耿鸭玩转C#之基础语法
文章目录
- 0. 简介
- 1. Hello,world!
- 2. 数据类型
-
- 2.1 值类型
- 2.2 引用类型
-
- 2.2.1 对象(Object)类型
- 2.2.2 动态(Dynamic)类型
- 2.1.2 字符串类型
- 2.3 指针类型
- 2.4 类型转换
- 3. 运算符
- 4. 变量
- 5. 常量
- 6. 判断和循环
- 7. 面向对象
-
- 7.1 访问修饰符
- 7.2 方法
- 7.3 属性(get/set访问器)
- 7.4 构造方法
- 7.5 析构方法
- 7.6 重载
- 7.7 引用类型参数ref和out
- 7.8 内部类和静态类
- 7.9 继承
- 7.10 多态
- 7.11 运算符重载
- 7.12 接口
- 8. 可空类型
- 9. 数组
-
- 9.1 一维数组
- 9.2 使用foreach遍历数组
- 9.3 多维数组
- 9.4 交错数组
- 9.5 参数数组
- 9.6 Array类
-
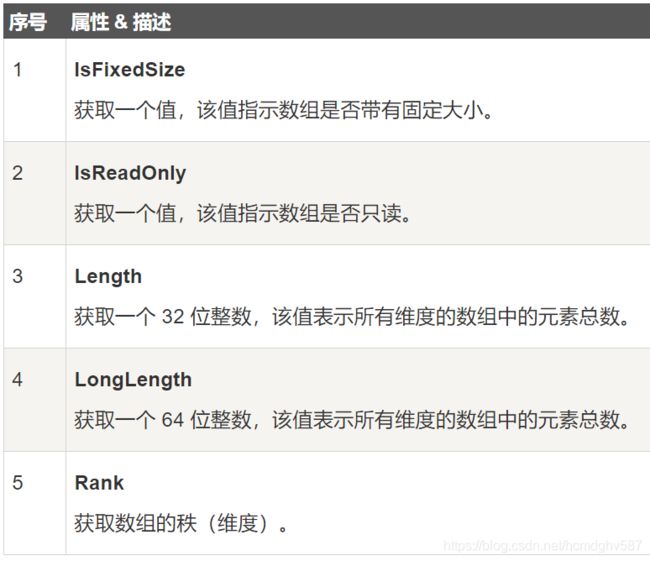
- Array类的常用属性
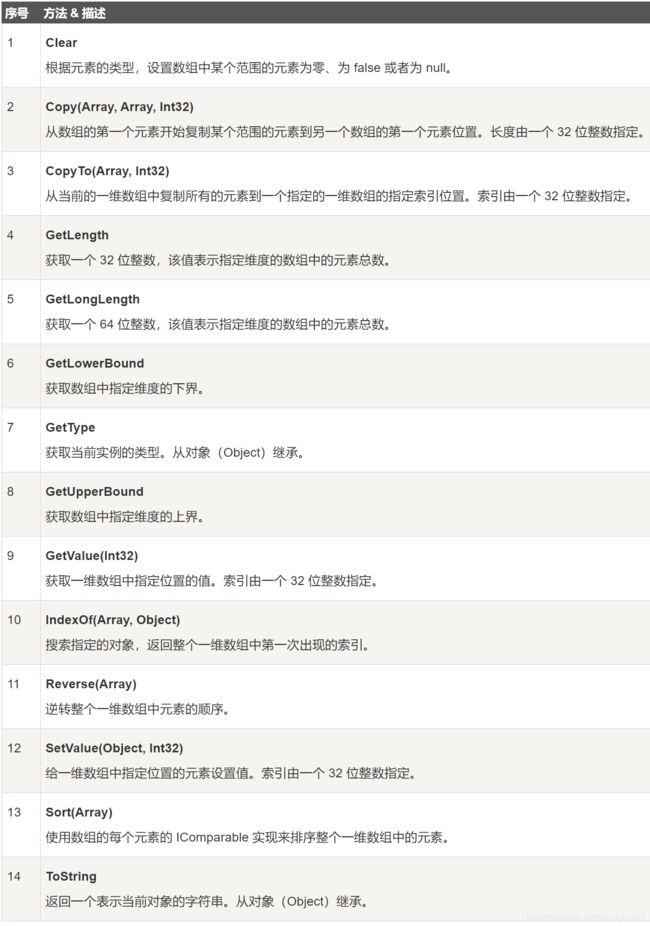
- Array类的常用方法
- 躬行
- 10. 字符串
-
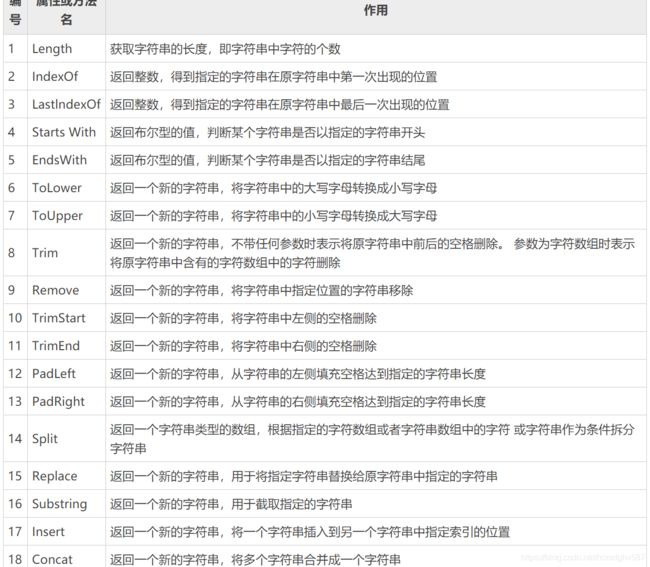
- 10.1 字符串的常用属性和方法
- 10.2 创建字符串的方法
- 11. 结构体
- 12. 枚举型
- 13. 命名空间
-
- 不使用using的示例
- 使用using的示例
- ∞. 常用类库简介
-
- Console类
- Math类
- Random类
- DateTime类
0. 简介
C# 语言是微软推出的一款面向对象的编程语言,凭借其通用的语法和便捷的使用方法受到了很多企业和开发人员的青睐。
C# 语言具备了面向对象语言的特征,即封装、继承、 多态,并且添加了事件和委托,增强了编程的灵活性。
Visual Studio 2015 是专门的一套基于组件的开发工具,主要用于 .NET 平台下的软件开发,C# 语言作为 .NET 平台下的首选编程语言,在该开发工具下可以开发控制台应用程序、Windows 窗体应用程序、ASP.NET 网站程序等。
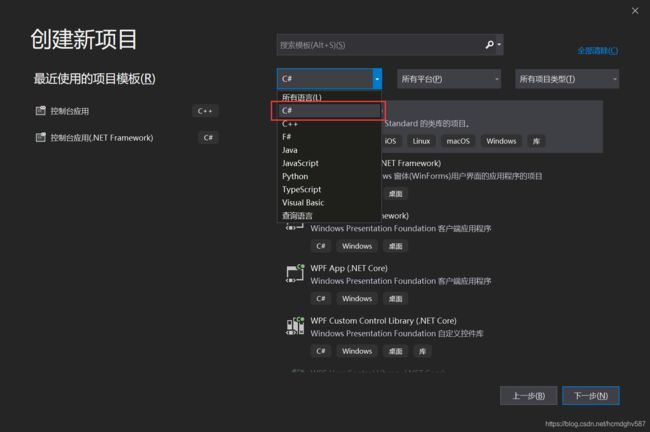
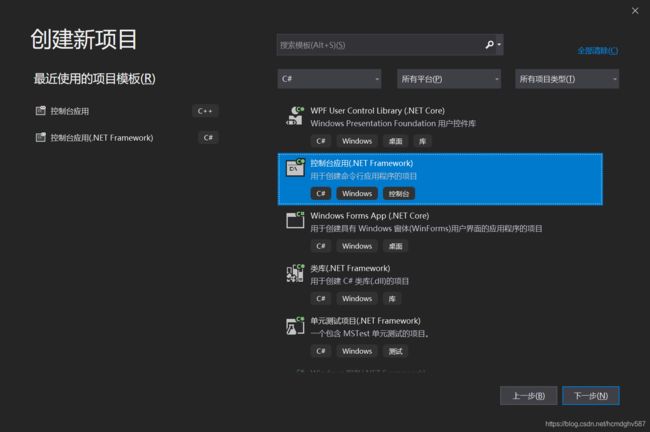
1. Hello,world!
以下步骤演示了如何创建一个C#的Hello world程序:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
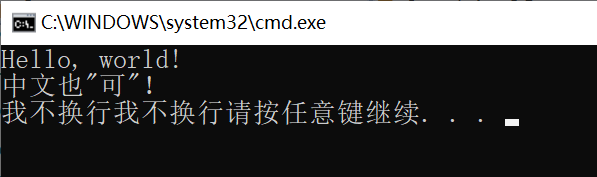
Console.WriteLine("Hello, world!");
Console.WriteLine("中文也\"可\"!");
Console.Write("我不换行");
Console.Write("我不换行");
}
}
}
2. 数据类型
在C#中,变量被分为以下几种类型:
- 值类型
- 引用类型
- 指针类型
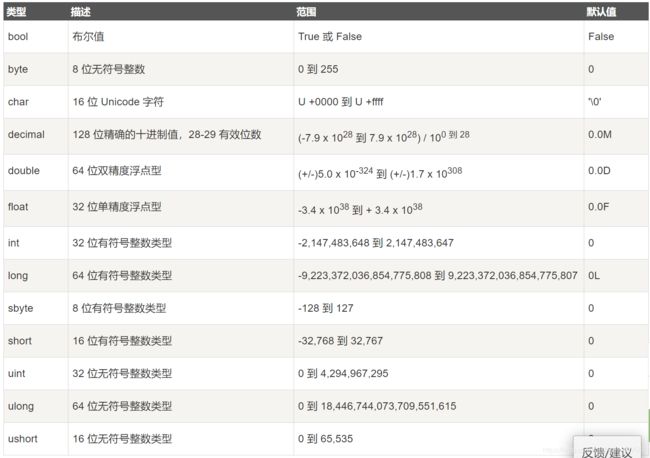
2.1 值类型
下表列出了可用的值类型:
注意三个特殊的——decimal、sbyte、long
如同C++一样,可以使用 sizeof 来获取某个类型的存储尺寸。
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Console.WriteLine("Size of int: {0}", sizeof(int)); // 4
Console.WriteLine("Size of long: {0}", sizeof(long)); // 8
Console.WriteLine("Size of bool: {0}", sizeof(bool)); // 1
}
}
}
2.2 引用类型
引用类型不包含存储在变量中的实际数据,但它们包含对变量的引用。
换句话说,它们指的是一个内存位置。使用多个变量时,引用类型可以指向一个内存位置。如果内存位置的数据是由一个变量改变的,其他变量会自动反映这种值的变化。内置的引用类型有:object、dynamic 和 string。
2.2.1 对象(Object)类型
对象(Object)类型是所有类型的基类。Object 是 System.Object 类的别名。所以对象(Object)类型可以被分配任何其他类型(值类型、引用类型、预定义类型或用户自定义类型)的值。但是,在分配值之前,需要先进行类型转换。
当一个值类型转换为对象类型时,则被称为装箱;另一方面,当一个对象类型转换为值类型时,则被称为拆箱。
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
object obj;
// 装箱
obj = 13;
Console.WriteLine(obj);
// 拆箱
int x = (int)obj;
Console.WriteLine(x);
// 拆箱抛出异常
double y = (double)obj; // System.InvalidCastException
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
}
2.2.2 动态(Dynamic)类型
说白了,动态类型就是把C#当成Python玩。
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
dynamic a = 3;
Console.WriteLine(a);
a = "haha";
Console.WriteLine(a);
a.shit(); // 编译时不报错,执行到这一句时报错
}
}
}
2.1.2 字符串类型
字符型只能存放一个字符,它占用两个字节,能存放一个汉字。C#内部存储为UTF-16编码,即每个字符用两个字节存储。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
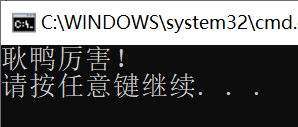
char a = '耿';
char b = '鸭';
string c = "厉害!";
Console.Write(a);
Console.Write(b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
}
}
}
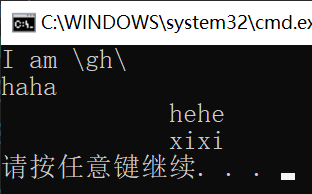
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
string str1 = @"I am \gh\";
string str2 = @"haha
hehe
xixi";
Console.WriteLine(str1);
Console.WriteLine(str2);
}
}
}
2.3 指针类型
指针类型变量存储另一种类型的内存地址。C# 中的指针与 C 或 C++ 中的指针有相同的功能。将在"不安全的代码"中讨论指针类型。
2.4 类型转换
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
int a = 123456;
// 显示类型转换
double b = a;
// 隐式类型转换
int c = (int)b;
// 转换为string
string str = a.ToString();
// string转换回int
int d = int.Parse(str); // 转换失败则抛出System.FormatException
Console.WriteLine(d);
}
}
}
3. 运算符
以下着重介绍sizeof、is、as,其他运算符与Java类似,故省略。
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
// 返回数据类型的大小
int a = sizeof(long);
// 判断对象是否为某一类型
bool b = a is int;
bool c = a is long;
// 强制类型转换
// 如果转换失败,将返回null,而不是异常
object x = 123;
string y = x as string;
Console.WriteLine(y is null);
}
}
}
4. 变量
与Java类似,因此仅给出一个示例:
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
int var1 = 100;
double var2 = 100.123;
bool var3 = true;
String var4 = "耿鸭";
Console.WriteLine("var1 = " + var1);
Console.WriteLine("var2 = " + var2);
Console.WriteLine("var3 = " + var3);
Console.WriteLine("var4 = " + var4);
}
}
}
5. 常量
常量使用关键词const定义:
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
const double PI = 3.14;
Console.WriteLine(PI);
}
}
}
注意:const在编译时确定值,因此不能引用变量,如以下写法是错误的:
int a = 3;
const int b = a + 1;
对于**@加在字符串常量之前**,可参见2.1.2节。
6. 判断和循环
if、switch、for、while、do-while、break、continue与Java完全相同,故不加赘述。
7. 面向对象
面向对象语言的三大特征分别是封装、继承、多态。(而不是wyh说的那些个orz)
7.1 访问修饰符
类的访问修饰符主要有两个:public和internal(可省略)
类中成员的访问修饰符有四个:
- public
成员可以被任何代码访问。 - private
成员仅能被同一个类中的代码访问,如果在类成员前未使用任何访问修饰符,则默认为private。 - internal
成员仅能被同一个项目中的代码访问。 - protected
成员只能由类或派生类中的代码访问。派生类是在继承中涉及的。
除此之外,还有修饰符:
- readonly:使用 readonly 修饰字段意味着只能读取该字段的值而不能给字段赋值,只能在声明或构造函数中初始化。
- static:使用 static 修饰的字段是静态字段,可以直接通过类名访问该字段。
以下给出一个示例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Student {
string name;
public readonly int age = 21;
public bool sex;
public static int haha = 24;
static int hehe = 13;
}
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Student stu = new Student();
/* 以下打了注释的行均会报错 */
// stu.name = "";
// stu.age = 21;
Console.WriteLine(stu.age);
// Console.WriteLine(Student.hehe);
Console.WriteLine(Student.haha);
}
}
}
7.2 方法
属性的命名规则为Pascal命名法,即单词首字母大写。(示例中忘了这一点orz)
方法的定义与Java类似,以下给出一个示例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Student {
string name;
int age = 21;
public void setName(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
public string getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Student stu = new Student();
Console.WriteLine(stu.getAge());
stu.setName("鸭鸭");
Console.WriteLine(stu.getName());
// Console.WriteLine(stu.name);
}
}
}
7.3 属性(get/set访问器)
属性的命名规则为Pascal命名法,即单词首字母大写。
get访问器和set访问器指定了读取和修改属性时的行为。两者省略哪一个都行。
以下给出一个示例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Student {
string name;
bool sex;
public string Name {
get {
return name;
}
set {
name = value;
}
}
public int Age {
get {
return 22;
}
}
public bool Sex {
set {
sex = value;
}
}
}
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Student stu = new Student();
/* 以下打了注释的行均会报错 */
stu.Name = "耿耿";
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
// stu.Age = 22;
Console.WriteLine(stu.Age);
stu.Sex = true;
// Console.WriteLine(stu.Sex);
}
}
}
如果是只读属性,还可以采用以下快速写法:
class Student {
public string Name {
get; } = "耿耿";
}
7.4 构造方法
与Java基本相同,见以下示例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Student {
public string name;
public int age;
public Student(string name) : this(name, 20) {
}
public Student(string name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Student stu = new Student("耿耿", 20);
Student stu2 = new Student("犇犇~");
}
}
}
7.5 析构方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Student {
public string name;
public int age;
public Student(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
~Student() {
Console.WriteLine(name + ",我人没了~");
}
}
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Student stu = new Student("耿鸭");
{
// 从结果看这个大括号没什么影响orz
Student stu2 = new Student("哥哥");
}
Student stu3 = new Student("犇犇");
}
}
}
7.6 重载
懒得讲了orz。
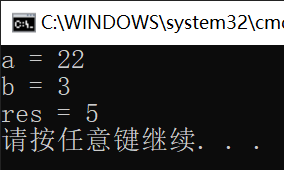
7.7 引用类型参数ref和out
总体来说,ref和out差别不大,都表示引用传递。但是out的变量可以不赋初始值,而ref一定要赋初始值。
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void swap(ref int a, ref int b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
static void calc(out int res) {
res = 5;
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
int a = 3, b = 22;
swap(ref a, ref b);
Console.WriteLine("a = " + a);
Console.WriteLine("b = " + b);
int res;
calc(out res);
Console.WriteLine("res = " + res);
}
}
}
7.8 内部类和静态类
静态类是不能实例化的类,其中只能有静态成员。
内部类相当于类中的成员。
注意,内部类与外部类没什么关系,只是挂一个名字而已。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class OuterClass {
public class Student {
public string name;
public int age;
}
public static class Teacher {
public static string name;
}
}
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
OuterClass.Student stu = new OuterClass.Student();
stu.age = 20;
// OuterClass.Teacher t = new OuterClass.Teacher();
OuterClass.Teacher.name = "haha";
}
}
}
7.9 继承
与Java一样,C#不支持多重继承,但是可以实现多个接口。
此外,以下示例还演示了调用父类的构造方法。
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Person {
public string name;
public void Introduce() {
Console.WriteLine("你好,我是{0}", name);
}
public Person() {
}
public Person(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
class Student : Person {
public void SayHello() {
Console.WriteLine("我是学生{0}", name);
}
}
interface ILearner {
void Learn();
}
// 不能继承多个类
// class Teacher : Person, Student { }
// 可以继承一个类和实现多个接口
class Teacher : Person, ILearner {
public void Learn() {
Console.WriteLine("我是{0},我爱学习!", name);
}
// 调用父类的构造方法(base)
public Teacher(string name) : base(name) {
}
}
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Student stu = new Student();
stu.name = "耿鸭";
stu.Introduce();
stu.SayHello();
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("耿老师");
teacher.Learn();
}
}
}
7.10 多态
实现多态要确保以下两点,缺一不可:
- 父类定义虚方法
- 子类重写父类的方法
示例:
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Person {
public string name;
public Person(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 父类定义虚方法
public virtual void Introduce() {
Console.WriteLine("你好,我是{0}", name);
}
}
class Student : Person {
public Student(string name) : base(name) {
}
// 子类重写父类的方法
public override void Introduce() {
Console.WriteLine("你好,我是学生{0}", name);
// 调用父类的方法
base.Introduce();
}
}
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Student stu = new Student("耿鸭");
stu.Introduce();
Person stu2 = new Student("菜鸭");
stu2.Introduce();
}
}
}
7.11 运算符重载
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class MyString {
public string str;
public MyString(string str) {
this.str = str;
}
public static MyString operator *(MyString s, int times) {
string res = "";
while (times-- > 0) {
res += s.str;
}
return new MyString(res);
}
}
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
MyString s1 = new MyString("耿鸭~");
MyString s2 = s1 * 3;
Console.WriteLine(s2.str);
// MyString s3 = 3 * s1;
// *= 运算符自动调用重载后的 * 方法
s1 *= 4;
Console.WriteLine(s1.str);
}
}
}
7.12 接口
C#中的接口与Java类似,故不加赘述。需要特别说明的是接口的命名规范是以“I”字母打头。
8. 可空类型
对于int、double、bool这些类型,无法赋值为null,而可空类型使得这一操作得以实现。
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
string str = null; // √
// int a = null; // ×
int? a = null;
Console.WriteLine(a); // nothing
Console.WriteLine(a == null); // True
a += 2;
Console.WriteLine(a == null); // True
// ??运算符将null替代为默认值
int? b = 123;
int aa = a ?? 1;
int bb = b ?? 1;
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", aa, bb); // 1, 123
}
}
}
9. 数组
9.1 一维数组
与Java中的一维数组的使用类似,下面给出创建并初始化数组的三种方法:
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
// 方法一
int[] arr = new int[3];
Console.WriteLine(arr[0]); // 0
Console.WriteLine(arr[1]); // 0
Console.WriteLine(arr[2]); // 0
arr[0] = arr[1] = arr[2] = 999;
// Console.WriteLine(arr[3]); // System.IndexOutOfRangeException
// 方法二
int[] arr2 = {
2, 3, 5, 7 };
Console.WriteLine(arr2.Length); // 4
// 方法三
int[] arr3;
arr3 = new int[] {
2, 3, 4, 8 };
Console.WriteLine(arr3.Length); // 4
}
}
}
9.2 使用foreach遍历数组
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; ++i) {
arr[i] = 10 + i;
}
foreach (int val in arr) {
Console.WriteLine(val);
}
}
}
}
9.3 多维数组
多维数组是与Java中的多维数组不同的。
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
// 初始化
int[,] arr = {
{
2, 3, 5 },
{
7, 11, 13 },
};
Console.WriteLine(arr.Length); // 6
Console.WriteLine(arr.GetLength(0)); // 2
Console.WriteLine(arr.GetLength(1)); // 3
// 下标索引
arr[0, 1]++;
// 遍历每个元素
foreach (int val in arr) {
Console.WriteLine(val); // 2 4 5 7 11 13
}
}
}
}
9.4 交错数组
和Java中的数组使用方法类似,即数组的数组。
9.5 参数数组
有时,当声明一个方法时,您不能确定要传递给函数作为参数的参数数目。C# 参数数组解决了这个问题,参数数组通常用于传递未知数量的参数给函数。
注意,数组形参前要加上 params 关键字。
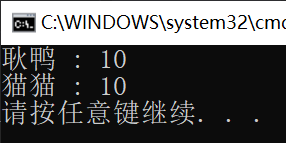
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Sum(string name, params int[] arr) {
int res = 0;
foreach (int val in arr) {
res += val;
}
Console.WriteLine("{0} : {1}", name, res);
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
int[] arr = {
1, 2, 3, 4 };
Sum("耿鸭", arr);
Sum("猫猫", 1, 2, 3, 4);
}
}
}
9.6 Array类
Array 类是 C# 中所有数组的基类,它是在 System 命名空间中定义。Array 类提供了各种用于数组的属性和方法。
Array类的常用属性
Array类的常用方法
躬行
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
int[] arr = {
1, 4, 2, 8, 5, 7 };
// 逆序
Array.Reverse(arr);
foreach (int val in arr) {
Console.WriteLine(val); // 7 5 8 2 4 1
}
// 搜索
int idx = Array.IndexOf(arr, 8);
Console.WriteLine(idx); // 2
idx = Array.IndexOf(arr, 9);
Console.WriteLine(idx); // -1
// 排序
Array.Sort(arr);
foreach (int val in arr) {
Console.WriteLine(val); // 1 2 4 5 7 8
}
}
}
}
10. 字符串
10.1 字符串的常用属性和方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
string str = "abcd";
// 下标索引
char ch = str[2];
Console.WriteLine(ch);
// 获取长度
str = "耿鸭100分";
int len = str.Length;
Console.WriteLine(len);
// 删除空白字符
str = " \t 归真返璞 \t\t\n";
Console.WriteLine(str);
string res = str.Trim();
Console.WriteLine(res);
// 分割字符串
str = "你好 我叫\t耿耿";
string[] arr = str.Split();
Console.WriteLine(arr.Length);
// 转换为char数组
str = "abc地以负";
char[] charr = str.ToCharArray();
foreach(char c in charr) {
Console.WriteLine(c);
}
}
}
}
10.2 创建字符串的方法
有以下四种创建字符串的方法,其中字符串格式化名堂较多,暂不深究。
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
// 1. 字符串拼接
string str1 = "ab" + "cd" + 12 + 34;
Console.WriteLine(str1); // abcd1234
// 2. 通过char数组
char[] chs = {
'你', '是', '笨', '笨' };
string str2 = new string(chs);
Console.WriteLine(str2.Length); // 4
Console.WriteLine(str2); // 你是笨笨
// 3. Join方法
string[] arr = {
"我是", "耿耿", "爱", "鸭鸭" };
string str3 = String.Join(" ", arr);
Console.WriteLine(str3); // 我是 耿耿 爱 鸭鸭
// 4. 字符串格式化
string str4 = String.Format("I am {0}, my age is {1}.", "耿耿", 21);
Console.WriteLine(str4);
}
}
}
11. 结构体
C#中的结构体具有以下几个特点:
- 结构体是值类型而不是引用类型
- 创建结构体变量可以不使用new,此时需要手动初始化每个字段后才能访问成员
- 结构可定义构造函数,但不能定义析构函数。但是,您不能为结构定义无参构造函数。无参构造函数(默认)是自动定义的,且不能被改变。
- 结构体中声明的字段不能赋初值
- 构造函数中必须为所有字段赋值
示例:
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
struct Student {
// 3. 结构体中声明的字段不能赋初值
public string name;
// public int age = 0;
public int age;
public bool sex;
// 4. 构造函数中必须为所有字段赋值
public Student(int x) {
name = null;
age = 0;
sex = false;
}
public void init() {
name = "猫猫";
age = 21;
sex = true;
}
public void introduce() {
Console.WriteLine("大家好,我是{0},我{1}岁了!", name, age);
}
}
class Program {
static void fake(Student stu) {
stu.name = "哈哈";
stu.age = -1;
}
static void real(ref Student stu) {
stu.name = "哈哈";
stu.age = -1;
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
// 1. 两种创建结构体变量的方法
// 1.1 通过new操作符,此时每个字段被初始化为0
Student stu = new Student();
stu.introduce(); // 全是零值
stu.init();
stu.introduce();
// 1.2 不使用new操作符,此时需要手动初始化每个字段后才能访问成员
Student stu2;
// stu2.introduce(); // 报错,因为字段未初始化
stu2.name = "耿鸭";
stu2.age = 0;
stu2.sex = false;
stu2.introduce();
// 2. 结构体是值类型而不是引用类型
fake(stu2);
stu2.introduce(); // 没有改变
real(ref stu2);
stu2.introduce(); // 改变了
}
}
}
12. 枚举型
枚举是一组命名整型常量。枚举类型是使用 enum 关键字声明的。C# 中枚举是值类型。
以下给出一个示例:
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
enum Day {
Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Webnesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday,
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
// 1. 枚举变量的使用
Day day = Day.Monday;
Console.WriteLine(day); // Monday
// 2. 枚举变量转int
// 下标默认从0开始
int d = (int)day;
Console.WriteLine(d); // 1
}
}
}
13. 命名空间
为了访问命名空间,使用“.”操作符。
使用 using 关键字引入命名空间,也可以起别名。
不使用using的示例
using System;
namespace space1 {
namespace space2 {
class Student {
}
}
}
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
space1.space2.Student stu = new space1.space2.Student();
}
}
}
使用using的示例
using System;
using space1;
using haha = space1.space2;
namespace space1 {
class Teacher {
}
namespace space2 {
class Student {
}
}
}
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Teacher t = new Teacher();
haha.Student s1 = new haha.Student();
}
}
}
∞. 常用类库简介
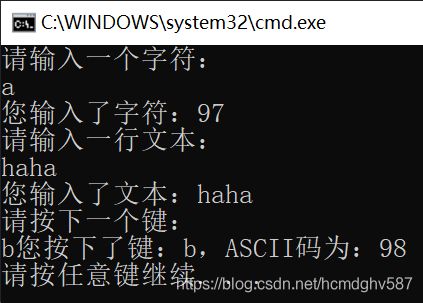
Console类
C# Console 类主要用于控制台应用程序的输入和输岀操作。
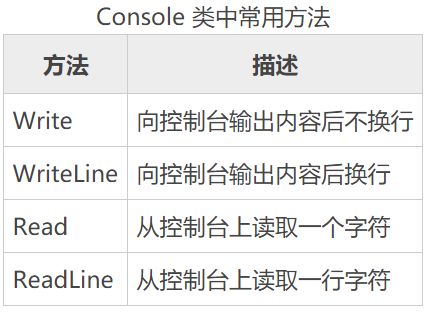
除此之外,还有ReadKey()方法读取一次键盘敲击。Write方法可以格式化输出。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Console.WriteLine("请输入一个字符:");
int ch = Console.Read();
Console.Read(); // 吸收换行符
Console.Read();
Console.WriteLine("您输入了字符:{0}", ch);
Console.WriteLine("请输入一行文本:");
string line = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("您输入了文本:{0}", line);
Console.WriteLine("请按下一个键:");
ConsoleKeyInfo consoleKeyInfo = Console.ReadKey();
char key = consoleKeyInfo.KeyChar;
Console.WriteLine("您按下了键:{0},ASCII码为:{1}", key, (int)key);
}
}
}
Math类
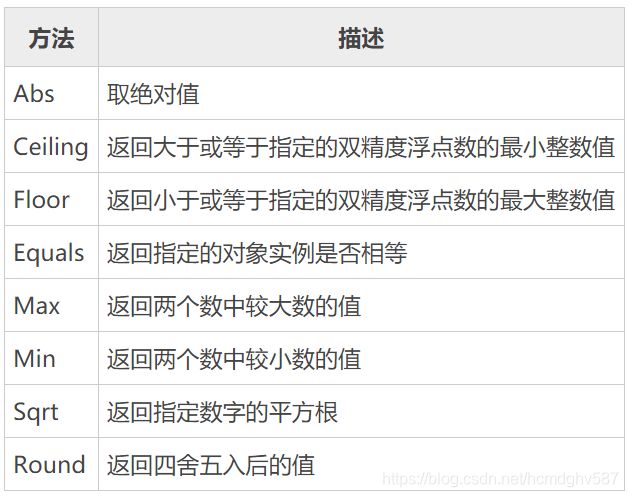
C# Math 类主要用于一些与数学相关的计算,并提供了很多静态方法方便访问,常用的方法如下表所示。
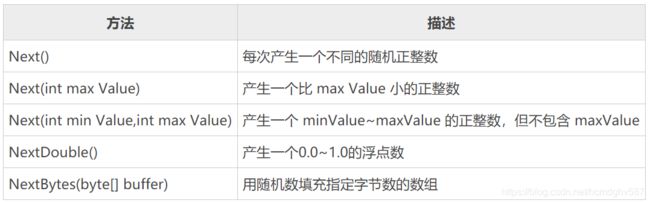
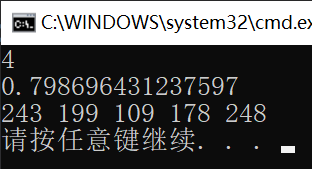
Random类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Random rd = new Random();
// 产生[1, 10)之间的随机整数
Console.WriteLine(rd.Next(1, 10));
// 产生[0, 1)之间的随机浮点数
Console.WriteLine(rd.NextDouble());
// 随机填充字节数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[5];
rd.NextBytes(bytes);
foreach (byte b in bytes) {
Console.Write(b + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
DateTime类
不想搞了,等用到了再说粑。