * BytesPerLong);
next_nonstatic_short_offset = next_nonstatic_word_offset +
(nonstatic_word_count * BytesPerInt);
next_nonstatic_byte_offset = next_nonstatic_short_offset +
(nonstatic_short_count * BytesPerShort);
计算出实际起始偏移量后就开始计算每种类型所对应的Java类中的字段的具体偏移量了。
for (AllFieldStream fs(fields, cp); !fs.done(); fs.next()) {
int real_offset;
FieldAllocationType atype = (FieldAllocationType) fs.offset();
switch (atype) {
case STATIC_OOP:
real_offset = next_static_oop_offset;
next_static_oop_offset += heapOopSize;
break;
case STATIC_BYTE:
real_offset = next_static_byte_offset;
next_static_byte_offset += 1;
break;
case STATIC_SHORT:
real_offset = next_static_short_offset;
next_static_short_offset += BytesPerShort;
break;
case STATIC_WORD:
real_offset = next_static_word_offset;
next_static_word_offset += BytesPerInt;
break;
case STATIC_DOUBLE:
real_offset = next_static_double_offset;
next_static_double_offset += BytesPerLong;
break;
case NONSTATIC_OOP:
if( nonstatic_oop_space_count > 0 ) {
real_offset = nonstatic_oop_space_offset;
nonstatic_oop_space_offset += heapOopSize;
nonstatic_oop_space_count -= 1;
} else {
real_offset = next_nonstatic_oop_offset;
next_nonstatic_oop_offset += heapOopSize;
}
// Update oop maps
if( nonstatic_oop_map_count > 0 &&
nonstatic_oop_offsets[nonstatic_oop_map_count - 1] ==
real_offset -
int(nonstatic_oop_counts[nonstatic_oop_map_count - 1]) *
heapOopSize ) {
// Extend current oop map
nonstatic_oop_counts[nonstatic_oop_map_count - 1] += 1;
} else {
// Create new oop map
nonstatic_oop_offsets[nonstatic_oop_map_count] = real_offset;
nonstatic_oop_counts [nonstatic_oop_map_count] = 1;
nonstatic_oop_map_count += 1;
if( first_nonstatic_oop_offset == 0 ) { // Undefined
first_nonstatic_oop_offset = real_offset;
}
}
break;
case NONSTATIC_BYTE:
if( nonstatic_byte_space_count > 0 ) {
real_offset = nonstatic_byte_space_offset;
nonstatic_byte_space_offset += 1;
nonstatic_byte_space_count -= 1;
} else {
real_offset = next_nonstatic_byte_offset;
next_nonstatic_byte_offset += 1;
}
break;
case NONSTATIC_SHORT:
if( nonstatic_short_space_count > 0 ) {
real_offset = nonstatic_short_space_offset;
nonstatic_short_space_offset += BytesPerShort;
nonstatic_short_space_count -= 1;
} else {
real_offset = next_nonstatic_short_offset;
next_nonstatic_short_offset += BytesPerShort;
}
break;
case NONSTATIC_WORD:
if( nonstatic_word_space_count > 0 ) {
real_offset = nonstatic_word_space_offset;
nonstatic_word_space_offset += BytesPerInt;
nonstatic_word_space_count -= 1;
} else {
real_offset = next_nonstatic_word_offset;
next_nonstatic_word_offset += BytesPerInt;
}
break;
case NONSTATIC_DOUBLE:
real_offset = next_nonstatic_double_offset;
next_nonstatic_double_offset += BytesPerLong;
break;
default:
ShouldNotReachHere();
}
fs.set_offset(real_offset);
}
gap填充
在64位平台上,如果开启了指针压缩策略,则对象头仅会占用12个内存单元,这就带来一个问题:它影响了后面的Java类字段的自然对齐效果,为了解决这一问题,JVM将int、short、byte等宽度小于等于4字节的字段往这个内存间隙插入。
if( nonstatic_double_count > 0 ) {
//填充gap间隙,如果对象头+父类非静态字段的末尾不是8字节对齐,在中间填充Java中非long/double类型的字段
//gap填充的顺序:int、short、byte、oopmap
int offset = next_nonstatic_double_offset;
next_nonstatic_double_offset = align_size_up(offset, BytesPerLong);
if( compact_fields && offset != next_nonstatic_double_offset ) {
// Allocate available fields into the gap before double field.
int length = next_nonstatic_double_offset - offset;
assert(length == BytesPerInt, "");
//先将int型字段填充进gap
nonstatic_word_space_offset = offset;
if( nonstatic_word_count > 0 ) {
nonstatic_word_count -= 1;
nonstatic_word_space_count = 1; // Only one will fit
length -= BytesPerInt;
offset += BytesPerInt;
}
//接着填充short
nonstatic_short_space_offset = offset;
while( length >= BytesPerShort && nonstatic_short_count > 0 ) {
nonstatic_short_count -= 1;
nonstatic_short_space_count += 1;
length -= BytesPerShort;
offset += BytesPerShort;
}
//继续填充byte
nonstatic_byte_space_offset = offset;
while( length > 0 && nonstatic_byte_count > 0 ) {
nonstatic_byte_count -= 1;
nonstatic_byte_space_count += 1;
length -= 1;
}
//继续填充oopmap
// Allocate oop field in the gap if there are no other fields for that.
nonstatic_oop_space_offset = offset;
if( length >= heapOopSize && nonstatic_oop_count > 0 &&
allocation_style != 0 ) { // when oop fields not first
nonstatic_oop_count -= 1;
nonstatic_oop_space_count = 1; // Only one will fit
length -= heapOopSize;
offset += heapOopSize;
}
}
}
Java字段内存分配总结
- 任何对象都是以8字节为粒度进行对齐的
- 类属性按照以下优先级排列:long/double–>int/float–>char/short–>byte/bool–>oop
- 不同继承关系中的成员不能混合排列,首先按照规则2处理父类中的成员
- 当父类最后一个属性和子类的第一个属性之间间隔不足4字节时,必须扩展到4字节的基本单位
- 如果子类的哥成员是一个long或double,并且父类没有用完8字节,JVM会破会规则2,按int->short->byte->referenct的顺序向未填满的空间填充
从源码看字段继承
private字段可以被继承吗
- 父类的私有成员变量的确是被子类继承的
- 子类虽然能够继承父类的私有变量,但是却没有权利直接支配,除非通过父类开放的接口
使用HSDB验证字段分配与继承
示例代码:
public abstract class MyClass {
private Integer i = 1;
protected long plong = 12L;
protected final short s = 6;
public char c = 'A';
}
public class Test extends MyClass {
private long l;
private Integer i = 3;
private long plong = 18L;
public char c = 'B';
public void add(int a, int b){
Test test = this;
int z = a+b;
int x = 3;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test test = new Test();
test.add(2,3);
System.exit(0);
}
}
启动HSDB:
java -cp .;"C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_181\lib/sa-jdi.jar" sun.jvm.hotspot.HSDB
universe查看内存分配情况
Heap Parameters:
Gen 0: eden [0x0000000012000000,0x00000000120fed40,0x00000000122b0000) space capacity = 2818048, 37.03897165697674 used
from [0x00000000122b0000,0x00000000122b0000,0x0000000012300000) space capacity = 327680, 0.0 used
to [0x0000000012300000,0x0000000012300000,0x0000000012350000) space capacity = 327680, 0.0 usedInvocations: 0
Gen 1: old [0x0000000012350000,0x0000000012350000,0x0000000012a00000) space capacity = 7012352, 0.0 usedInvocations: 0
scanoops 0x0000000012000000 0x0000000012a00000 Test在内存中搜索Test类实例
0x00000000120f6108 Test
inspect 0x00000000120f6108查看这个地址的oop全部数据:
instance of Oop for Test @ 0x00000000120f6108 @ 0x00000000120f6108 (size = 72)
_mark: 1
_metadata._klass: InstanceKlass for Test
i: Oop for java/lang/Integer @ 0x0000000012094768 Oop for java/lang/Integer @ 0x0000000012094768
plong: 12
s: 6
c: 'A'
l: 0
i: Oop for java/lang/Integer @ 0x0000000012094798 Oop for java/lang/Integer @ 0x0000000012094798
plong: 18
c: 'B'
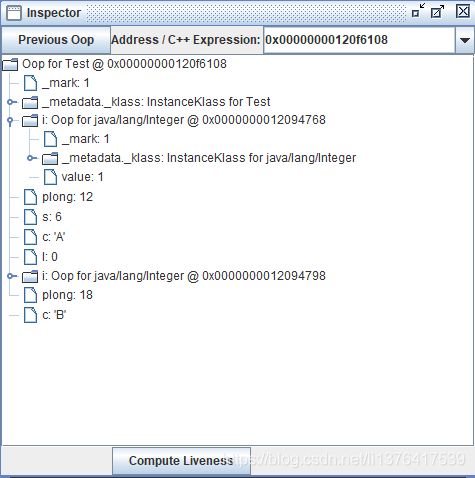
父类的四个字段分别是i,plong,s,c,子类的四个字段分别是I,i,plong,c
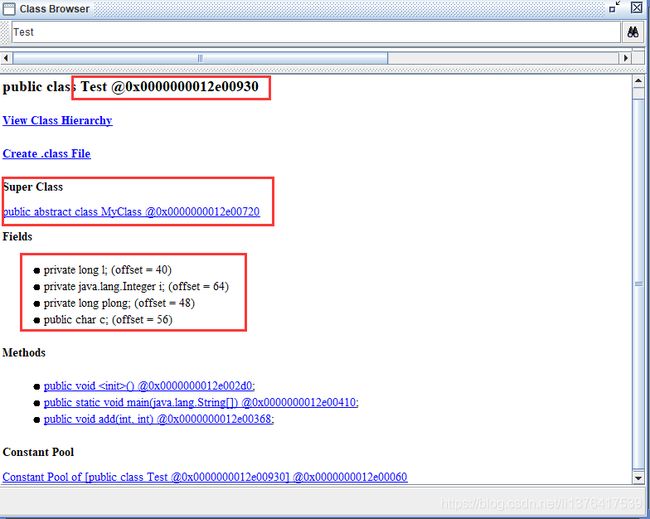
classBrowser查看Test类中各个字段偏移量:
父类MyClass中各个字段偏移量:
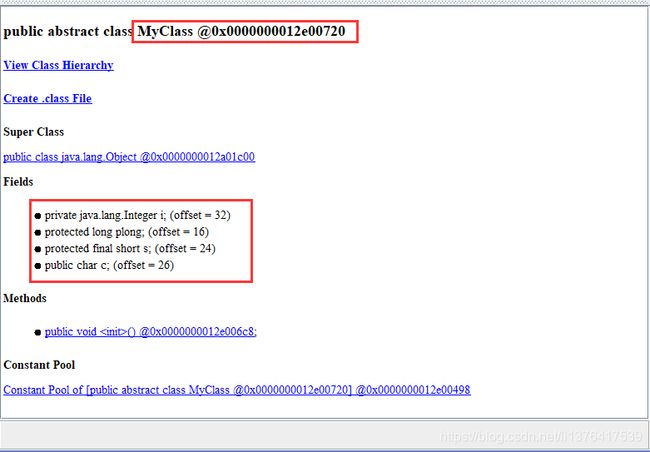
可以看到,偏移量最小的是plong,偏移量是16正好位于Test类oop对象头之后,然后是s,c,空白填充4字节,然后是Test中的字段域。
如果子类中定义了与父类同名同类的字段,无论父类中访问权限是什么,也无论是否被final修饰,子类不会覆盖父类的字段,JVM会在内存中同时为父类和子类的相同字段各分配一段内存空间。
总结
Hotspot解析Java类非静态字段和分配堆内存空间的主要逻辑总结为如下几部
- 计息常量池,统计Java类中非静态字段的总数量,按照5大类型分别统计
- 计算Java类字段的起始偏移量,起始偏移位置从父类继承的字段域的末尾开始
- 按照分配策略,计算五大类型中的每一个类型的起始偏移量
- 以五大类型各个类型的起始偏移量为基准,计算每一个大类型下各个具体字段的偏移量
- 计算Java类在堆内存中所需要的内存空间
**当全部解析玩Java类之后,Java类的全部字段信息以及其偏移量会保存到Hotspot所构建出来的instanceKlass中,当Java程序中使用new关键字创建Java类的实例对象时,Hotspot会从instanceKlass中读取Java类所需要的堆内存大小并分配对应的内存空间。