高通QM215 高速串口调试总结
高通QM215 高速串口调试总结
- 参考文档
-
- 硬件和复用情况确认
- 修改如下
- 串口调试
- 测试程序代码:
- 将串口设置为高速串口,AP端收到的数据一直为0XFD
参考文档
1、sp80-pk881-6_a_qm215_linux_android_software_porting_manual.pdf
2、80-pk881-21_a_qm215_linux_peripheral_(uart,_spi,_i2c)_overview.pdf
3、80-ne436-1_j_bam_low-speed_peripherals_for_linux_kernel_configuration_and_debugging_guide.pdf
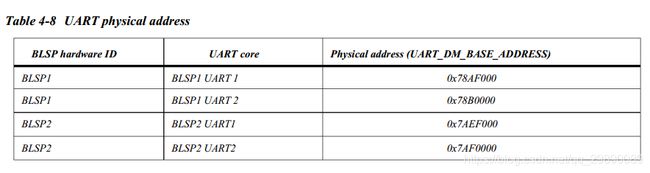
硬件和复用情况确认
首先确认要使用的UART号,得到其使用的TX,RX,TXS,RXS,并查看是否被复用为其他功能引脚,如SPI、SIM等等
以QM215 UART6为例,其用到的引脚如下,使用到了gpio20,gpio21,gpio22,gpio23,且查看设备树,发现并未被复用为其他功能.


修改如下
1、 msm-4.9/arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/msm8917-pinctrl.dtsi
//配置 gpio20 gpio21 gpio22 gpio23 功能为uart
blsp2_uart2 {
//uart6
blsp2_uart2_active: blsp2_uart2_active {
mux {
pins = "gpio20", "gpio21","gpio22", "gpio23";
function = "blsp_uart6";
};
config {
pins = "gpio20", "gpio21","gpio22", "gpio23";
drive-strength = <2>;
bias-disable;
};
};
blsp2_uart2_sleep: blsp2_uart2_sleep {
mux {
pins = "gpio20", "gpio21","gpio22", "gpio23";
function = "blsp_uart6";
};
config {
pins = "gpio20", "gpio21","gpio22", "gpio23";
drive-strength = <2>;
bias-disable;
};
};
};
2、msm-4.9/arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/msm8917.dtsi
//配置uart6为高速串口
blsp2_uart2: uart@7af0000 {
compatible = "qcom,msm-hsuart-v14";
reg = <0x7af0000 0x200>,
<0x7ac4000 0x1f000>;
reg-names = "core_mem", "bam_mem";
interrupt-names = "core_irq", "bam_irq", "wakeup_irq";
#address-cells = <0>;
interrupt-parent = <&blsp2_uart2>;
interrupts = <0 1 2>;
#interrupt-cells = <1>;
interrupt-map-mask = <0xffffffff>;
interrupt-map = <0 &intc 0 307 0
1 &intc 0 239 0
2 &tlmm 21 0>;
qcom,inject-rx-on-wakeup;
qcom,rx-char-to-inject = <0xfd>;
qcom,bam-tx-ep-pipe-index = <2>;
qcom,bam-rx-ep-pipe-index = <3>;
qcom,master-id = <84>;
clock-names = "core_clk", "iface_clk";
clocks = <&clock_gcc clk_gcc_blsp2_uart2_apps_clk>,
<&clock_gcc clk_gcc_blsp2_ahb_clk>;
pinctrl-names = "sleep", "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&blsp2_uart2_sleep>;
pinctrl-1 = <&blsp2_uart2_active>;
qcom,msm-bus,name = "blsp2_uart2";
qcom,msm-bus,num-cases = <2>;
qcom,msm-bus,num-paths = <1>;
qcom,msm-bus,vectors-KBps =
<84 512 0 0>,
<84 512 500 800>;
};
//配置uart6为低速串口
blsp2_uart2: serial@7af0000 {
//uart6
compatible = "qcom,msm-uartdm-v1.4",
"qcom,msm-uartdm";
reg = <0x7af0000 0x200>;
interrupts = <0 307 0>;
clocks = <&clock_gcc clk_gcc_blsp2_uart2_apps_clk>,
<&clock_gcc clk_gcc_blsp2_ahb_clk>;
clock-names = "core", "iface";
status = "disabled";
};
3、 msm-4.9/arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/qm215-qrd.dtsi
//使能UART6
&blsp2_uart2 {
status = "ok";
pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep";
pinctrl-0 = <&blsp2_uart2_active>;
pinctrl-1 = <&blsp2_uart2_sleep>;
};
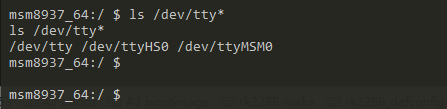
串口调试
编译并烧写成功,在dev目录下查看uart6是否生成.
高速串口:ttyHS*
低速串口:ttyMSM*
测试程序代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<termios.h>
#include<strings.h>
int set_opt(int fd,int nSpeed, int nBits, char nEvent, int nStop)
{
struct termios newtio,oldtio;
if( tcgetattr( fd,&oldtio) != 0) {
perror("tcgetattr error");
return -1;
}
bzero( &newtio, sizeof( newtio ) );
newtio.c_cflag |= CLOCAL | CREAD;
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
switch( nBits )
{
case 7:
newtio.c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
newtio.c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
}
switch( nEvent )
{
case 'O':
newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB;
newtio.c_cflag |= PARODD;
newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);
break;
case 'E':
newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);
newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB;
newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
break;
case 'N':
newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
break;
}
switch( nSpeed )
{
case 2400:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B2400);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B2400);
break;
case 4800:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B4800);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B4800);
break;
case 9600:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600);
break;
case 115200:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B115200);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B115200);
break;
case 460800:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B460800);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B460800);
break;
case 500000:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B500000);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B500000);
break;
case 576000:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B576000);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B576000);
break;
case 921600:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B921600);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B921600);
break;
case 1000000:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B1000000);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B1000000);
break;
case 1152000:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B1152000);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B1152000);
break;
default:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600);
break;
}
if( nStop == 1){
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
}else if ( nStop == 2 ){
newtio.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
}
newtio.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;
newtio.c_cc[VMIN] = 0;
tcflush(fd,TCIFLUSH);
if((tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&newtio))!=0)
{
perror("set error");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int fd,ret_set,ret_read,ret;
char buf_read[1024];
char buf_write[1024];
char tty[20]="/dev/";
if(3 < argc)
{
strcat(tty,argv[1]);
fd = open(tty, O_RDWR);
if(fd == -1)
{
printf("Open %s failed! Exit!\n",tty);
exit(1);
}
printf("open %s successfully!\n",tty);
ret_set = set_opt(fd, atoi(argv[2]), 8, 'N', 1);
if (ret_set == -1)
{
printf("Set %s failed! Exit!\n",tty);
exit(1);
}
printf("Set %s successfully!\n",tty);
printf("Baud rate: %s\n",argv[2]);
memset(buf_write, 0, sizeof(buf_write));
memcpy(buf_write,argv[3],sizeof(buf_write));
buf_write[99] = '\n';
printf("Data: %s, size: %lu\n",buf_write,strlen(buf_write));
while (1)
{
memset(buf_read, 0, sizeof(buf_read));
ret = write(fd, buf_write, strlen(buf_write)+1);
if( ret > 0){
printf("Write data: %s\n",buf_write);
}else{
printf("Write data failed! Exit!\n");
exit(1);
}
ret_read = read(fd, buf_read, 100);
if(ret_read > 0){
printf("Read data: %s\n\n", buf_read);
}
sleep(3);
}
close(fd);
}else{
printf("Usage: uart [tty node] [baud rate] [data] [data size < 1024]\n");
printf("Sample: uart ttyHSL1 115200 test\n");
}
return 0;
}
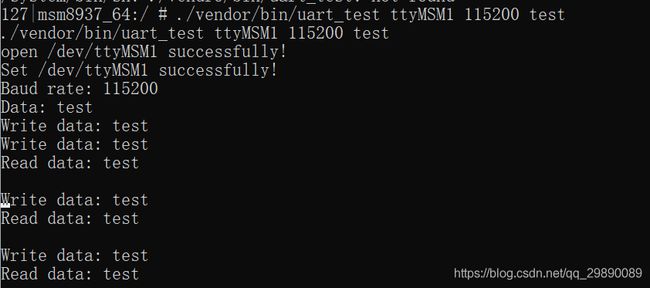
短接TX和RX,运行测试程序,得到以下结果,uart调试成功
将串口设置为高速串口,AP端收到的数据一直为0XFD
将串口设置为高速串口,与电脑通信,则AP端收到的数据一直为0XFD(原因不明),修改msm-4.9/drivers/tty/serial/msm_serial_hs.c如下,接收发送皆正常.
