mybatis常用知识点复习详解
文章目录
-
- 1 mybatis是什么
- 2 如何使用mybatis
- 3 配置映射的两种方法
-
- 3.1 使用xml配置
- 3.2 使用注解配置
- 4 连接池
- 5 resultMap和resultType的区别
- 6 mybatis中的动态sql语句
- 7 子查询,使用foreach标签
- 8 配置别名
- 9 mybatis表关系一对一,一对多,多对多
-
- 9.1 数据库表关系
- 9.2 一对一
- 9.3 一对多
- 9.4 多对多
- 10 mybatis延迟加载
- 11 mybatis的缓存
-
- 11.1 一级缓存
- 11.2 二级缓存
- 12 mybatis注解开发
-
- 12.1 模糊查询的两种写法
- 12.2 注解开发中解决数据库列名与实体类属性名不一致问题
- 12.3 注解开发中的一对多查询和多对多查询
- 12.4 注解开发中开启二级缓存
1 mybatis是什么
mybatis是持久层框架
DAO:(data access object)数据访问层
2 如何使用mybatis
mybatis的环境搭建
第一步:创建maven工程并导入坐标
第二步:创建实体类和dao的接口
第三步:创建Mybatis的主配置文件
SqlMapConifg.xml
第四步:创建映射配置文件
UserDao.xml
环境搭建的注意事项:
第一个:创建UserDao.xml 和 UserDao.java时名称是为了和我们之前的知识保持一致。
在Mybatis中它把持久层的操作接口名称和映射文件也叫做:Mapper
所以:UserDao 和 UserMapper是一样的
第二个:在idea中创建目录的时候,它和包是不一样的
包在创建时:com.itheima.dao它是三级结构
目录在创建时:com.itheima.dao是一级目录
第三个:mybatis的映射配置文件位置必须和dao接口的包结构相同
第四个:映射配置文件的mapper标签namespace属性的取值必须是dao接口的全限定类名
第五个:映射配置文件的操作配置(select),id属性的取值必须是dao接口的方法名
当我们遵从了第三,四,五点之后,我们在开发中就无须再写dao的实现类。
-
domain实体类User继承自Serializable接口
public class User implements Serializable { } -
dao持久层接口
/** * 用户的持久层接口 */ public interface UserDao { /** * 查询所有操作 * @return */ List<User> findAll(); } -
resources下配置mybatis的主配置文件SqlMapConf.xml
<configuration> <environments default="mysql"> <environment id="mysql"> <transactionManager type="JDBC">transactionManager> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisdb"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="xiaoxi123"/> dataSource> environment> environments> <mappers> <mapper resource="com/xiaoxi/dao/UserDao.xml"/> mappers> configuration> -
resource下新建com.xiaoxi.dao包,新建UserDao.xml文件
<mapper namespace="com.xiaoxi.dao.UserDao"> <select id="findAll" resultType="com.xiaoxi.domain.User"> select * from user select> mapper> -
测试代码是否完成
test文件夹下新建com.xiaoxi.test.MybatisTest.java文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1.读取配置文件 InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConf.xml"); //2.创建SqlSessionFactory工厂 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(in); //3.使用工厂生产SqlSession对象 SqlSession session = factory.openSession(); //4.使用SqlSession创建Dao接口的代理对象 UserDao userDao = session.getMapper(UserDao.class); //5.使用代理对象执行方法 List<User> users = userDao.findAll(); for(User user: users) { System.out.println(user); } //6.释放资源 session.close(); in.close(); }
3 配置映射的两种方法
3.1 使用xml配置
resource下新建com.xiaoxi.dao包,新建UserDao.xml文件
<mapper namespace="com.xiaoxi.dao.UserDao">
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.xiaoxi.domain.User">
select * from user
select>
mapper>
指定映射配置文件使用resource属性
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/xiaoxi/dao/UserDao.xml"/>
mappers>
3.2 使用注解配置
在com.xiaoxi.dao.UserDao中代码添加注解:
public interface UserDao {
/**
* 查询所有操作
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user")
List<User> findAll();
}
指定映射配置文件使用class属性
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.xiaoxi.dao.UserDao"/>
mappers>
4 连接池
连接池:
我们在实际开发中都会使用连接池,因为它可以减少我们获取连接所消耗的时间。
连接池就是用于存储连接的一个容器,容器其实就是一个集合对象,该集合必须是线程安全的,不能两个线程拿到一个同一个连接。
该集合还必须实现队列的特性:先进先出
mybatis连接池提供了3种方式的配置:
-
配置的位置:
主配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml中的dataSource标签,type属性就是表示采用何种连接池方式<environments default="mysql"> <environment id="mysql"> <transactionManager type="JDBC">transactionManager> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisdb?serverTimezone=UTC"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="xiaoxi123"/> dataSource> environment> environments> -
type属性的取值:
-
POOLED:采用传统的javax.sql.DataSource规范中的连接池,mybatis中有针对规范的实现
-
UNPOOLED:采用传统的获取连接的方式,虽然也实现Javax.sql.DataSource接口,但是并没有使用池的思想
-
JNDI:采用服务器提供的JNDI技术实现,来获取DataSource对象,不同的服务器能拿到的DataSource是不一样的,
注意:如果不是web或者maven的war工程,是不能使用的
tomcat服务器使用的是dbcp连接池
-
5 resultMap和resultType的区别
<resultMap id="唯一的标识" type="映射的pojo对象">
<id column="表的主键字段,或者可以为查询语句中的别名字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="映射pojo对象的主键属性" />
<result column="表的一个字段(可以为任意表的一个字段)" jdbcType="字段类型" property="映射到pojo对象的一个属性(须为type定义的pojo对象中的一个属性)"/>
<association property="pojo的一个对象属性" javaType="pojo关联的pojo对象">
<id column="关联pojo对象对应表的主键字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="关联pojo对象的主席属性"/>
<result column="任意表的字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="关联pojo对象的属性"/>
association>
<collection property="pojo的集合属性" ofType="集合中的pojo对象">
<id column="集合中pojo对象对应的表的主键字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="集合中pojo对象的主键属性" />
<result column="可以为任意表的字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="集合中的pojo对象的属性" />
collection>
resultMap>
resultMap要更强大一些 ,可自定义。因为resultMap要配置一下,表和类的一一对应关系,所以说就算你的字段名和你的实体类的属性名不一样也没关系,都会给你映射出来,但是,resultType就比较鸡肋了,必须字段名一样,比如说 cId和c_id 这种的都不能映射 。
<resultMap id="user" type="com.xiaoxi.domain.User">
<id column="id" property="id">id>
<result column="username" property="username">result>
<result column="address" property="address">result>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday">result>
resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="user">
select * from user;
select>
6 mybatis中的动态sql语句
在查询语句中,如果需要模糊查询,比如可能查询性别,生日,地址中的一项或者多项,如何写?
1=1 永真, 1<>1 永假。
select * from sys_voter where 1<>1 这句查询出来的是 只要表结构不要表数据;
select * from sys_voter t where 1=1 查询全部数据
相当于 select * from sys_voter t ;
那么这句的话有啥作用呢??
sql语句a : select * from sys_voter t where 1=1 and t.id_='c7d958305c8144c7a1cdf8c7045583d'
当你的 字段 id_ 值为空时,保证 sql语句a 还能一直运行不报错,
也就是说 用户在条件查询时候 你用了 where 1=1 ;无论用户是否查询了 你都可以不用判断某个字段 为空不为空!!!
写法一:
<select id="findUserByCondition" parameterType="com.xiaoxi.domain.User" resultMap="user">
select * from user where 1=1
<if test="username != null">
and username = #{username}
if>
<if test="sex != null">
and sex = #{sex}
if>
select>
写法二:
<select id="findUserByCondition" parameterType="com.xiaoxi.domain.User" resultMap="user">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="username != null">
and username = #{username}
if>
<if test="sex != null">
and sex = #{sex}
if>
where>
select>
7 子查询,使用foreach标签
select * from user where id in (42, 43, 44);
步骤一:在com.xiaoxi.domain中新建QueryVo类:
public class QueryVo {
private User user;
private List<Integer> ids;
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
public List<Integer> getIds() {
return ids;
}
public void setIds(List<Integer> ids) {
this.ids = ids;
}
}
步骤二:在UserDao.xml中配置,使用foreach标签,整个sql语句相当于
select * from user where ids != null and ids.size() > 0 and id in (#{ids});
<select id="findUserInIds" parameterType="com.xiaoxi.domain.QueryVo" resultMap="user">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="ids != null and ids.size() > 0">
<foreach collection="ids" open="and id in (" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
foreach>
if>
where>
select>
8 配置别名
设置 MyBatis 的全局配置文件 SqlMapConfig 中的 typeAliases 属性后,就可以为 sql 映射文件中的输入 / 输出参数设置类型别名,然后在 sql 映射配置文件中指定输入输出参数类型时使用的别名
为domain实体类配置别名使用typeAliases标签
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.xiaoxi.domain"/>
typeAliases>
为映射文件配置别名使用mappers标签
<mappers>
<package name="com.xiaoxi.dao"/>
mappers>
配置之后在使用resultMap和resultType时就不需要使用com.xiaoxi.domain.User了,直接可以使用User
9 mybatis表关系一对一,一对多,多对多
9.1 数据库表关系
1 一对一关系实例
* 一个人对应一张身份证,一张身份证对应一个人
![]()
一对一关系是最好理解的一种关系,在数据库建表的时候可以将人表的主键放置与身份证表里面,也可以将身份证表的主键放置于人表里面
2、一对多关系实例
* 一个班级拥有多个学生,一个学生只能够属于某个班级
![]()
- 班级是1端,学生是多端,结合面向对象的思想,1端是父亲,多端是儿子,所以多端具有1端的属性,也就是说多端里面应该放置1端的主键,那么学生表里面应该放置班级表里面的主键
- java中在多端实体中应该包含一个一端实体的对象引用
3、多对多实例
* 一个学生可以选修多门课程,一个课程可以被多个学生选修
![]()
对于多对多关系,需要转换成1对多关系,那么就需要一张中间表来转换,这张中间表里面需要存放学生表里面的主键和课程表里面的主键,此时学生与中间表示1对多关系,课程与中间表是1对多关系,学生与课程是多对多关系
总而言之,最重要的关系就是1对多关系,根据面向对象思想在建表的时候将1端主键置于多端即可。
9.2 一对一
用户和账户,一个用户可以对应多个账户,一个账户只能属于一个用户,属于一对多的关系,对于账户来说,对用户是一对一
从account表中找出对应的user表中的uid
sql语句为:select a.*, u.username, u.address from account a, user u where a.uid = u.id
一对一关系映射:在多端实体中应该包含一个一端实体的对象引用,也就是在从表实体中包含一个主表实体的引用
在Account类中,包含一个User类型的私有属性
public class Account implements Serializable {
//其他省略
private User user;
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
}
然后在AccountDao.xml中使用resultMap定义映射关系,使用association:
<resultMap id="accountMap" type="account">
<id property="id" column="aid">id>
<result property="uid" column="uid">result>
<result property="money" column="money">result>
<association property="user" javaType="user" column="uid">
<id property="id" column="uid">id>
<result property="username" column="username">result>
<result property="address" column="address">result>
<result property="sex" column="sex">result>
<result property="birthday" column="birthday">result>
association>
resultMap>
<select id="findAllAccountUser" resultMap="accountMap">
select a.*, u.username, u.address from account a, user u where a.uid = u.id
select>
9.3 一对多
一对多关系映射:在主表实体中包含从表实体的集合引用
sql语句为select * from user u left outer join account a on u.id = a.uid
public class User implements Serializable {
//其他省略
private List<Account> accounts;
public List<Account> getAccounts() {
return accounts;
}
public void setAccounts(List<Account> accounts) {
this.accounts = accounts;
}
}
然后在UserDao.xml中使用resultMap定义映射关系,使用collection:
<resultMap id="userAccountMap" type="user">
<id column="id" property="id">id>
<result column="username" property="username">result>
<result column="address" property="address">result>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday">result>
<result column="sex" property="sex">result>
<collection property="accounts" ofType="account">
<id column="id" property="id">id>
<result column="uid" property="uid">result>
<result column="money" property="money">result>
collection>
resultMap>
<select id="findAllUserAccount" resultMap="userAccountMap">
select * from user u left outer join account a on u.id = a.uid
select>
9.4 多对多
示例:用户和角色
一个用户可以有多个角色
一个角色可以赋予多个用户
步骤:
1 建立两张表:用户表,角色表
让用户表和角色表具有多对多关系,需要使用中间表,中间表中包含各自的主键,在中间表中是外键
2 建立两个实体类:用户实体类和角色实体类
让用户和角色的实体类能体现出来多对多的关系,各自包含对方一个集合引用
多对多就相当于两个一对一的操作
查询角色表中,并得到用户的信息
sql:
select r.id as rid, r.ROLE_NAME, r.ROLE_DESC , u.* from role r left outer join user_role ur on r.id = ur.RID
left outer join user u on ur.UID = u.id
10 mybatis延迟加载
问题:在一对多中,当我们有一个用户,它有100个账户
在查询用户时,要不要把关联的账户查出来?
在查询用户时,用户下的账户信息应该是,什么时候使用,什么时候查询
在查询账户时,要不要把关联的用户查出来?
在查询账户时,账户的所属用户信息应该是随着账户查询时一起查询出来
问题:什么是延迟加载?
在真正使用数据时才发起查询,不用的时候不查询。按需加载(懒加载)
问题:什么是立即加载?
不管用不用,只要一调用方法,马上发起查询
在对应的四种表关系中:一对多,多对一,一对一,多对多
一对多,多对多:通常情况下我们都是采用延迟加载
多对一,一对一:通常情况下我们都是采用立即加载
settings中的配置:
| 设置名 | 描述 | 有效值 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| lazyLoadingEnabled | 延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载。 特定关联关系中可通过设置 fetchType 属性来覆盖该项的开关状态。 |
true | false | false |
| aggressiveLazyLoading | 开启时,任一方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有延迟加载属性。 否则,每个延迟加载属性会按需加载(参考 lazyLoadTriggerMethods)。 |
true | false | false (在 3.4.1 及之前的版本中默认为 true) |
SqlMapConfig.xml中的配置:
<settings>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="false"/>
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="true"/>
settings>
11 mybatis的缓存
Mybatis中的缓存
什么是缓存?存在于内存中的临时数据。
**为什么使用缓存?**减少和数据库的交互次数,提高执行效率。
什么样的数据能使用缓存,什么样的数据不能使用?
-
适用于缓存:
经常查询并且不经常改变的。
数据的正确与否对最终结果影响不大的。 -
不适用于缓存:
经常改变的数据
数据的正确与否对最终结果影响很大的。例如:商品的库存,银行的汇率,股市的牌价。
11.1 一级缓存
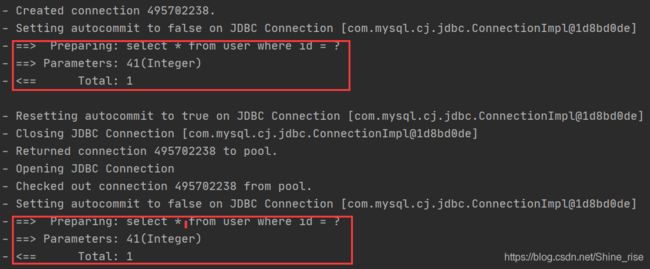
一级缓存:它指的是Mybatis中SqlSession对象的缓存。
当我们执行查询之后,查询的结果会同时存入到SqlSession为我们提供一块区域中。
该区域的结构是一个Map。当我们再次查询同样的数据,mybatis会先去sqlsession中查询是否有,有的话直接拿出来用。
当SqlSession对象消失时,mybatis的一级缓存也就消失了。
SqlSession中有一个**clearCache()**方法也可以清除一级缓存
当调用SqlSession的修改update,添加insert,删除delete,commit(),close()等方法时,就会清空一级缓存
11.2 二级缓存
它指的是Mybatis中SqlSessionFactory对象的缓存。由同一个SqlSessionFactory对象创建的SqlSession共享其缓存。
二级缓存的使用步骤:
- 第一步:让Mybatis框架支持二级缓存(在SqlMapConfig.xml中配置)
- 第二步:让当前的映射文件支持二级缓存(在UserDao.xml中配置)
- 第三步:让当前的操作支持二级缓存(在select标签中配置)
| 设置名 | 描述 | 有效值 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| cacheEnabled | 全局性地开启或关闭所有映射器配置文件中已配置的任何缓存。 | true | false | true |
未开启二级缓存时:
开启二级缓存:
-
第一步:在SqlMapConfig.xml中配置
<settings> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> settings> -
第二步:在UserDao.xml中配置
<cache/> -
第三步:在select标签中配置
<select id="findById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="user" useCache="true"> select * from user where id = #{id} select>
但是user1 == user2返回的是false,原因:二级缓存中存放的是数据{id:41, username:“xiaoxi”, address:“华科”},不是对象,使用时用这些数据创建一个新的对象,所以user1 == user2返回的是false
12 mybatis注解开发
12.1 模糊查询的两种写法
注解开发,模糊查询的两种写法:
//模糊查询的两种写法
// @Select("select * from user where username like #{username}") //该写法在写测试类时需要userDao.findUserByUsername("%王%")
@Select("select * from user where username like %${username}%") 该写法在写测试类时只需userDao.findUserByUsername("王")
List<User> findUserByUsername(String username);
12.2 注解开发中解决数据库列名与实体类属性名不一致问题
比如,mysql数据库表中列名为id, username, address, sex, birthday,
而User实体类中定义的属性名为userId, userName, userAddress, userSex, userBirthday,这种情况下直接查询是查不出来数据的
需要对应修改,方法:
-
方法一:在使用select注解时对每一项都使用别名,如select u.id as userId, u.username as userName …(麻烦,不推荐)
-
方法二:使用results注解
@Select("select * from user") @Results(id = "userMap", value = { @Result(id=true, column = "id", property = "userId"), @Result(column = "username", property = "userName"), @Result(column = "address", property = "userAddress"), @Result(column = "sex", property = "userSex"), @Result(column = "birthday", property = "userBirthday") }) List<User> findAll();
12.3 注解开发中的一对多查询和多对多查询
在注解中使用@Results注解,同时@One中的fetchType属性表示延迟加载还是立即加载
@Select("select * from user")
@Results(id = "userMap", value = {
@Result(id=true, column = "id", property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "username", property = "userName"),
@Result(column = "address", property = "userAddress"),
@Result(column = "sex", property = "userSex"),
@Result(column = "birthday", property = "userBirthday"),
@Result(property = "accounts", column = "id",
one = @One(select = "com.xiaoxi.dao.AccountDao.findAccoutByUid",
fetchType = FetchType.LAZY))
})
List<User> findAll();
12.4 注解开发中开启二级缓存
开启二级缓存:
-
第一步:在SqlMapConfig.xml中配置cacheEnabled,默认为true
<settings> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> settings> -
第二步:在com.xiaoxi.dao.UserDao中配置@CacheNamespace,默认为false,配置为true:
@CacheNamespace(blocking = true) public interface UserDao { @Select("select * from user") List<User> findAll(); //其他省略 }