Android资源 res文件夹的使用
Update time:2019-2-28 Author:要你命三千又三千 type:学习笔记
文章目录
- ColorStateList(颜色状态列表)
- Drawable (可绘制对象资源)
-
- 位图文件
- xml位图
- NinePatch
- XML 九宫格
- LayerDrawable
- StateListDrawable
- LevelListDrawable
- 转换可绘制对象TransitionDrawable
- 布局资源
-
- 补充:incule可以覆盖掉布属性android:layout_* attributes
- 字符串资源
-
- String
- String Array
- 字符串的格式和样式设置
-
- \"和\'
- 设置字符串格式
- 使用 HTML 标记**设置样式**
- 使用 Spannable 设置样式
- 样式资源
- 字体资源
-
- 捆绑到文件字体
- 字体系列
- 可下载字体
- 其他
ColorStateList(颜色状态列表)
A ColorStateList是您可以在XML中定义的对象,您可以将其应用为颜色,但实际上会根据View应用它的对象的状态更改颜色。
状态匹配规则:
非最佳匹配规则
在每次状态更改期间,状态列表将从上到下遍历,并且将使用与当前状态匹配的第一个项目。
- 文件位置
res/color/filename.xml
文件名将被用作资源ID - 资源的访问方式
In Java: R.color.filename
In XML: @[package:]color/filename
使用举例
res/color/button_text.xml(默认颜色值一般最后一项)
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:state_pressed="true"
android:color="#ffff0000"/>
<item android:state_focused="true"
android:color="#ff0000ff"/>
<item android:color="#ff000000"/>
selector>
使用
<Button
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/button_text"
android:textColor="@color/button_text" />
Drawable (可绘制对象资源)
包含两类:
- 位图文件(.png、.9.png、.jpg、.gif)
- 编译为可绘制对象资源子类型的 XML 文件
位图文件
- 文件类型:.png、.jpg 或 .gif 文件
当将这些文件保存到 res/drawable/ 目录中时,Android 将为它们创建 Drawable 资源。 - 数据类型为:BitmapDrawable
- 资源引用:
- 在 Java 中:R.drawable.filename
- 在 XML 中:@[package:]drawable/filename
示例:
当图像保存为 res/drawable/myimage.png 后,此布局 XML 会将图像应用到视图:
<ImageView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/myimage" />
以下应用代码将图像作为 Drawable 检索:
Resources res = getResources();
Drawable drawable = res.getDrawable(R.drawable.myimage);
xml位图
什么是xml位图
XML 位图是在 XML 中定义的资源,指向位图文件
- res/drawable/filename.xml
文件名用作资源 ID - 产生的数据类型为:BitmapDrawable
- 资源引用:
在 Java 中:R.drawable.filename
在 XML 中:@[package:]drawable/filename
举例:
<bitmap xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:src="@drawable/icon"
android:tileMode="repeat" />
NinePatch
- NinePatch 是一种 PNG 图像
- 与普通位图一样,您可以直接引用九宫格文件,也可以从 XML 定义的资源引用
- 文件位置:
res/drawable/filename.9.png
文件名用作资源 ID - 数据类型:NinePatchDrawable
使用举例
<Button
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/myninepatch" />
XML 九宫格
XML 九宫格是在 XML 中定义的资源,指向九宫格文件
举例
<nine-patch xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:src="@drawable/myninepatch"
android:dither="false" />
LayerDrawable
参考:https://developer.android.google.cn/guide/topics/resources/drawable-resource#LayerList
管理其他可绘制对象阵列的可绘制对象。
- 文件位置:
res/drawable/filename.xml
文件名用作资源 ID
实例
<layer-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item>
<bitmap android:src="@drawable/android_red"
android:gravity="center" />
item>
<item android:top="10dp" android:left="10dp">
<bitmap android:src="@drawable/android_green"
android:gravity="center" />
item>
<item android:top="20dp" android:left="20dp">
<bitmap android:src="@drawable/android_blue"
android:gravity="center" />
item>
layer-list>
<ImageView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/layers" />
StateListDrawable
参考:https://developer.android.google.cn/guide/topics/resources/drawable-resource#StateList)
StateListDrawable 是在 XML 中定义的可绘制对象,它根据对象的状态,使用多个不同的图像来表示同一个图形
- 资源引用
在 Java 中:R.drawable.filename
在 XML 中:@[package:]drawable/filename
实现方式
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:state_pressed="true"
android:drawable="@drawable/button_pressed" />
<item android:state_focused="true"
android:drawable="@drawable/button_focused" />
<item android:state_hovered="true"
android:drawable="@drawable/button_focused" />
<item android:drawable="@drawable/button_normal" />
selector>
使用方式
<Button
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/button" />
LevelListDrawable
管理大量备选可绘制对象的可绘制对象
- 使用方法
使用 setLevel() 设置可绘制对象的级别值会加载级别列表中 android:maxLevel 值大于或等于传递到方法的值的可绘制对象资源。 - 文件位置:
res/drawable/filename.xml
文件名用作资源 ID
<level-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<item
android:drawable="@drawable/status_off"
android:maxLevel="0" />
<item
android:drawable="@drawable/status_on"
android:maxLevel="1" />
level-list>
转换可绘制对象TransitionDrawable
参考文章:https://developer.android.google.cn/guide/topics/resources/drawable-resource#Transition
在两种可绘制对象资源之间交错淡出的可绘制对象
- 不支持超过两个项目
- 文件位置:
res/drawable/filename.xml
文件名用作资源 ID
其他可绘制图像参考:https://developer.android.google.cn/guide/topics/resources/drawable-resource#Bitmap
布局资源
可重用布局的的使用
建立需要重用的布局资源titlebar.xml
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/titlebar_bg"
tools:showIn="@layout/activity_main" >
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/gafricalogo" />
FrameLayout>
第二步
补充:incule可以覆盖掉布属性android:layout_* attributes
需要注意的是
为了使其他布局属性生效,您必须同时覆盖android:layout_hight和android:layout_Width。
< merge />在一个布局中包含一个布局时,该标记有助于消除视图层次结构中的冗余视图组。例如,如果主布局是一个垂直 LinearLayout,其中两个连续视图可以在多个布局中重复使用,则放置两个视图的可重用布局需要自己的根视图。但是,使用另一个LinearLayout作为可重用布局的根将导致垂直LinearLayout内部的垂直 LinearLayout。嵌套LinearLayout除了降低UI性能之外没有任何其他用途
字符串资源
字符串资源为您的应用提供具有可选文本样式和格式设置的文本字符串
String
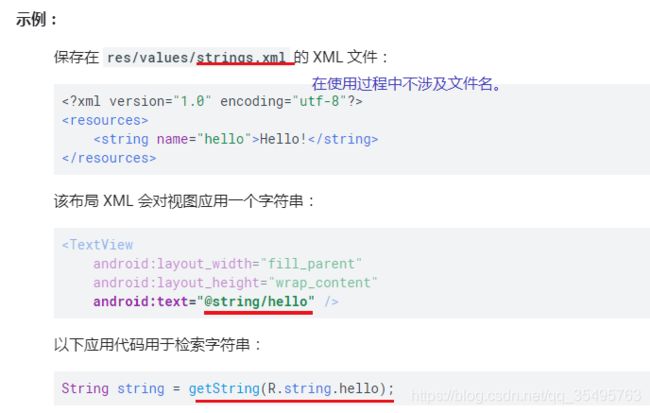
可从应用或从其他资源文件(如 XML 布局)引用的单个字符串
字符串是一种使用 name 属性(并非 XML 文件的名称)中提供的值进行引用的简单资源。 因此,您可以在一个 XML 文件中将字符串资源与其他简单资源合并在一起,放在 < resources> 元素之下
- 资源引用:
在 Java 中:R.string.string_name
在 XML 中:@string/string_name - 文件位置:
res/values/filename.xml
filename 是任意值。 元素的 name 将用作资源 ID
<resources>
<string
name="string_name"
>text_stringstring>
resources>
String Array
可从应用引用的字符串数组
- 字符串数组是一种使用 name 属性(并非 XML 文件的名称)中提供的值进行引用的简单资源。 因此,您可以在一个 XML 文件中将字符串数组资源与其他简单资源合并在一起,放在 < resources> 元素之下
- 资源引用:
在 Java 中:R.array.string_array_name - 文件位置:
res/values/filename.xml
filename 是任意值。 元素的 name 将用作资源 ID
实例
<resources>
<string-array name="planets_array">
<item>Mercuryitem>
<item>Venusitem>
<item>Earthitem>
<item>Marsitem>
string-array>
resources>
Resources res = getResources();
String[] planets = res.getStringArray(R.array.planets_array);
Quantity Strings
这里是了解以下Quantity Strings专们用于那些语言中对数量又要求的字符串。不同语言在语法数量一致上具有不同的规则,实现方式
第一步:第一单位数量规则
<resources>
<plurals name="numberOfSongsAvailable">
<item quantity="one">%d song found.item>
<item quantity="other">%d songs found.item>
plurals>
resources>
int count = getNumberOfsongsAvailable();
Resources res = getResources();
String songsFound = res.getQuantityString(R.plurals.numberOfSongsAvailable, count, count);
使用 getQuantityString() 方法时,如果您的字符串包括的字符串格式设置带有数字,则需要传递 count 两次。 例如,对于字符串 %d songs found,第一个 count 参数选择相应的复数字符串,第二个 count 参数将插入 %d 占位符内。 如果您的复数字符串不包括字符串格式设置,则无需向 getQuantityString 传递第三个count。
- count是数量值,第二个count是format传递(将%d替换成count值)
字符串的格式和样式设置
"和’
<string name="good_example">This is a \"good string\".string>
<string name="bad_example">This is a "bad string".string>
<string name="bad_example_2">'This is another "bad string".'string>
设置字符串格式
使用 HTML 标记设置样式
举例实现字体加粗
<resources>
<string name="welcome">Welcome to <b>Androidb>!string>
resources>
既包含html样式设置又包含字符格式的使用
正常情况下,这是行不通的,因为 String.format(String, Object…) 方法会去除字符串中的所有样式信息。 这个问题的解决方法是编写带转义实体的 HTML 标记,在完成格式设置后,这些实体可通过 fromHtml(String) 恢复.
<resources>
<string name="welcome_messages">Hello, %1$s! You have <b>%2$d new messages</b>.string>
resources>
Resources res = getResources();
String text = String.format(res.getString(R.string.welcome_messages), username, mailCount);
CharSequence styledText = Html.fromHtml(text);
如果传递的字符串带有(可能包含“<”或“&”之类的字符),则必须在设置格式前进行转义。在通过 fromHtml(String) 传递带格式字符串时,字符就能以原始形式显示出来。
String escapedUsername = TextUtil.htmlEncode(username);
Resources res = getResources();
String text = String.format(res.getString(R.string.welcome_messages), escapedUsername, mailCount);
CharSequence styledText = Html.fromHtml(text);
使用 Spannable 设置样式
Spannable 是一种文本对象,让您可以使用颜色和字体粗细等字体属性进行样式设置
样式资源
样式是使用name属性中提供的值(而不是XML文件的名称)引用的简单资源。因此,您可以将样式资源与一个XML文件中的其他简单资源组合在一个< resources>元素下。
- 文件位置:
res/values/filename.xml
文件名是任意的。元素name将用作资源ID - 资源使用方式
在XML中: @[package:]style/style_name
实例:
<resources>
<style
name="style_name"
parent="@[package:]style/style_to_inherit">
- "[package:]style_property_name"
>style_value
style>
resources>
- parent:引用一个样式,该样式应从中继承样式属性。这里说明了一个样式的继承性
- < item>是定义了样式的属性。
实例
<resources>
<style name="CustomText" parent="@style/Text">
- "android:textSize"
>20sp
- "android:textColor">#008
style>
resources>
使用:
<EditText
style="@style/CustomText"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello, World!" />
样式的继承
继承现有样式的属性,然后只定义您想要更改或添加的属性。 您可以从自行创建的样式或平台内建的样式继承属性。 例如,您可以继承 Android 平台的默认文本外观,然后对其进行修改:
<style name="GreenText" parent="@android:style/TextAppearance">
- "android:textColor"
>#00FF00
style>
自行定义的样式继承属性,则不必使用 parent 属性, 而是只需将您想继承的样式的名称以前缀形式添加到新样式的名称之中,并以句点进行分隔。
<style name="CodeFont.Red">
- "android:textColor"
>#FF0000
style>
这种通过将名称链接起来的继承方法只适用于由您自己的资源定义的样式。 您无法通过这种方法继承 Android 内建样式。 要引用内建样式(例如 TextAppearance),您必须使用 parent 属性。
- 如果您应用样式的 View 不支持所有样式属性,该 View 将只应用那些受支持的属性,并直接忽略其他属性。
问题:如何区别应用样式与主题关系
- 设置样式的方法有两种:
- 如果是对单个视图应用样式,请为布局 XML 中的 View 元素添加 style 属性。
- 或者,如果是对整个 Activity 或应用来应用样式,请为 Android androidMainfest.xml中的 < activity> 或 < application> 元素添加 android:theme 属性
答:应用的主题与应用样式的最大区别在于:样式是不可的应用不会传递到子view中,
- 您可以通过以主题形式应用样式,使所应用的样式作用于所有 View 元素。
问题一:如何设置activity 和应用的主题样式。
在AndroidManifest.xml 文件并编辑 < application> 标记
<application android:theme="@style/CustomTheme">
修改主题的方法
步骤一:喜欢某个主题,但想做些调整,只需将该主题添加为您的自定义主题的 parent
<color name="custom_theme_color">#b0b0ffcolor>
<style name="CustomTheme" parent="android:Theme.Light">
- "android:windowBackground"
>@color/custom_theme_color
- "android:colorBackground"
>@color/custom_theme_color
style>
android:windowBackground 只能支持对另一资源的引用。无法是提供颜色字面量。
使用平台内建样式和主题
- Android 平台提供了庞大的样式和主题集合,供您在应用中使用。 您可以在 R.style 类中找到所有可用样式的参考资料。 要使用此处所列样式,请将样式名称中的所有下划线替换为句点。
字体资源
Android 8.0 (API level 26)中可以使用字体资源。若要在运行Android4.1(API级别16)及更高版本的设备上使用InXML特性,请使用SupportLibrary 26。
字体资源定义了您可以在应用程序中使用的自定义字体。可以是单独的字体文件,也可以是字体文件的集合,称为字体系列,用XML定义。
捆绑到文件字体
您可以将字体作为资源捆绑在应用中。字体在R文件中编译, 并在系统中作为资源自动提供。
- 档案位置:font文件下
res/font/filename.ttf (.ttf,.ttc,.otf,或 .xml)
文件名被用作资源ID。
字体系列
建立字体系列
<font-family xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<font
android:fontStyle="normal"
android:fontWeight="400"
android:font="@font/lobster_regular" />
<font
android:fontStyle="italic"
android:fontWeight="400"
android:font="@font/lobster_italic" />
font-family>
在VIew中的使用方式
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:fontFamily="@font/lobster"/>
- Android 系统基于修个是元素的文本样式选择具体的字体
在样式中的使用方式
<style name="customfontstyle" parent="@android:style/TextAppearance.Small">
- "android:fontFamily"
>@font/lobster
style>
在java代码中设置文本的字体
val typeface = resources.getFont(R.font.myfont)
textView.typeface = typeface
在支持库中使用java的访问方式 https://developer.android.google.cn/guide/topics/ui/look-and-feel/fonts-in-xml.html#using-support-lib
可下载字体
定义了可在应用程序中使用的自定义字体。该字体在应用程序本身中不可用; 而是从字体提供者检索字体。
- 档案位置:
res/font/filename.xml 文件名用作资源ID。 - 资源引用:
在XML中:@[package:]font/font_name
其他
资源类型