使用Linux C 简易实现LS(实现过程)
ls实现过程
参考书籍:Unix-Linux编程实践教程
可以说这个是我写的第一个项目,也是我成长的最多的一个项目,因为这个项目我整整写了四个版本,也大概是4个程序实现的过程,一个从39行到380行的进步
第一版 ls实现列出每个文件名的功能
青涩的代码
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: ls1.cpp
> Author: ldc
> Mail: litesla
> Created Time: 2018年09月21日 星期五 19时17分38秒
************************************************************************/
#include样例截图
总结
这次的实现只是属于尝试版本,因为涉及到的结构体,有点陌生所以拿来练练手,但是当我看到屏幕输出的时候还是非常兴奋的
问题与改进
这个只是ls的基础功能,但是没有实现 -l 的功能,为此我做了第二版改进
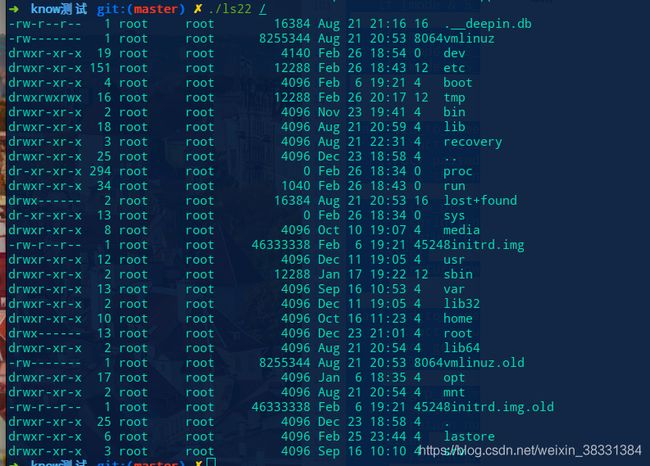
第二版 ls -l实现
测试代码
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: ls2.cpp
> Author: ldc
> Mail: litesla
> Created Time: 2018年09月21日 星期五 19时44分01秒
************************************************************************/
#include不是那么青涩的代码
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: ls2.cpp
> Author: ldc
> Mail: litesla
> Created Time: 2018年09月21日 星期五 19时44分01秒
************************************************************************/
#include样例截图
总结
可以看到这一版和上一版,你不会想到是一个人在隔了一天写出的代码,可以看出来进步是多么明显
问题与改进
这个与上个实现的功能的不同,只能实现-l的功能,不能传递参数,而且没有颜色的功能,一般的ls都是有功能的,所以我做出了第三版本
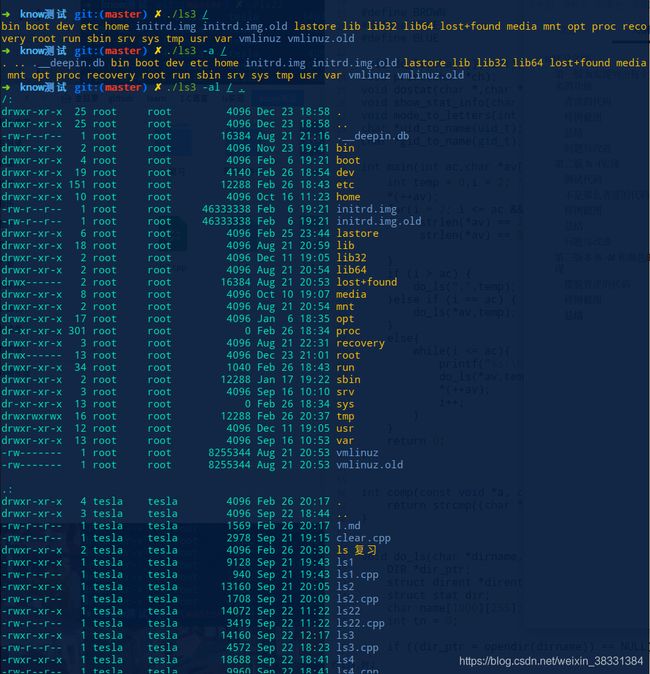
第三版本 ls -al 和颜色的实现
摆脱青涩的代码
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: ls2.cpp
> Author: ldc
> Mail: litesla
> Created Time: 2018年09月21日 星期五 19时44分01秒
************************************************************************/
#include样例截图
总结
这次可以说是比较完美的了,而且他还可以解析多个文件加,文件名也对齐了
问题与总结
完美总是想着跟完美,所以我就进行了我当时能做的最后一步
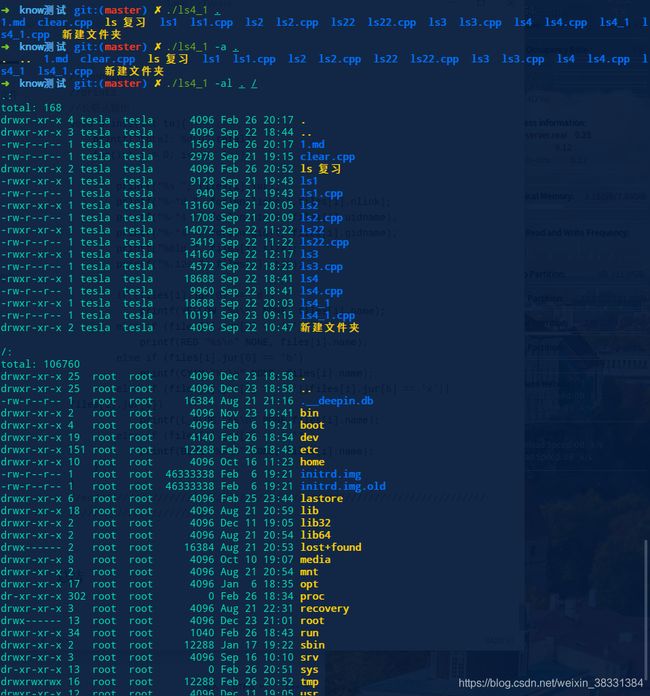
第四版 ls 模块化+解析
开始成熟的代码
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: ls4_1.cpp
> Author: ldc
> Mail: litesla
> Created Time: 2018年09月22日 星期六 19时07分39秒
************************************************************************/
#include测试样例
总结
虽然显示与上次没有什么差别,但是思想却差别巨大,已经有了封装的雏形
问题与改进
其实这次的代码还是有不完美的地方,比如函数接口处理部分,比如ls软连接部等
经典操作
位运算读取存储参数
int opp = 0, i = 2; //00 la
*(++av);
for(i = 2; i <= ac && (*av)[0] == '-'; *(++av),i++){
strlen(*av) == 2 && (*av)[1] =='a'&& (opp |=1,1)||(*av)[1] == 'l' && (opp |= 2,1);
strlen(*av) == 3 && ((*av)[1] == 'a' && (*av)[2] == 'l' ||
(*av)[1] == 'l' && (*av)[2] == 'a') && (opp |= 3,1);
}
op = opp;