2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> ![]()
1. 目的
通过源码分析SqlSession功能实现、如何创建以及在Spring中是如何集成的。
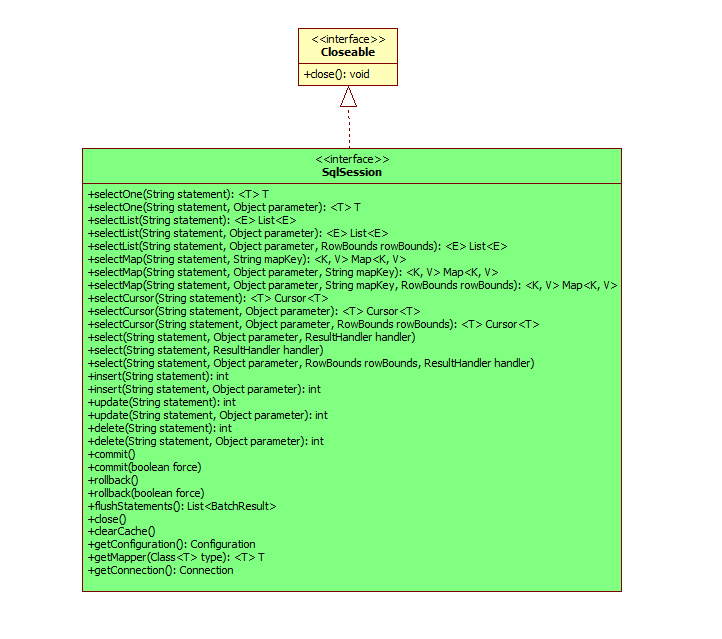
2. SqlSession 功能介绍
MyBatis工作的主要Java接口,通过这些接口你可以执行命令,获取mapper和管理事务
--代码注释
查看大图
在图中可以看到,我们操作数据库的方法都在里面。
3. SqlSession 具体功能实现
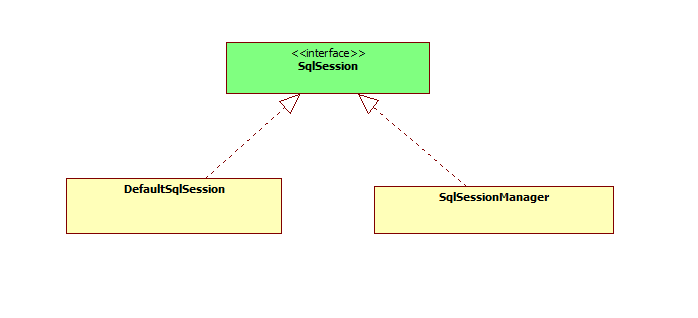
从类图可以看到SqlSession 有 DefaultSqlSession、SqlSessionManager2个实现类
- DefaultSqlSession 是SqlSession的默认实现类,非线程安全
- SqlSessionManager 为线程安全的SqlSession实现,使用了ThreadLocal保存创建的SqlSession
3.1 DefaultSqlSession 源码分析
/**
*
* The default implementation for {@link SqlSession}.
* Note that this class is not Thread-Safe.
* SqlSession 默认实现,非线程安全
*
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
this.dirty = false;
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
/**
* 返回单个查询结果
* @param statement 唯一标识匹配的语句.
* @param parameter 查询参数.
* @param
* @return
*/
@Override
public T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
//期待返回一条记录,但返回了多条
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 返回集合结果
* @param statement 唯一标识匹配的语句
* @param parameter 查询参数
* @param rowBounds 返回结果的大小控制
* @param
* @return
*/
@Override
public List selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
/**
* 返回Map对象
* @param statement 唯一标识匹配的语句.
* @param parameter 查询参数
* @param mapKey key值,字段的属性别名
* @param rowBounds 返回结果的大小控制
* @param
* @param
* @return
*/
@Override
public Map selectMap(String statement, Object parameter, String mapKey, RowBounds rowBounds) {
final List list = selectList(statement, parameter, rowBounds);
final DefaultMapResultHandler mapResultHandler = new DefaultMapResultHandler(mapKey,
configuration.getObjectFactory(), configuration.getObjectWrapperFactory(), configuration.getReflectorFactory());
final DefaultResultContext context = new DefaultResultContext();
for (V o : list) {
context.nextResultObject(o);
mapResultHandler.handleResult(context);
}
return mapResultHandler.getMappedResults();
}
/**
* 游标查询
* @param
* @return
*/
@Override
public Cursor selectCursor(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
Cursor cursor = executor.queryCursor(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds);
registerCursor(cursor);
return cursor;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
/**
* @param statement 唯一标识匹配的语句
* @param parameter 查询参数
* @param rowBounds 返回结果的大小控制
* @param handler 外部结果处理器
*/
@Override
public void select(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
/**
* 增加
* @return
*/
@Override
public int insert(String statement, Object parameter) {
return update(statement, parameter);
}
/**
* 修改
* @return
*/
@Override
public int update(String statement) {
return update(statement, null);
}
/**
* 增删改公用方法
* @param statement 唯一标识匹配的执行语句
* @param parameter 参数
* @return 返回影响的行数
*/
@Override
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
/**
* 删除
* @return
*/
@Override
public int delete(String statement) {
return update(statement, null);
}
/**
* 提交
* @param force forces connection commit
*/
@Override
public void commit(boolean force) {
try {
executor.commit(isCommitOrRollbackRequired(force));
dirty = false;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error committing transaction. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
/**
* 回滚
* @param force forces connection rollback
*/
@Override
public void rollback(boolean force) {
try {
executor.rollback(isCommitOrRollbackRequired(force));
dirty = false;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error rolling back transaction. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
/**
* 提交批处理执行
* @return 批处理提交更新记录
*/
@Override
public List flushStatements() {
try {
return executor.flushStatements();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error flushing statements. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
/**
* 关闭
*/
@Override
public void close() {
try {
executor.close(isCommitOrRollbackRequired(false));
closeCursors();
dirty = false;
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
/**
* 获取Mapper
* @param type Mapper对应的Class类型
* @param
* @return
*/
@Override
public T getMapper(Class type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
// 省略其他代码
}
3.2 SqlSessionManager 源码分析
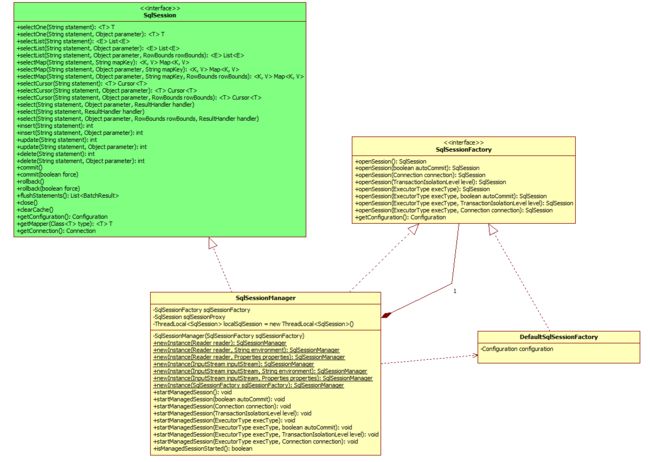
先看类图:
查看大图
从图中可以看出 SqlSessionManager实现了SqlSessionFactory接口,又封装了DefaultSqlSessionFactory
代码如下:
public class SqlSessionManager implements SqlSessionFactory, SqlSession {
//省略其他代码
public static SqlSessionManager newInstance(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionManager(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
SqlSessionManager与DefaultSqlSessionFactory区别主要有2个:
- SqlSessionManager 在本地创建一个本地线程变量,ThreadLocal
localSqlSession,每当通过startManagedSession()获取 SqlSession实例的时候,都会保存到SqlSession本地线程变量中。
public void startManagedSession() {
this.localSqlSession.set(openSession());
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
在DefaultSqlSessionFactory中每次openSession都会产生一个新的DefaultSqlSession
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
try {
//新建DefaultSqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
}
}
更详细的源码参考下节中:DefaultSqlSessionFactory 源码分析
- SqlSessionManager实现了SqlSession接口,SqlSessionMananger集成了SqlSessionFactory 和 SqlSession的功能,通过SqlSessionManager,开发者可以不在理会SqlSessionFacotry的存在,直接面向Session编程。
SqlSessionManager 内部提供了一个sqlSessionProxy,这个sqlSessionProxy提供了所有SqlSession接口的实现,而实现中正是使用了上面提到的本地线程保存的Sqlsession实例。
这样,在同一个线程实现不同的sql操作,可以复用本地线程Sqlsession,避免了DefaultSqlSessionFactory实现的每一个sql操作都要创建新的Sqlsession实例。
让我们具体来看下sqlSessionProxy 的实现:
public class SqlSessionManager implements SqlSessionFactory, SqlSession {
private SqlSessionManager(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
//创建SqlSession代理对象
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{SqlSession.class},
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
@Override
public T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
//使用代理对象执行数据库操作
return sqlSessionProxy. selectOne(statement, parameter);
}
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
public SqlSessionInterceptor() {
// Prevent Synthetic Access
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//从本地线程变量中获取SqlSession实例
final SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionManager.this.localSqlSession.get();
if (sqlSession != null) {
//不为null
try {
return method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
} else {
//为null 则打开新连接
final SqlSession autoSqlSession = openSession();
try {
final Object result = method.invoke(autoSqlSession, args);
autoSqlSession.commit();
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
autoSqlSession.rollback();
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
} finally {
autoSqlSession.close();
}
}
}
}
//省略其他代码
}
4. SqlSession 如何创建
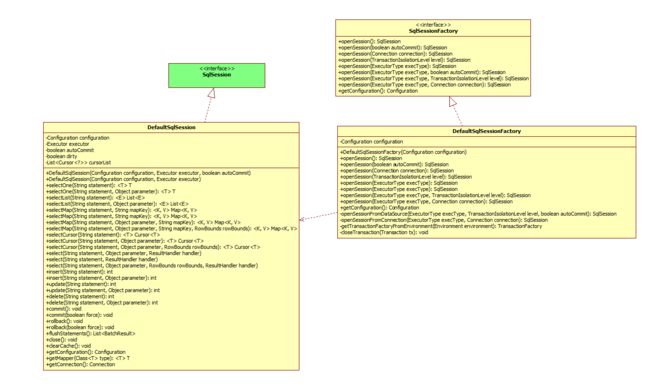
要了解SqlSession具体如何创建,我们就需要知道SqlSessionFactory,也就是SqlSession工厂。
查看大图
从类图可以看出 SqlSessionFactory 为具体SqlSession工厂定义
DefaultSqlSessionFactory 实现了SqlSessionFactory,SqlSession是由DefaultSqlSessionFactory生成
4.1 SqlSessionFactory 接口定义
/**
* 通过外部传入的connection 或 database 创建(打开) SqlSession
* 方法重载,通过参数不同创建SqlSession
*/
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
SqlSession openSession();
SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(Connection connection);
SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection);
Configuration getConfiguration();
}
4.2 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 源码分析
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private final Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) { #1
this.configuration = configuration;
}
//省略...
/**
* #mark 创建SqlSession
* @param execType 执行器类型
* @param level 事务隔离级别
* @param autoCommit 是否自动提交
* @return
*/
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { #2
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//传入的configuration获取环境变量对象、Environment可以配置多个环境配置
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//从环境对象中获取事务工厂对象
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//根据DataSource、事务隔离级别、自动提交创建事务对象
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//#mark 新建执行者 20170820
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//#mark 创建默认SqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
//异常情况关闭事务
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() (可能已经获取到数据库连接,因此执行关闭)
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
//重置错误上下文
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
//省略...
private TransactionFactory getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(Environment environment) {
if (environment == null || environment.getTransactionFactory() == null) {
return new ManagedTransactionFactory();
}
return environment.getTransactionFactory();
}
private void closeTransaction(Transaction tx)
if (tx != null) {
try {
tx.close();
} catch (SQLException ignore) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
}
详细说明:
-
标注#1 通过构造方法传入Configuration 配置对象,Configuration是一个贯穿全剧的对象
-
标注#2 openSessionFromDataSource 顾名思义,从DataSource打开SqlSession,调用new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit) 构建SqlSession,具体实现查看源码备注
Executor 、ErrorContext 后续详细介绍
4.3 MyBatis如何执行SqlSession创建
从前面的描述中,我们知道SqlSession由DefaultSqlSessionFactory 产生。通过IDEA关联搜索功能,我们找到了具体的调用类为:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder。 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 主要是获取配置输入流,创建DefaultSqlSessionFactory实例
先看下类图:
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 源码分析
/**
* Builds {@link SqlSession} instances.
* SqlSession 工厂构造器
*
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
//省略
/**
* 通过字符流构建
* @param reader 字符流
* @param environment 环境变量
* @param properties 属性配置
* @return
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) { #1
try {
//从字符流中创建XML配置对象
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
//省略
/**
* 通过字节流构建
* @param inputStream
* @param environment
* @param properties
* @return
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
/**
* #mark SqlSessionFactory 初始化
* @param config
* @return
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
}
- 标注#1 通过字符流构建 SqlSessionFactory对象,所有的build方法都调用:new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config) 构建
4.4 SqlSession 单元测试
依据测试规范,我们找到测试类 SqlSessionTest,这个类方法比较多,我精简出需要的部分。
/**
* #mark 源码学习入口
*/
public class SqlSessionTest extends BaseDataTest {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlMapper;
@BeforeClass
public static void setup() throws Exception {
//初始化数据源,使用内存数据库、运行一次自动销毁
createBlogDataSource();
//资源文件地址
final String resource = "org/apache/ibatis/builder/MapperConfig.xml";
//获取资源文件字符流
final Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource);
//构建 SqlSessionFactory
sqlMapper = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
}
/**
* 测试SqlSession 开启和关闭
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void shouldOpenAndClose() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel.SERIALIZABLE);
session.close();
}
/**
* 测试提交一个未使用的SqlSession
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void shouldCommitAnUnUsedSqlSession() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel.SERIALIZABLE);
session.commit(true);
session.close();
}
/**
* 测试提交一个未使用的SqlSession
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void shouldRollbackAnUnUsedSqlSession() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel.SERIALIZABLE);
session.rollback(true);
session.close();
}
/**
* 跟踪一个完整查询
* 查出所有作者 #20170831
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void shouldSelectAllAuthors() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel.SERIALIZABLE);
try {
List authors = session.selectList("org.apache.ibatis.domain.blog.mappers.AuthorMapper.selectAllAuthors");
assertEquals(2, authors.size());
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
//省略部分代码
@BeforeClass
public static void setup() throws Exception {}
在这个方法中包含了具体的SqlSession的创建过程
5. SqlSession在Spring集成实现
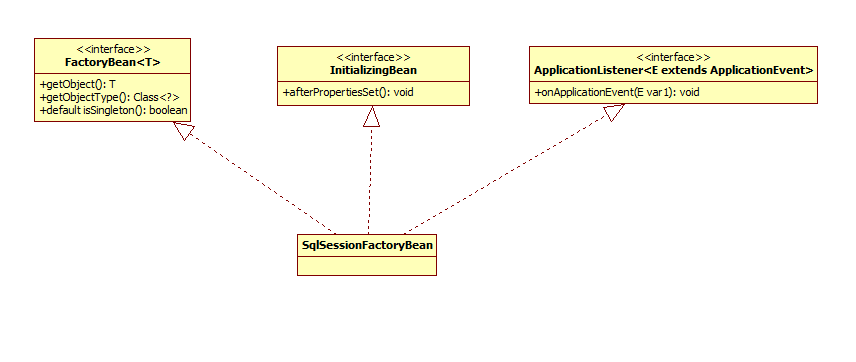
5.1 SqlSessionFactoryBean 介绍
SqlSessionFactoryBean在基本的 MyBatis 中,session 工厂可以使用 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 来创建。而在 MyBatis-Spring 中,则使用 SqlSessionFactoryBean 来替代。
-- 官方文档
那我们下载MyBatis-Spring源码 具体看看
查看大图
SqlSessionFactoryBean实现了Spring 的3个重要接口:
- InitializingBean
接口由bean实现,当BeanFactory设置了它们的所有属性后需要做出反应:例如,执行自定义初始化,或仅检查是否已设置所有必需属性。
关键代码
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
//参数检测
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
//sqlSessionFactory 实例化
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
/**
* Build a {@code SqlSessionFactory} instance.
*
* The default implementation uses the standard MyBatis {@code XMLConfigBuilder} API to build a
* {@code SqlSessionFactory} instance based on an Reader.
* Since 1.3.0, it can be specified a {@link Configuration} instance directly(without config file).
*
* @return SqlSessionFactory
* @throws IOException if loading the config file failed
*/
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
Configuration configuration;
//省略 configuration 创建代码
//返回创建的SqlSessionFactory
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration);
}
- FactoryBean
用于创建复杂的Bean对象,一般的Bean可以通过XML文件配置,但复杂Bean对象使用XML比较困难。
关键代码
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
//返回创建好的SqlSessionFatory对象
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
- ApplicationListener
当ApplicationContext被初始化或刷新时引发的事件,当Spring容器完全启动后执行。
关键代码
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (failFast && event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) {
// fail-fast -> check all statements are completed
//检测MyBatis所有配置文件语句是否完成
this.sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getMappedStatementNames();
}
}
6. 参考资料
- MyBatis官方文档 - http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html
- MyBatis-Spring官方文档 - http://www.mybatis.org/spring/zh/index.html
- MyBatis源码 - https://gitee.com/rainwen/mybatis
- MyBatis-Spring源码 - https://github.com/rainwen/spring
- SqlSessionManager 详解 - http://blog.csdn.net/teamlet/article/details/52173731
关于MyBatis源码解读之SqlSession就介绍到这里。如有疑问,欢迎留言,谢谢。