深度优先遍历(DFS)例题
深度优先要比广度优先难一些。
一般来说,一个DFS由三段组成,依次是:结束搜索,状态更新,状态转换。
举两个栗子
1. 神奇的口袋
有一个神奇的口袋,总的容积是40,用这个口袋可以变出一些物品,这些物品的总体积必须是40。John现在有n个想要得到的物品,每个物品的体积分别是a1,a2……an。John可以从这些物品中选择一些,如果选出的物体的总体积是40,那么利用这个神奇的口袋,John就可以得到这些物品。现在的问题是,John有多少种不同的选择物品的方式。
DFS解法:
- 结束搜索
1.1 当剩余空间恰好为零时(成功)
1.2 当剩余空间为负、或遍历完物品仍不满足时(失败) - 状态更新
对于每个物品,无非是放入口袋和不放入口袋两种情况,用dfs(id,rem)表示第id个物品放入后的剩余空间为rem,那么放入第id+1个物品的状态是dfs(id+1,rem-v[id]),不放入的状态便是dfs(id+1,rem)。 - 状态转移
递归调用两个状态即可。
#include但这样还是有一点动态规划的感觉,因为考虑了放与不放的两个状态转移。
还有一种更容易理解的dfs思想:对于每一次访问,都遍历所有还未被遍历的结点。若容量小于40,则继续遍历;等于40,则方式数加一;大于40,则回溯。
#include2.A Knight’s Journey
Background
The knight is getting bored of seeing the same black and white squares again and again and has decided to make a journey around the world. Whenever a knight moves, it is two squares in one direction and one square perpendicular to this. The world of a knight is the chessboard he is living on. Our knight lives on a chessboard that has a smaller area than a regular 8 * 8 board, but it is still rectangular. Can you help this adventurous knight to make travel plans?
Problem
Find a path such that the knight visits every square once. The knight can start and end on any square of the board.
Input
The input begins with a positive integer n in the first line. The following lines contain n test cases. Each test case consists of a single line with two positive integers p and q, such that 1 <= p * q <= 26. This represents a p * q chessboard, where p describes how many different square numbers 1, . . . , p exist, q describes how many different square letters exist. These are the first q letters of the Latin alphabet: A, . . .
Sample Input
1
4 3
Sample Output
A1B3C1A2B4C2A3B1C3A4B2C4
此题并不难,不过有几点小启示:
- 可以使用string作为参数来记录递归的过程(路线),debug困难时也可以尝试用此方法来查找问题。(文后附用sstream类来进行字符串与数字互相转化的一种方法)
- 不可忘记取消
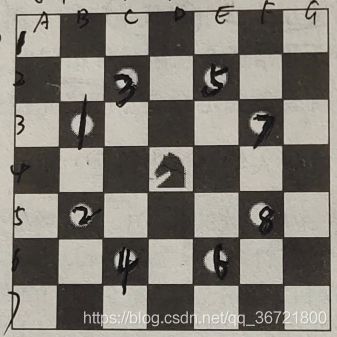
visit标记。第30行的标记取消是因为此时需要回溯,就需要将该点置为未访问;而第19行的标记取消一直到求助了大佬后才想到。原因是我一直想不通为什么仅仅输出了一个解路线就会终止。(当然,该题目仅要求输出一条ascii码序最小的路线,不取消19行的标记才是正确的,因为这样可以抑制后面的输出。但要知道原因) - 关于ascii码序如何处理。直接在遍历时考虑他们的相对位置。如图编号为1的点为B3,编号为2的点为B5,ascii中B3的优先级就高于B5,所以将B3排在前。这样最终得到的整个序列也必定是ascii序最小的序列。
#include附:
1. 字符串---->数字
以前都是用atof()、atoi()、atol() 实现这一系列转化,但总觉得不方便。索性学了sstream类,用C++中的流来实现这一目的。
#include2. 数字---->字符串
对于单个字符或许可以用char c = '0' + num;的形式来转化,但若是多位数字还这样做就太不方便了。当然也可以用C++11支持的to_string()方法。不过 ostringstream也可以解决这个问题。
#include