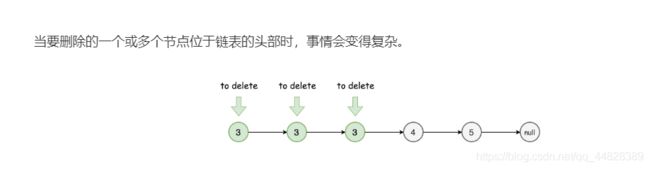
【数据结构】2.2经典的单链表练习题
目录
1. 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
方法一:哨兵结点
方法二:尾插法
2.反转单链表
方法一:指针转方向
方法二:头插法
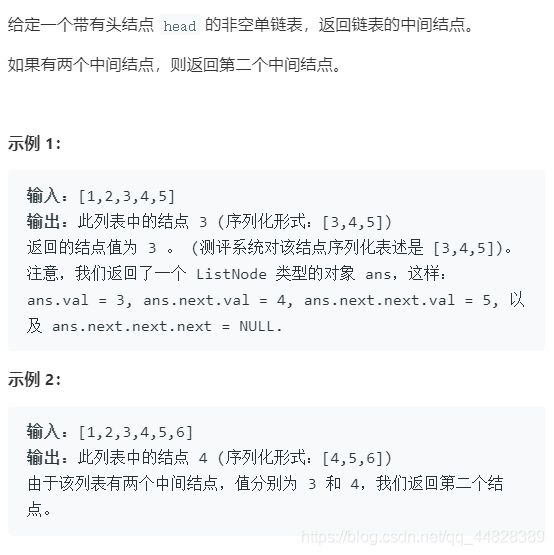
3.链表的中间结点
方法一:计算链表长度
方法二:快慢指针
4.合并有序单链表
5.链表的分割
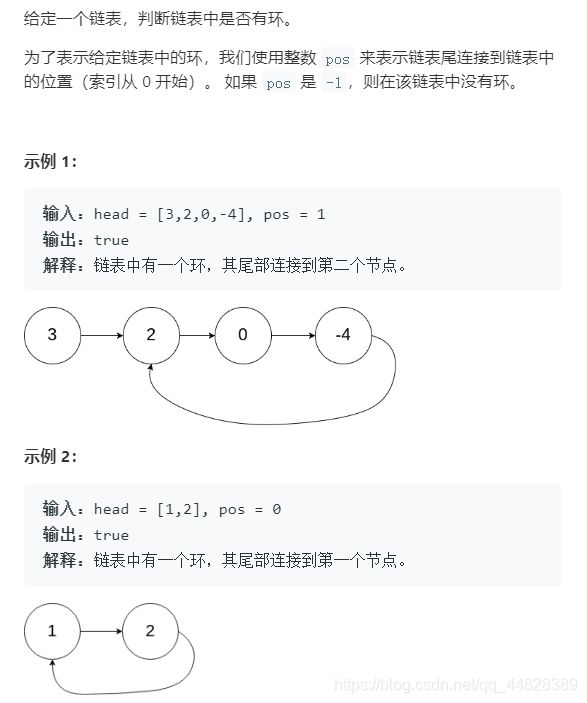
6.带环问题(判断链表是否带环)
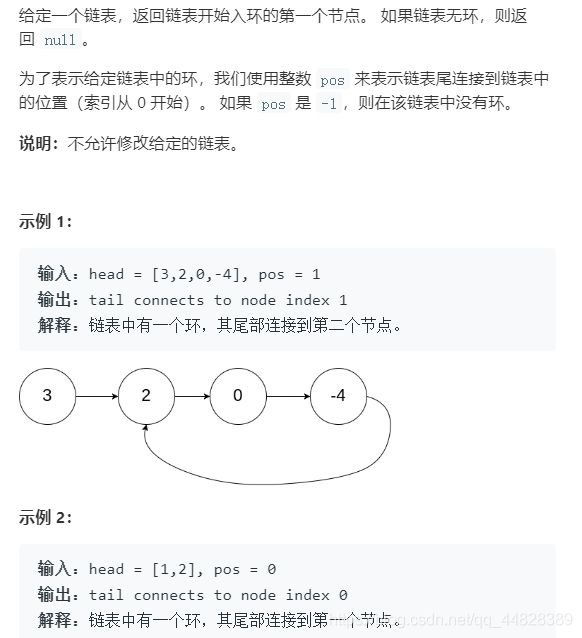
7.求环的入口点
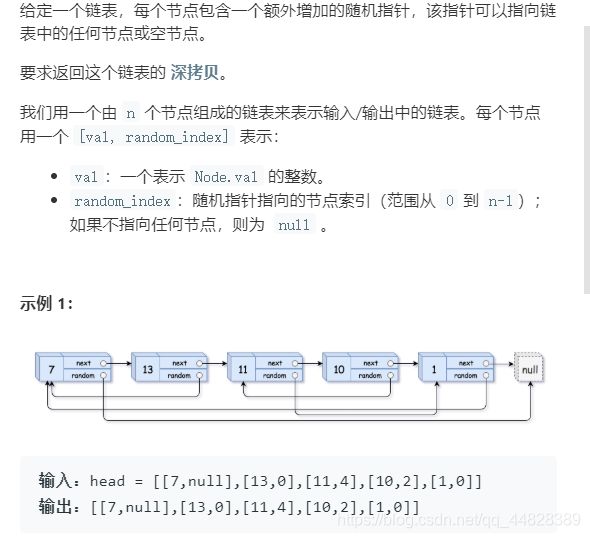
8.复杂链表的复制
一些命名的介绍
cur:当前结点
prev:前继结点
next:后继结点
1-5题单链表的经典例题
6-8题单链表的带环问题
1. 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
题目分析:
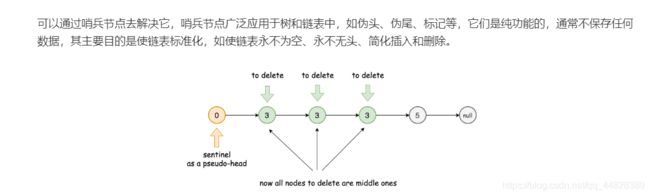
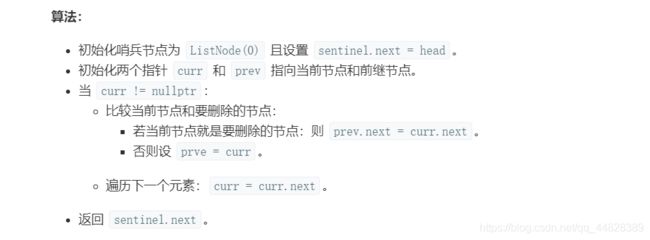
方法一:哨兵结点
本题用的方法是在head前设一个新的结点 给prev head的位置给cur
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
ListNode *sentinel =(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));//开辟一个哨兵结点
sentinel->next = head;//让哨兵结点指向head
ListNode *cur = head; //cur指向head
ListNode *prev = sentinel;//prev指向哨兵结点
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->val == val)//当cur中的值 = 输入的值时 进入循环
{
prev->next = cur->next;//让prev指向next;
}
else
{
prev = cur;//将prev移动到cur的位置
}
cur = cur->next;//cur移动到下一个位置
}
head = sentinel->next ;
free(sentinel);//新开辟的空间最后要free一下 防止内存泄漏
return head;
}
方法二:尾插法
/* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode
{
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* }; */
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* newhead = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
newhead->next = NULL;
ListNode* newtail = newhead;
while(cur)
{ //保存下一个
ListNode* next = cur->next;
if(cur->val == val)
{
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
else
{
newtail->next = cur;
newtail = cur;
newtail->next = NULL;
cur = next;
}
}
ListNode* first = newhead->next;
free(newhead);
return first;
}2.反转单链表
方法一:指针转方向
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode Node;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
{
return head;
}
Node* n1 = head;
Node* n2 = n1->next;
Node* n3 = n2->next;
head->next = NULL;
while(n2 != NULL)
{
//反转
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2 ;
n2 = n3 ;
if(n3 != NULL)
{
n3 = n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
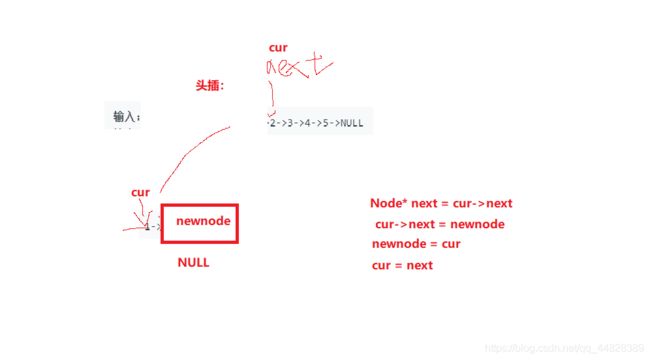
}方法二:头插法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode Node;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
Node* newnode = NULL;
Node* cur = head;
Node* next;
//cur遍历原链表,取结点头插到新链表
while(cur != NULL)
{
next = cur->next;
cur->next = newnode;
newnode = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newnode;
}3.链表的中间结点
方法一:计算链表长度
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
int length = 0;
struct ListNode *cur = head ;
while(tmp! = NULL)
{
length++;
cur=cur->next;
}
length=length/2;
while(length--)
{
head=head->next;
}
return head;
}
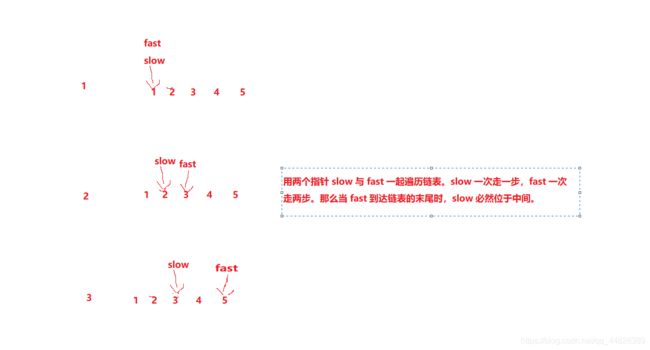
方法二:快慢指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
//快慢指针 只遍历一次
typedef struct ListNode Node;
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
Node* slow = head;
Node* fast = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}4.合并有序单链表
方法:尾插法
/* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* }; */
typedef struct ListNode Node;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2)
{
if( l1 == NULL )
return l2;
else if ( l2 == NULL )
return l1 ;
Node* head = NULL;
Node* tail = NULL;
head = tail = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
while(l1 && l2)//直到一个走到NULL 退出循环
{
//取小的进行尾插
if(l1->val < l2->val )
{
tail->next = l1 ;
tail = tail->next;
l1 = l1->next ;
}
else
{
tail->next = l2 ;
tail = tail->next;
l2 = l2->next ;
}
}
if(l1)
tail->next = l1 ;
else
tail->next = l2 ;
Node* list = head->next ;
free(head);
return list;
}5.链表的分割
6.带环问题(判断链表是否带环)
解题思路:快慢指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode Node;
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
Node* slow = head;
Node* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next )
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast )
return true;
}
return false;
}7.求环的入口点
解题思路:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode Node;
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
Node* slow = head;
Node* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)//判断链表是否带环
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast )//相遇点
{
Node* meet = slow; //相遇点meet
Node* start = head; //让start从头开始走 因为start走到环入口的距离和meet走到环入口的距离相等。
while(meet != start)
{
meet = meet->next;//没相遇继续进行
start = start->next;//没相遇继续进行
}
return meet;
}
}
return NULL;//表示链表不带环
}8.复杂链表的复制
解题思路:
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *next;
* struct TreeNode *random;
* };
*/
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{
Node* cur = head;
while(cur)//1.拷贝链表,并插入到原结点的后面
{
Node* next = cur->next;
Node* copy = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
//插入
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next ;
//迭代往下走
cur = next ;
}
cur = head;//再次让cur指向head
while(cur)//2.通过cur去置copy结点的random
{
Node* copy = cur->next;
if(cur->random != NULL)//置copy结点的random
{
copy->random = cur->random->next;
}
else
{
copy->random = NULL;
}
cur = copy->next;
//3.解拷贝结点 , 链接拷贝结点
Node* copyHead = NULL;//拷贝结点头指针
Node* copyTail = NULL;//拷贝结点尾指针
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* copy = cur->next;
Node* next = cur->next;
//copy解下来尾插
if(copyTail == NULL)//copy的第一个结点
{
copyHead = copyTail = copy;
}
else//后面的结点进行尾插
{
copyTail->next = copy;
copyTail = copy;
}
cur->next = next ;//原链表重新链接起来
cur = next ; //迭代往下走
}
return copyHead;
}
}