编程c语言中,向上取整函数_C编程中的函数
编程c语言中,向上取整函数
什么是功能? (What is a Function?)
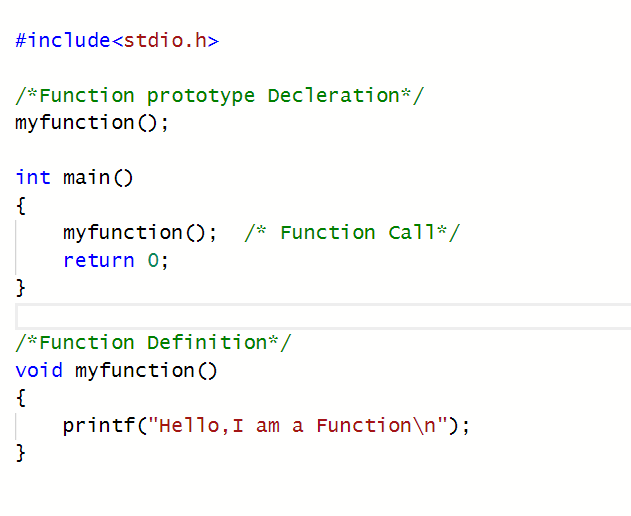
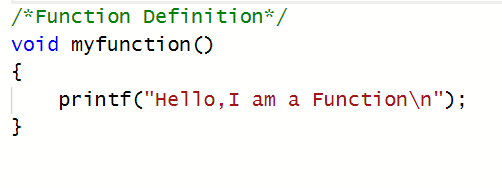
A Function is a block of statements that performs a specific task of some kind. Every C program can be thought of as the Collection of these Functions. The below Example shows how we can write a simple function.
函数是执行某种特定任务的语句块。 每个C程序都可以视为这些函数的集合。 下面的示例显示了我们如何编写一个简单的函数。
In the above Example, we have made a function. After creating the Function we can call it from main(). Functions can also call each other. A function can even call itself. The Function which calls itself is known as Recursion.
在上面的示例中,我们做了一个函数。 创建函数后,我们可以从main()中调用它。 函数也可以互相调用。 函数甚至可以调用自身。 调用自身的函数称为递归。
可以从上述计划中得出的结论 (Conclusions that can be drawn from above Program)
- A C program is a Collection of one or more Functions. AC程序是一个或多个功能的集合。
- If a C program contains only one function, it must be main(). 如果C程序仅包含一个函数,则它必须是main()。
- If a C program contains more than one function, then one of them is main() because the program execution begins with main(). 如果C程序包含多个函数,则其中一个函数是main(),因为该程序的执行从main()开始。
- There can be as many functions in a program as possible. 程序中可以有尽可能多的功能。
为什么需要功能? (Why do we need Functions?)
- It divides the program into separate well-defined functions so that each function can be written and tested separately. 它将程序划分为单独的定义明确的函数,以便可以分别编写和测试每个函数。
- Understanding, coding and testing becomes very easy as they are separated. 由于将它们分开,所以理解,编码和测试变得非常容易。
- Writing functions avoids rewriting the same code over and over. 编写函数可以避免一遍又一遍地重写相同的代码。
- As the functions are divided the workload can also be divided among the programmers. 由于功能被划分,工作量也可以在程序员之间分配。
C中的函数声明 (Function Declaration in C)
Basic Syntax:
基本语法:
return_data_type function_name (data_type var1, data_type var2, …..);Where,
哪里,
function_name: the name for the function should be valid. It should be a meaningful name that should clarify what all tasks it will perform.
function_name : 函数的名称应有效。 它应该是一个有意义的名称,它应该阐明它将执行的所有任务。
return_data_type: it is used for specifying the data type of the value that is returned to the calling function after the processing.
return_data_type :用于指定处理后返回到调用函数的值的数据类型。
data_type var1, data_type var2: function arguments and their data types.
data_type var1,data_type var2 :函数参数及其数据类型。
返回数据类型 (Return Data Types)
The return value has a type as other values in C. It can be int, float, char or anything else. The type of return value determines the type of your function.
返回值的类型与C中的其他值相同。它可以是int,float,char或其他任何类型。 返回值的类型决定了函数的类型。
The default return type of function is int or integer.
函数的默认返回类型为int或integer。
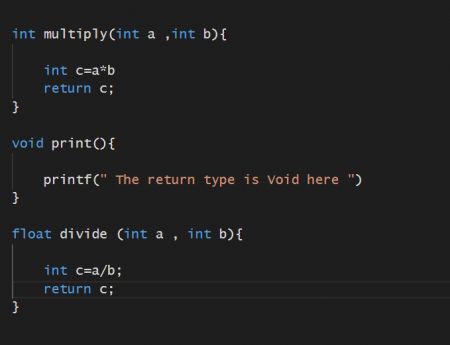
In the above Program, we have 3 Functions:
在以上程序中,我们具有3个功能:
- multiply(): Its return type is int, therefore it will return an integer type value. multiple():其返回类型为int,因此它将返回整数类型值。
- print(): Its return type is void, therefore it will not return anything, it will simply execute the code within. print():其返回类型为void,因此它将不返回任何内容,仅执行其中的代码。
- divide(): Its return type is a float, therefore it will return a decimal type value. split():其返回类型为浮点型,因此它将返回一个十进制类型的值。
C中的函数定义 (Function Definition in C)
Whenever a function is defined, its space is allocated in the memory.
每当定义函数时,其空间就会分配到内存中。
Syntax:
句法:
return_data_type function_name (data_type var1, data_type var2, …..);
{
…...................
statements;
…...................
return (variable);
}The statements written within the curly braces ({}) are the body of the function which contains the code to be performed.
花括号({})中编写的语句是包含要执行的代码的函数的主体。
在C中调用函数 (Calling a Function in C)
Whenever the function is invoked the compiler skips on to the called function for executing its statements. We mean that the control passes to the function The activity of main() is temporarily suspended.
无论何时调用该函数,编译器都会跳至被调用函数以执行其语句。 我们的意思是该控件传递给了函数main()的活动被暂时挂起。
Once the called function is executed the control of the program is passed back to the calling function.
一旦执行了被调用的函数,程序的控制权就会传回到调用函数。
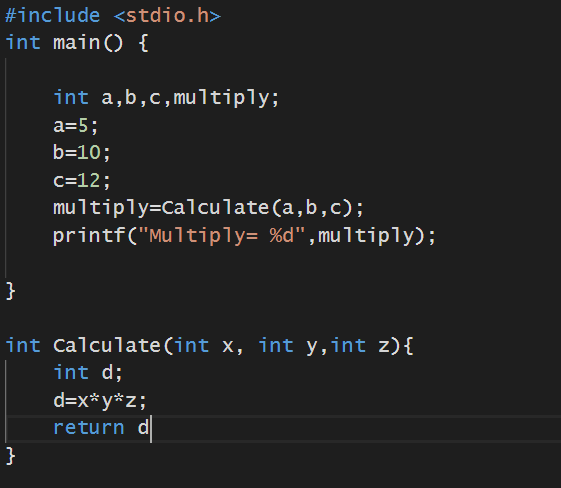
在函数之间传递值 (Passing values between functions)
In the above Program, the variable a, b, c are called actual arguments. The variables x, y, z are called as formal arguments.
在上面的程序中,变量a,b,c被称为实际参数。 变量x,y,z被称为形式参数。
在C中按值调用 (Call by Value in C)
In this parameter passing method, values of actual parameters are copied to function’s formal parameters and the two types of parameters are stored in different memory locations. So any changes made inside functions are not reflected in actual parameters of the caller.
在此参数传递方法中,将实际参数的值复制到函数的形式参数中,并将两种类型的参数存储在不同的存储位置中。 因此,在函数内部进行的任何更改都不会反映在调用者的实际参数中。
While calling a function, we pass the values of variables to it. Such functions are known as “Call By Values”.
在调用函数时,我们将变量的值传递给它。 这些功能称为“按值调用”。
C program to illustrate call by value
C程序说明按值调用
#include
void swapx(int x, int y);
int main()
{
int a = 100, b = 200;
// Pass by Values
swapx(a, b);
printf("a=%d b=%d\n", a, b);
return 0;
}
void swapx(int x, int y)
{
int t;
t = x;
x = y;
y = t;
printf("x=%d y=%d\n", x, y);
} Output:
输出 :
The actual values of a and b remain unchanged even after exchanging the values of x and y.
即使在交换x和y的值之后,a和b的实际值仍保持不变。
在C中通过引用调用 (Call by Reference in C)
While calling a function, instead of passing the values of variables, we pass the address of variables (pointers) to the function known as “Call By References.
在调用函数时,我们不传递变量的值,而是将变量(指针)的地址传递给称为“按引用调用”的函数。
Both the actual and formal parameters refer to the same locations, so any changes made inside the function are actually reflected in the actual parameters of the caller.
实际参数和形式参数都指向相同的位置,因此在函数内部所做的任何更改实际上都会反映在调用者的实际参数中。
C program to illustrate Call by Reference
C程序说明按引用调用
#include
void swapx(int*, int*);
int main()
{
int a = 100, b = 200;
// Pass reference
swapx(&a, &b);
printf("a=%d b=%d\n", a, b);
return 0;
}
void swapx(int* x, int* y)
{
int t;
t = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = t;
printf("x=%d y=%d\n", *x, *y);
} Output:
输出 :
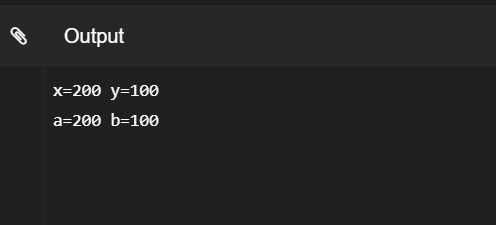
The actual values of a and b get changed after exchanging values of x and y.
在交换x和y的值之后,a和b的实际值将更改。
什么是递归函数? (What is a Recursive Function?)
A function which calls itself is called a Recursive function.
调用自身的函数称为递归函数 。
While using the recursive functions, it is important to be careful to define the exit condition from the function or then it may result in an infinite loop.
使用递归函数时,一定要小心,以定义函数的退出条件,否则可能导致无限循环。
They are used for calculating factorial of a number, Fibonacci series, etc.
它们用于计算数字,斐波那契数列等的阶乘。
#include
int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
getchar();
return 0;
} 翻译自: https://www.journaldev.com/30509/functions-in-c-programming
编程c语言中,向上取整函数