Seaborn绘制热力图
Seaborn绘制热力图
Seaborn.heatmap (data, vmin=None, vmax=None, camp=None,
center=None, robust=False, annot=None, fmt=’.2g’, annot_kws=None, linewidths=0, linecolor=’white’, cbar=True, cbar_kws=None, cbar_ax=None, square=False, xticklabels=’auto’ ,yticklabels=’auto’, mask=None, ax=None, **kwargs)
1. 热力图输入数据参数:
data: 矩阵数据集,可以是numpy的数组(array),也可以是pandas的DataFrame。如果是DataFrame,则df的index/column信息会分别对应到heatmap的columns和rows,即pt.index是热力图的行标,pt.columns是热力图的列标。
2. 热力图矩阵块颜色参数:
vmin,vmax:分别是热力图的颜色取值最大和最小范围,默认是根据data数据表里的取值确定。
camp:从数字到色彩空间的映射,取值是matplotlib包里的colormap名称或颜色对象,或者表示颜色的列表,如果没有提供,默认值将取决于是否设置了center。
center:数据表取值有差异时,设置热力图的色彩中心对齐值;通过设置center值,可以调整生成的图像颜色的整体深浅;设置center数据时,如果有数据溢出,则手动设置的vmax、vmin会自动改变 。
robust:默认取值False;如果是False,且没设定vmin和vmax的值,热力图的颜色映射范围根据具有鲁棒性的分位数设定,而不是用极值设定。
3.热力图矩阵块注释参数:
annot(annotate的缩写):默认取值False;如果是True,在热力图每个方格写入数据;如果是矩阵,在热力图每个方格写入该矩阵对应位置数据
fmt:字符串格式代码,矩阵上标识数字的数据格式,比如保留小数点后几位数字 。
annot_kws:默认取值False;如果是True,设置热力图矩阵上数字的大小颜色字体,matplotlib包text类下的字体设置。
4. 热力图矩阵块之间间隔及间隔线参数
linewidths:定义热力图里“表示两两特征关系的矩阵小块”之间的间隔大小
linecolor:切分热力图上每个矩阵小块的线的颜色,默认值是’white’
5. 热力图颜色刻度条参数:
cbar:是否在热力图侧边绘制颜色刻度条,默认值是True
cbar_kws:热力图侧边绘制颜色刻度条时,相关字体设置,默认值是None
cbar_ax:热力图侧边绘制颜色刻度条时,刻度条位置设置,默认值是None
square:设置热力图矩阵小块形状,默认值是False
xticklabels, yticklabels:xticklabels控制每列标签名的输出;yticklabels控制每行标签名的输出。默认值是auto。如果是True,则以DataFrame的列名作为标签名。如果是False,则不添加行标签名。如果是列表,则标签名改为列表中给的内容。如果是整数K,则在图上每隔K个标签进行一次标注。 如果是auto,则自动选择标签的标注间距,将标签名不重叠的部分(或全部)输出
mask:控制某个矩阵块是否显示出来。默认值是None。如果是布尔型的DataFrame,则将DataFrame里True的位置用白色覆盖掉
ax:设置作图的坐标轴,一般画多个子图时需要修改不同的子图的该值
**kwargs: All other keyword arguments are passed to ax.pcolormesh
下面用python实现
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sns.set()
np.random.seed(0)
uniform_data=np.random.rand(10,12)
ax=sns.heatmap(uniform_data)
plt.show()
ax2=sns.heatmap(uniform_data,vmin=0,vmax=1)
plt.show()
#以0为中心的数据绘制一张热图
ax3=sns.heatmap(uniform_data,center=0)
plt.show()# #===================================例2: 首先造一张数据表====================================
region=['Azerbaijan','Bahamas', 'Bangladesh', 'Belize', 'Bhutan',
'Cambodia', 'Cameroon', 'Cape Verde', 'Chile', 'China']
kind=['Afforestation & reforestation', 'Biofuels', 'Biogas', 'Biomass', 'Cement']
np.random.seed(20180316)#原来每次运行代码时设置相同的seed,则每次生成的随机数也相同,如果不设置seed,则每次生成的随机数都会不一样
arr_region=np.random.choice(region,size=(200,))
'''
numpy.random.choice(a, size=None, replace=True, p=None)
a:一维数组或者一个整数
如果是ndarray,则从数组元素生成随机样本。
如果是整数,则随机样本的生成是np .arange(n)
size:可选,整型或者tuple形式
replace:布尔型,表示样本是否有更换
p:一维数组类型,可选。表示从a 中以概率P,随机选择。如果没有给定,样本假设a中的所有项的分布是均匀的。
'''
list_region=list(arr_region)
arr_kind=np.random.choice(kind,size=(200,))
list_kind=list(arr_kind)
values=np.random.randint(100,200,200)
list_values=list(values)
df=pd.DataFrame({'region':list_region,'kind':list_kind,'values':list_values})
print(df)
'''
#
# region kind values
# 0 Cameroon Cement 140
# 1 Bhutan Afforestation & reforestation 178
# 2 China Biofuels 161
# 3 Cambodia Afforestation & reforestation 100
# 4 Bahamas Biofuels 129
# 5 Azerbaijan Cement 121
# 6 China Afforestation & reforestation 142
# 7 Azerbaijan Afforestation & reforestation 157
# 8 Bahamas Afforestation & reforestation 134
# 9 Belize Cement 125
# 10 Cameroon Biogas 177
# 11 Bangladesh Biomass 163
# 12 Bangladesh Biogas 127
# 13 Bangladesh Cement 128
# 14 Bahamas Cement 181
# 15 Cambodia Biomass 105
# 16 Cameroon Cement 193
# 17 Cape Verde Cement 160
# 18 Bahamas Biofuels 181
# 19 Belize Biomass 117
# 20 Bahamas Biogas 165
# 21 Cape Verde Biogas 183
# 22 Bahamas Biomass 153
# 23 Cambodia Cement 134
# 24 Bhutan Biomass 199
# 25 Belize Biogas 123
# 26 Belize Cement 173
# 27 Cameroon Biogas 182
# 28 Azerbaijan Biofuels 177
# 29 Bahamas Afforestation & reforestation 109
# .. ... ... ...
# 170 Cambodia Cement 163
# 171 Cambodia Biomass 107
# 172 Bhutan Biomass 185
# 173 Belize Cement 151
# 174 Cameroon Cement 183
# 175 Bangladesh Biofuels 192
# 176 Bhutan Cement 133
# 177 Bahamas Biofuels 126
# 178 Azerbaijan Biomass 179
# 179 Bangladesh Cement 127
# 180 China Biomass 181
# 181 Cameroon Cement 138
# 182 Chile Biofuels 175
# 183 Cape Verde Biogas 176
# 184 Cambodia Cement 192
# 185 Cape Verde Afforestation & reforestation 155
# 186 Cape Verde Biofuels 188
# 187 Cambodia Biogas 139
# 188 Cambodia Biogas 191
# 189 Cameroon Cement 135
# 190 Cape Verde Biogas 134
# 191 Bangladesh Biogas 174
# 192 Belize Biomass 174
# 193 Cameroon Biomass 153
# 194 Azerbaijan Biomass 177
# 195 Belize Biofuels 119
# 196 China Biofuels 183
# 197 Cameroon Biogas 114
# 198 China Afforestation & reforestation 143
# 199 Belize Afforestation & reforestation 149
#
# [200 rows x 3 columns]
#
# '''
print(df['kind'].value_counts())
'''
Cement 47
Biogas 44
Biofuels 41
Afforestation & reforestation 38
Biomass 30
Name: kind, dtype: int64
'''
#将DataFrame数据表转换成“数据透视表”
pt=df.pivot_table(index='kind',columns='region',values='values',aggfunc=np.sum)
print(pt)
#index是行,columns是列,values是表中展示的数据,aggfunc是表中展示每组数据使用的运算
'''
region Azerbaijan Bahamas ... Chile China
kind ...
Afforestation & reforestation 568 571 ... 225 608
Biofuels 515 903 ... 313 782
Biogas 499 614 ... 715 130
Biomass 834 153 ... 164 749
Cement 431 549 ... 194 747
[5 rows x 10 columns]
''' #======================================center的用法(颜色)==================================
f,(ax1,ax2)=plt.subplots(figsize=(6,4),nrows=2)
cmap=sns.cubehelix_palette(start=1.5,rot=3,gamma=0.8,as_cmap=True)#从数字到色彩空间的映射
sns.heatmap(pt,linewidths=0.05,ax=ax1,cmap=cmap,center=None)
ax1.set_title('center=None')
ax1.set_xlabel('')
ax1.set_xticklabels([]) #设置x轴图例为空值
ax1.set_ylabel('kind')
# 当center设置小于数据的均值时,生成的图片颜色要向0值代表的颜色一段偏移
sns.heatmap(pt, linewidths = 0.05, ax = ax2, cmap=cmap, center=200)
ax2.set_title('center=3000')
ax2.set_xlabel('region')
ax2.set_ylabel('kind')
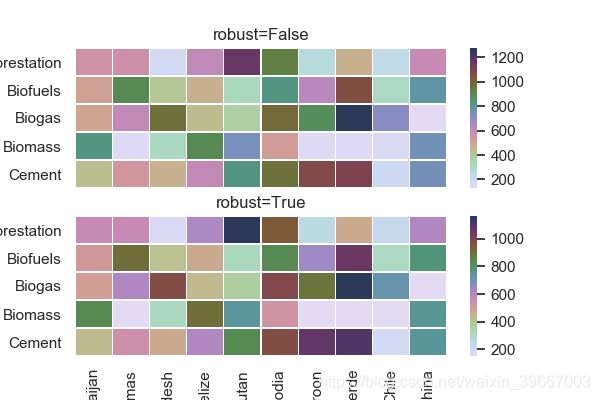
plt.show()#robust的用法(颜色)
f, (ax1,ax2) = plt.subplots(figsize = (6,4),nrows=2)
cmap = sns.cubehelix_palette(start = 1.5, rot = 3, gamma=0.8, as_cmap = True)
sns.heatmap(pt, linewidths = 0.05, ax = ax1, cmap=cmap, center=None, robust=False )
ax1.set_title('robust=False')
ax1.set_xlabel('')
ax1.set_xticklabels([]) #设置x轴图例为空值
ax1.set_ylabel('kind')
sns.heatmap(pt, linewidths = 0.05, ax = ax2, cmap=cmap, center=None, robust=True )
ax2.set_title('robust=True')
ax2.set_xlabel('region')
ax2.set_ylabel('kind')
plt.show()#=================================热力图矩阵块注释参数=======================================
np.random.seed(20180316)
x = np.random.randn(4, 4)
f, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6), nrows=2)
sns.heatmap(x, annot=True, ax=ax1)
sns.heatmap(x, annot=True, ax=ax2, annot_kws={'size': 9, 'weight': 'bold', 'color': 'blue'})
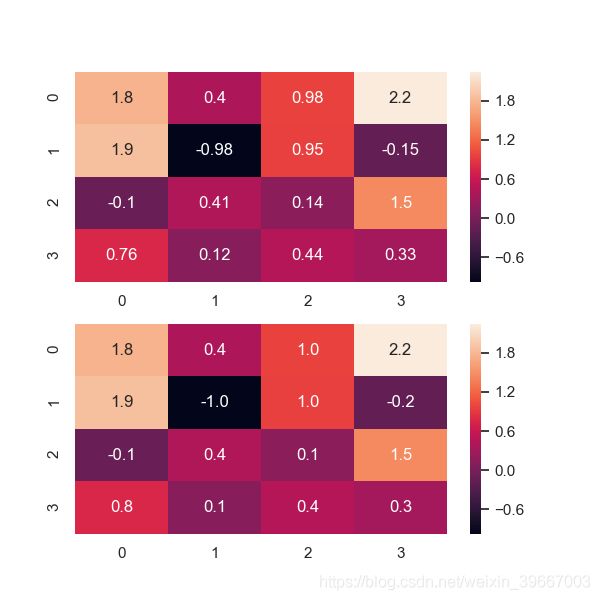
#fmt(字符串格式代码,矩阵上标识数字的数据格式,比如保留小数点后几位数字)
np.random.seed(0)
x = np.random.randn(4,4)
f, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,6),nrows=2)
sns.heatmap(x, annot=True, ax=ax1)
sns.heatmap(x, annot=True, fmt='.1f', ax=ax2)
plt.show()
#==============================热力图矩阵块之间间隔及间隔线参数===========================
# linewidths(矩阵小块的间隔),linecolor(切分热力图矩阵小块的线的颜色)
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 4))
cmap = sns.cubehelix_palette(start=1, rot=3, gamma=0.8, as_cmap=True)
sns.heatmap(pt, cmap=cmap, linewidths=0.05, linecolor='red', ax=ax)
ax.set_title('Amounts per kind and region')
ax.set_xlabel('region')
ax.set_ylabel('kind')
plt.show()# xticklabels,yticklabels横轴和纵轴的标签名输出
f, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 5), nrows=2)
cmap = sns.cubehelix_palette(start=1.5, rot=3, gamma=0.8, as_cmap=True)
p1 = sns.heatmap(pt, ax=ax1, cmap=cmap, center=None, xticklabels=False)
ax1.set_title('xticklabels=None', fontsize=8)
p2 = sns.heatmap(pt, ax=ax2, cmap=cmap, center=None, xticklabels=2, yticklabels=list(range(5)))
ax2.set_title('xticklabels=2, yticklabels is a list', fontsize=8)
ax2.set_xlabel('region')
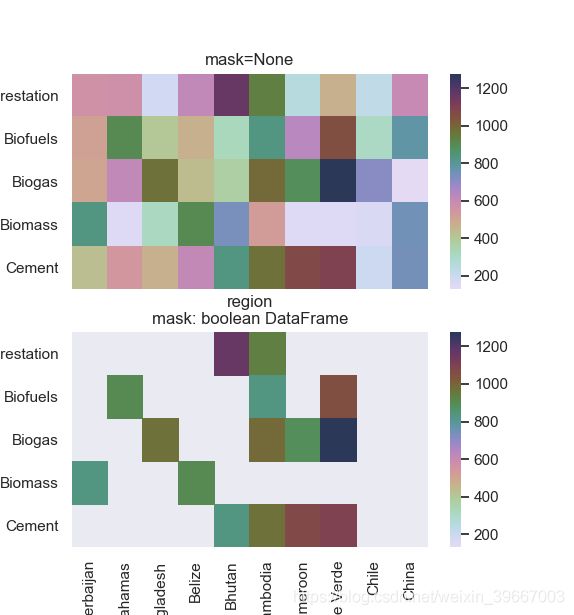
plt.show()# mask对某些矩阵块的显示进行覆盖
f, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 5), nrows=2)
cmap = sns.cubehelix_palette(start=1.5, rot=3, gamma=0.8, as_cmap=True)
p1 = sns.heatmap(pt, ax=ax1, cmap=cmap, xticklabels=False, mask=None)
ax1.set_title('mask=None')
ax1.set_ylabel('kind')
p2 = sns.heatmap(pt, ax=ax2, cmap=cmap, xticklabels=True, mask=(pt < 800))
# mask对pt进行布尔型转化,结果为True的位置用白色覆盖
ax2.set_title('mask: boolean DataFrame')
ax2.set_xlabel('region')
ax2.set_ylabel('kind')
#用mask实现,突出某些数据
f,(ax1,ax2) = plt.subplots(figsize=(4,6),nrows=2)
x = np.array([[1,2,3],[2,0,1],[-1,-2,0]])
sns.heatmap(x, annot=True, ax=ax1)
sns.heatmap(x, mask=x < 1, ax=ax2, annot=True, annot_kws={"weight": "bold"}) #把小于1的区域覆盖掉
plt.show()