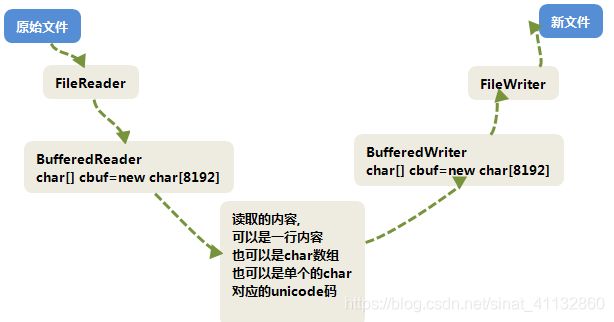
java 字符缓冲流BufferedReader和BufferedWriter
本节概要:
目录
BufferedReader
BufferedWriter
字符缓冲流复制文本文件:
BufferedReader
继承自Reader
构造方法:
private static int defaultCharBufferSize = 8192;
//可以手动设置缓存去char数组的大小
public BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz) {
super(in);
if (sz <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
this.in = in;
cb = new char[sz];
nextChar = nChars = 0;
}
//创建一个char数组,大小为8192,用来缓存
public BufferedReader(Reader in) {
this(in, defaultCharBufferSize);
}工作过程:使用BufferedReader时,先从Reader对象(FileReader)中读取数据写入到char[],然后从 自身的char数组中访问数据,当char数组的数据被访问完毕,就调用fill()方法重新填充char数组。关闭BufferedReader时,其构造参数的Reader也被关闭
特有方法:
String readLine() 从BufferedReader自身的char数组中读取一行文本,遇到以下字符会认为完成一行的读取,换行('\n'),回车('\r')或者回车后直接换行,返回包含该行内容的字符串,如果达到流末尾,返回null
看下BufferedReader的read方法:read()访问的BufferedReader本身的char数组,当数组的内容被访问完毕时调用调用fill()方法重新填充char数组。
private Reader in;
public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
if ((off < 0) || (off > cbuf.length) || (len < 0) ||
((off + len) > cbuf.length) || ((off + len) < 0)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = read1(cbuf, off, len);
if (n <= 0) return n;
while ((n < len) && in.ready()) {
int n1 = read1(cbuf, off + n, len - n);
if (n1 <= 0) break;
n += n1;
}
return n;
private int read1(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (nextChar >= nChars) {
if (len >= cb.length && markedChar <= UNMARKED && !skipLF) {
return in.read(cbuf, off, len);
}
fill();
}
if (nextChar >= nChars) return -1;
if (skipLF) {
skipLF = false;
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n') {
nextChar++;
if (nextChar >= nChars)
fill();
if (nextChar >= nChars)
return -1;
}
}
int n = Math.min(len, nChars - nextChar);
System.arraycopy(cb, nextChar, cbuf, off, n);
nextChar += n;
return n;
}
BufferedReader示例:
源文件word.txt内容:
好啊
你好
天天
///
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedReaderTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
try (
BufferedReader br =new BufferedReader(new FileReader("word.txt"));
){
String s;
//每次读取一行,读到末尾处为null
while ((s=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println( s);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
out:
好啊
你好
天天
BufferedWriter
继承自Writer
构造方法:
private static int defaultCharBufferSize = 8192;
//创建默认8192大小的char数组,用来缓存
public BufferedWriter(Writer out) {
this(out, defaultCharBufferSize);
}
//根据指定大小创建char数组,用来缓存
public BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz) {
super(out);
if (sz <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
this.out = out;
cb = new char[sz];
nChars = sz;
nextChar = 0;
}工作工程: BufferedWriter先将数据写入自身的char数组,当调用write方法时,将内容写到自身的char数组,再调用参数Writer对象的write方法从char数组中读取内容写入到文件中
关闭BufferedWriter时,自动关闭作为参数的Writer对象
特有方法:
newLine()换行
write方法,可以写字符串和char数组,可以指定他们的起始位置和长度,看下write的源码:
先将内容保存到自身的char数组中,再访问自身char数组,再将内容写入到文件中
private Writer out;//构造方法中传入的Writer对象
private char cb[];
//调用flushBuffer方法来写
public void write(int c) throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
if (nextChar >= nChars)
flushBuffer();
cb[nextChar++] = (char) c;
}
}
//调用out的write方法,out是创建BufferedWriter对象时,传进来的Writer对象
void flushBuffer() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
if (nextChar == 0)
return;
out.write(cb, 0, nextChar);
nextChar = 0;
}
}
示例:
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class BufferedWriterTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
try (
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("test\\test6.txt"));
){
bw.write("我们要加油");
bw.newLine();//换行
char [] charArr={'我','们','热','爱','祖','国'};
bw.write(charArr,0,4);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
out:
test6.txt的内容为:
我们要加油
我们热爱字符缓冲流复制文本文件:
import java.io.*;
public class FileCopy02 {
public static void main(String[] args){
try (
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("word1.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("test\\test7.txt"));
){
String s;
//通过每次读取一行,提高效率
while((s=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
out:
源文件word1.txt内容:
好吗
天天
目标文件test7.txt内容:
好吗
天天
画个示意图: