左神算法基础class5—题目6并查集实现
左神算法基础class5—题目6并查集实现
- 1.介绍:并查集
-
- (1)并查集的结构
- (2)并查集的原理
- 2.分析
-
- (1)类的设计
- (2)查找代表节点
- (3)判断是否是同一集合
- (4)合并两个集合
- 3.完整代码
- 4.运行结果
1.介绍:并查集
并查集的作用主要有两点:
①快速查两个元素是同一集合
②合并两个集合。
(1)并查集的结构
当集合中只有一个元素时,这个集合的代表节点即为该元素,该元素的father也是自己。

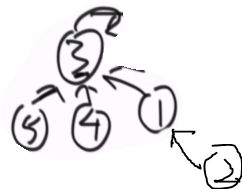
当一个集合中有多个节点时,下层节点的father为上层节点,最上层节点的father指向自己,最上层的节点叫做这个集合的代表节点。如下图5,4的father是3,3的father是其自己。

(2)并查集的原理
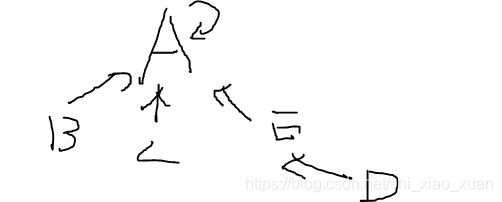
①查找:假设查找a,b是否在同一个集合,对a,b查找其代表节点,若他们的代表节点不同则不在同一个集合,相同在同一个集合。如下图,2,5不在同一集合,4,5在同一集合

②合并
在两个集合不是同一集合的情况下,将长度短集合的代表节点的father指到长度长的代表节点上。
2.分析
(1)类的设计
并查集使用两个map实现,第一个fatherMap用来查找其father元素,key表示当前节点,value是其father节点。第二个sizeMap用来记录其集合的总长度,key表示当前节点,value是其集合的长度。
class UnionFindSet
{
private:
hash_map<char,char> fatherMap;
hash_map<char,int> sizeMap;
public:
UnionFindSet(vector<char> data);//构造
char findHead(char cur); //找集合的代表节点
bool isameset(char a,char b); //判断是否是同一个集合
void Union(char a,char b); //合并集合
};
构造函数
UnionFindSet::UnionFindSet(vector<char> data)
{
{
fatherMap.clear();
sizeMap.clear();
//将vector的元素各自形成一个集合
for(auto var:data)
{
fatherMap.insert(pair<char,char>(var,var));//单个节点father指向自己
//sizeMap[var] = 1;
sizeMap.insert(pair<char,int>(var,1));//单个节点长度是1
}
}
}
(2)查找代表节点
代表节点的特点是其father节点是自己,整体思路是通过fatherMap一步步通过当前节点与其father节点是否相同来找代表节点。
//递归版
char UnionFindSet::findHead(char cur)
{
char father = fatherMap[cur]; //找到当前节点的father
if(father != cur) //father和当前节点不同表示当前节点不是代表节点,继续找
{
cur = father;
father = findHead(cur); //递归放入father继续找
}
fatherMap[cur] = father; //递归后father是代表节点,对每个子节点father节点都改为代表节点
return father;
}
//非递归版
char UnionFindSet::findHead(char cur)
{
stack<char> child;
while(fatherMap[cur] != cur)
{
child.push(cur); //将沿途非代表节点入栈
cur = fatherMap[cur]; //将当前节点father变为当前节点继续判断
}
//运行至此处时,cur是代表节点
while(!child.empty())
{
fatherMap[child.top()] = cur; //将栈中的非代表节点的father指向代表节点,完成扁平化
child.pop(); //出栈
}
return cur;
}
(3)判断是否是同一集合
bool UnionFindSet::isameset(char a,char b)
{
return findHead(a) == findHead(b);
}
(4)合并两个集合
在两个代表节点不同的情况下,比较连个集合的长度,短的集合的代表节点指向长的集合,再把两个集合的总长度加到代表节点上。
注:非代表节点的长度没有意义,比较时只比较代表节点的总长度。
void UnionFindSet::Union(char a,char b)
{
//找出两个集合的代表节点
char head1 = findHead(a);
char head2 = findHead(b);
if(head1 == NULL || head2 == NULL)//边界问题,空集合直接返回
return;
if(head1!=head2) //不在同一集合时合并
{
//记录两个代表节点的长度
int size1 = sizeMap[head1];
int size2 = sizeMap[head2];
//将短的接入长的中
if(size1 <= size2)
{
fatherMap[head1] = head2;
sizeMap[head2] = size1 + size2;
}
else
{
fatherMap[head2] = head1;
sizeMap[head1] = size1 + size2;
}
}
}
3.完整代码
#include