OcTree可视化-matlab
来源:
https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/mlc-downloads/downloads/submissions/40732/versions/3/download/zip/OcTree.zip
OcTree.m
classdef OcTree < handle
% OcTree point decomposition in 3D
% OcTree is used to create a tree data structure of bins containing 3D
% points. Each bin may be recursively decomposed into 8 child bins.
%
% OT = OcTree(PTS) creates an OcTree from an N-by-3 matrix of point
% coordinates.
%
% OT = OcTree(...,'PropertyName',VALUE,...) takes any of the following
% property values:
%
% binCapacity - Maximum number of points a bin may contain. If more
% points exist, the bin will be recursively subdivided.
% Defaults to ceil(numPts/10).
% maxDepth - Maximum number of times a bin may be subdivided.
% Defaults to INF.
% maxSize - Maximum size of a bin edge. If any dimension of a bin
% exceeds maxSize, it will be recursively subdivided.
% Defaults to INF.
% minSize - Minimum size of a bin edge. Subdivision will stop after
% any dimension of a bin gets smaller than minSize.
% Defaults to 1000*eps.
% style - Either 'equal' (default) or 'weighted'. 'equal'
% subdivision splits bins at their central coordinate
% (ie, one bin subdivides into 8 equally sized bins).
% 'weighted' subdivision divides bins based on the mean
% of all points they contain. Weighted subdivision is
% slightly slower than equal subdivision for a large
% number of points, but it can produce a more efficient
% decomposition with fewer subdivisions.
%
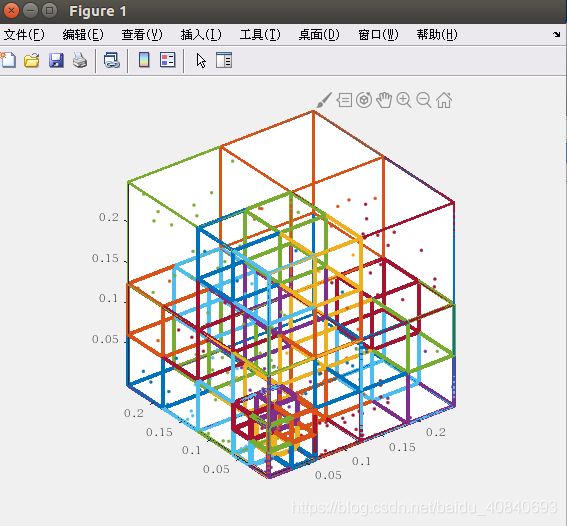
% Example 1: Decompose 200 random points into bins of 20 points or less,
% then display each bin with its points in a separate colour.
% pts = (rand(200,3)-0.5).^2;
% OT = OcTree(pts,'binCapacity',20);
% figure
% boxH = OT.plot;
% cols = lines(OT.BinCount);
% doplot3 = @(p,varargin)plot3(p(:,1),p(:,2),p(:,3),varargin{:});
% for i = 1:OT.BinCount
% set(boxH(i),'Color',cols(i,:),'LineWidth', 1+OT.BinDepths(i))
% doplot3(pts(OT.PointBins==i,:),'.','Color',cols(i,:))
% end
% axis image, view(3)
%
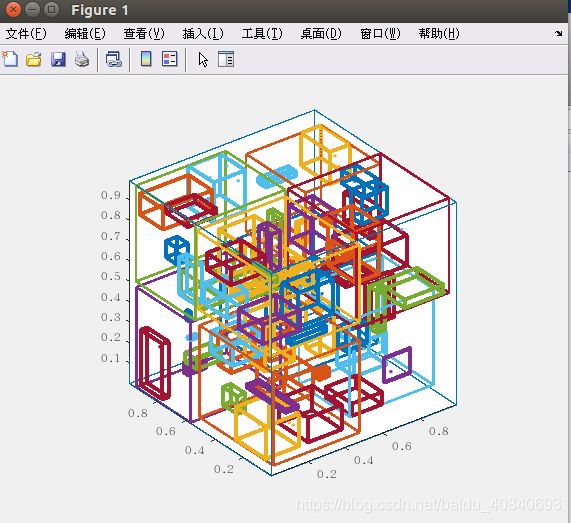
% Example 2: Decompose 200 random points into bins of 10 points or less,
% shrunk to minimallly encompass their points, then display.
% pts = rand(200,3);
% OT = OcTree(pts,'binCapacity',10,'style','weighted');
% OT.shrink
% figure
% boxH = OT.plot;
% cols = lines(OT.BinCount);
% doplot3 = @(p,varargin)plot3(p(:,1),p(:,2),p(:,3),varargin{:});
% for i = 1:OT.BinCount
% set(boxH(i),'Color',cols(i,:),'LineWidth', 1+OT.BinDepths(i))
% doplot3(pts(OT.PointBins==i,:),'.','Color',cols(i,:))
% end
% axis image, view(3)
%
%
% OcTree methods:
% shrink - Shrink each bin to tightly encompass its children
% query - Ask which bins a new set of points belong to.
% plot, plot3 - Plots bin bounding boxes to the current axes.
%
% OcTree properties:
% Points - The coordinate of points in the decomposition.
% PointBins - Indices of the bin that each point belongs to.
% BinCount - Total number of bins created.
% BinBoundaries - BinCount-by-6 [MIN MAX] coordinates of bin edges.
% BinDepths - The # of subdivisions to reach each bin.
% BinParents - Indices of the bin that each bin belongs to.
% Properties - Name/Val pairs used for creation (see help above)
%
% See also qtdecomp.
% Created by Sven Holcombe.
% 1.0 - 2013-03 Initial release
% 1.1 - 2013-03 Added shrinking bins and allocate/deallocate space
%
% Please post comments to the FEX page for this entry if you have any
% bugs or feature requests.
properties
Points;
PointBins;
BinCount;
BinBoundaries;
BinDepths;
BinParents = zeros(0,1);
Properties;
end
methods
function this = OcTree(pts,varargin)
% This is the OcTree header line
validateattributes(pts,{'numeric'},...
{'real','finite','nonnan','ncols', 3},...
mfilename,'PTS')
% Initialise a single bin surrounding all given points
numPts = size(pts,1);
this.BinBoundaries = [min(pts,[],1) max(pts,[],1)];
this.Points = pts;
this.PointBins = ones(numPts,1);
this.BinDepths = 0;
this.BinParents(1) = 0;
this.BinCount = 1;
% Allow custom setting of Properties
IP = inputParser;
IP.addParamValue('binCapacity',ceil(numPts)/10);
IP.addParamValue('maxDepth',inf);
IP.addParamValue('maxSize',inf);
IP.addParamValue('minSize',1000 * eps);
IP.addParamValue('style','equal');
IP.parse(varargin{:});
this.Properties = IP.Results;
% Return on empty or trivial bins
if numPts<2, return; end
% Start dividing!
this.preallocateSpace;
this.divide(1);
this.deallocateSpace;
end
% MATLAB performs better if arrays that grow are initialised,
% rather than grown during a loop. These two functions do just that
% before and after the identification of new beens.
function preallocateSpace(this)
numPts = size(this.Points,1);
numBins = numPts;
if isfinite(this.Properties.binCapacity)
numBins = ceil(2*numPts/this.Properties.binCapacity);
end
this.BinDepths(numBins) = 0;
this.BinParents(numBins) = 0;
this.BinBoundaries(numBins,1) = 0;
end
function deallocateSpace(this)
this.BinDepths(this.BinCount+1:end) = [];
this.BinParents(this.BinCount+1:end) = [];
this.BinBoundaries(this.BinCount+1:end,:) = [];
end
function divide(this, startingBins)
% Loop over each bin we will consider for division
for i = 1:length(startingBins)
binNo = startingBins(i);
% Prevent dividing beyond the maximum depth
if this.BinDepths(binNo)+1 >= this.Properties.maxDepth
continue;
end
% Prevent dividing beyond a minimum size
thisBounds = this.BinBoundaries(binNo,:);
binEdgeSize = diff(thisBounds([1:3;4:6]));
minEdgeSize = min(binEdgeSize);
maxEdgeSize = max(binEdgeSize);
if minEdgeSize < this.Properties.minSize
continue;
end
% There are two conditions under which we should divide
% this bin. 1: It's bigger than maxSize. 2: It contains
% more points than binCapacity.
oldCount = this.BinCount;
if nnz(this.PointBins==binNo) > this.Properties.binCapacity
this.divideBin(binNo);
this.divide(oldCount+1:this.BinCount);
continue;
end
if maxEdgeSize>this.Properties.maxSize
this.divideBin(binNo);
this.divide(oldCount+1:this.BinCount);
continue;
end
end
end
function divideBin(this,binNo)
% Gather the new points (a bit more efficient to copy once)
binPtMask = this.PointBins==binNo;
thisBinsPoints = this.Points(binPtMask,:);
% Get the old corner points and the new division point
oldMin = this.BinBoundaries(binNo,1:3);
oldMax = this.BinBoundaries(binNo,4:6);
if strcmp('weighted',this.Properties.style) && any(binPtMask)
newDiv = mean(thisBinsPoints,1);
else
newDiv = mean([oldMin; oldMax], 1);
end
% Build the new boundaries of our 8 subdivisions
minMidMax = [oldMin newDiv oldMax];
newBounds = minMidMax([...
1 2 3 4 5 6;
1 2 6 4 5 9;
1 5 3 4 8 6;
1 5 6 4 8 9;
4 2 3 7 5 6;
4 2 6 7 5 9;
4 5 3 7 8 6;
4 5 6 7 8 9]);
% Determine to which of these 8 bins each current point belongs
binMap = cat(3,[0 0 0],[0 0 1],[0 1 0],[0 1 1],...
[1 0 0],[1 0 1],[1 1 0],[1 1 1]);
gtMask = bsxfun(@gt, thisBinsPoints, newDiv);
[~,binAssignment] = max(all(bsxfun(@eq,gtMask,binMap),2),[],3);
% [~, binAssignment] = ismember(gtMask,binMap,'rows'); % A little slower than above.
% Make the new bins and reassign old points to them
newBinInds = this.BinCount+1:this.BinCount+8;
this.BinBoundaries(newBinInds,:) = newBounds;
this.BinDepths(newBinInds) = this.BinDepths(binNo)+1;
this.BinParents(newBinInds) = binNo;
this.PointBins(binPtMask) = newBinInds(binAssignment);
this.BinCount = this.BinCount + 8;
end
function shrink(this)
% Shrink all bins to bound only the points they contain
% WARNING: this operation creates gaps in the final space not
% covered by a bin. Only shrink OcTree structures when you only
% intend to use the points used to create the tree to query the
% tree space.
binChildren = arrayfun(@(i)find(this.BinParents==i),1:this.BinCount,'Un',0)';
binIsLeaf = cellfun(@isempty, binChildren);
for i = find(binIsLeaf(:))'
binShrink_recurse(i, true)
end
function binShrink_recurse(binNo, isLeafBin)
% Build a list of all points that fall within one of the
% bins to be checked, and the list of which point falls in
% which bin.
oldBoundaryMin = this.BinBoundaries(binNo,1:3);
oldBoundaryMax = this.BinBoundaries(binNo,4:6);
if isLeafBin
% Shrink bin based on child POINTS
ptsMask = this.PointBins==binNo;
if ~any(ptsMask)
% No points, shrink the bin to infinitely small
proposedBoundaries = [oldBoundaryMin oldBoundaryMin];
else
pts = this.Points(ptsMask,:);
proposedBoundaries = [...
max([oldBoundaryMin; min(pts,[],1)]) ...
min([oldBoundaryMax; max(pts,[],1)])];
end
else
% Shrink bin based on child BINS
childBoundaries = this.BinBoundaries(binChildren{binNo},:);
proposedBoundaries = [min(childBoundaries(:,1:3),[],1) max(childBoundaries(:,4:6),[],1)];
end
if ~isequal(proposedBoundaries, [oldBoundaryMin oldBoundaryMax])
% We just shrunk the boundary. Make it official and
% check the parent
this.BinBoundaries(binNo,:) = proposedBoundaries;
parentBin = this.BinParents(binNo);
if parentBin>0
binShrink_recurse(parentBin, false)
end
end
end
end
function binNos = query(this, newPts, queryDepth)
% Get the OcTree bins that new query points belong to.
%
% BINS = OT.query(NEWPTS) searches the OcTree object OT and
% returns an N-by-1 vector of BINS giving the bin index in
% which each of the N points in NEWPTS is contained. For any
% query points outside all bins in OT, the index -1 is
% returned.
%
% BINS = OT.query(NEWPTS,DEPTH) restricts the search to DEPTH
% levels in the OT bin tree. Note that the first bin
% (containing all other bins in OT) has DEPTH = 1.
if nargin<3
queryDepth = max(this.BinDepths);
end
numPts = size(newPts,1);
newPts = permute(newPts,[3 2 1]);
binNos = ones(numPts,1)*-1;
binChildren = arrayfun(@(i)find(this.BinParents==i),1:this.BinCount,'Un',0)';
binIsLeaf = cellfun(@isempty, binChildren);
ptQuery_recurse(1:numPts, this.BinParents==0, 0)
function ptQuery_recurse(newIndsToCheck_, binsToCheck, depth)
% Build a list of all points that fall within one of the
% bins to be checked, and the list of which point falls in
% which bin.
boundsToCheck = this.BinBoundaries(binsToCheck,:);
[ptInBounds, subBinNo] = max(all(...
bsxfun(@ge, newPts(:,:,newIndsToCheck_), boundsToCheck(:,1:3)) & ...
bsxfun(@le, newPts(:,:,newIndsToCheck_), boundsToCheck(:,4:6))...
,2),[],1);
if ~all(ptInBounds)
% Special case usually when depth=0, where a point may
% fall outside the bins entirely. This should only
% happen once so let's fix it once and let subsequent
% code rely on all points being in bounds
binNos(newIndsToCheck_(~ptInBounds)) = -1;
newIndsToCheck_(~ptInBounds) = [];
subBinNo(~ptInBounds) = [];
end
binNosToAssign = binsToCheck(subBinNo);
newIndsToAssign = newIndsToCheck_;
binNos(newIndsToAssign) = binNosToAssign;
% Allow a free exit when we reach a certain depth
if depth>=queryDepth
return;
end
% Otherwise, for all of the points we just placed into
% bins, check which of the children of those bins those
% same points fall into
[unqBinNos, ~, unqGrpNos] = unique(binNosToAssign);
for i = 1:length(unqBinNos)
thisPtMask = unqGrpNos==i;
if ~binIsLeaf(unqBinNos(i))
ptQuery_recurse(newIndsToCheck_(thisPtMask), binChildren{unqBinNos(i)}, depth+1)
end
end
end
end
function h = plot(this,varargin)
% OcTree.plot plots bin bounding boxes of an OcTree object
%
% H = OT.plot('name',value,...) allows you to specify any
% properties of the bounding box lines that you would normally
% supply to a plot(...,'name',value) command, and returns plot
% object handles (one per bin) to H.
hold on;
h = zeros(this.BinCount,1);
for i = 1:this.BinCount
binMinMax = this.BinBoundaries(i,:);
pts = cat(1, binMinMax([...
1 2 3; 4 2 3; 4 5 3; 1 5 3; 1 2 3;...
1 2 6; 4 2 6; 4 5 6; 1 5 6; 1 2 6; 1 2 3]),...
nan(1,3), binMinMax([4 2 3; 4 2 6]),...
nan(1,3), binMinMax([4 5 3; 4 5 6]),...
nan(1,3), binMinMax([1 5 3; 1 5 6]));
h(i) = plot3(pts(:,1),pts(:,2),pts(:,3),varargin{:});
end
end
function h = plot3(this,varargin)
% OcTree.plot plots bin bounding boxes of an OcTree
%
% See also OcTree.plot
h = this.plot(varargin{:});
end
end
end
main.m
pts = (rand(200,3)-0.5).^2;
OT = OcTree(pts,'binCapacity',20);
figure
boxH = OT.plot;
cols = lines(OT.BinCount);
doplot3 = @(p,varargin)plot3(p(:,1),p(:,2),p(:,3),varargin{:});
for i = 1:OT.BinCount
set(boxH(i),'Color',cols(i,:),'LineWidth', 1+OT.BinDepths(i))
doplot3(pts(OT.PointBins==i,:),'.','Color',cols(i,:))
end
axis image, view(3)
pts = rand(200,3);
OT = OcTree(pts,'binCapacity',10,'style','weighted');
OT.shrink
figure
boxH = OT.plot;
cols = lines(OT.BinCount);
doplot3 = @(p,varargin)plot3(p(:,1),p(:,2),p(:,3),varargin{:});
for i = 1:OT.BinCount
set(boxH(i),'Color',cols(i,:),'LineWidth', 1+OT.BinDepths(i))
doplot3(pts(OT.PointBins==i,:),'.','Color',cols(i,:))
end
axis image, view(3)