android基础篇------------java基础(11)(文件解析xml and Json )
一:xml文件解析
首先看一下:我们要解析的内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="gbk" ?> - <bookstore> - <book id="1"> <title tid="1">Harry Potter</title> <author>J K Rowling</author> <year>2005</year> <price>29.99</price> </book> - <book id="2"> <title tid="2">Harry Potter</title> <author>J K Rowling</author> <year>2006</year> <price>39.99</price> </book> - <book id="3"> <title tid="1">明朝那些事儿</title> <author>当年明月</author> <year>2009</year> <price>19.99</price> </book> </bookstore>
我们看一下:我们的DOM结构图:
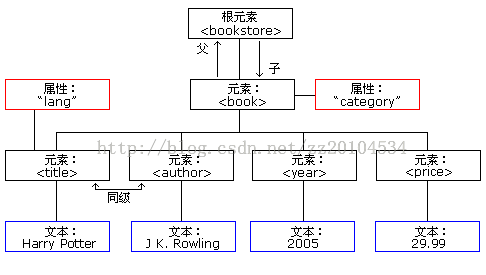
通过上面的图:我们首先了解了一个book.xml中各个结点都叫什么,但是,值得注意的是:
<book id="1">
中的id是:属性结点。
那么解析的过程是这样的。
public class TestDOMBook {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、得到DOM解析器的工厂实例
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
try {
// 2、从DOM工厂获得DOM解析器
DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
// 3、解析XML文档,得到一个Document,即DOM树
Document doc = db.parse("e:/book.xml");
// 4、得到所有book节点列表信息
NodeList petList = doc.getElementsByTagName("book");
// 5、轮循书本信息
System.out.println("XML文件中book的初始化信息:");
for (int i = 0; i < petList.getLength(); i++) {
// 得到book元素
Element book = (Element) petList.item(i);
// 得到book元素下的id属性的值
String strId = book.getAttributeNode("id").getNodeValue();
System.out.println("ID:" + strId);
// 得到book下的title子元素节点下的子文本节点的值
String strTitle = book.getElementsByTagName("title").item(0)
.getFirstChild().getNodeValue();
// 得到book下的title子元素节点
Element title = (Element) book.getElementsByTagName("title")
.item(0);
// 得到title元素节点的tid属性节点的值
String strTid = title.getAttributeNode("tid").getNodeValue();
String strAuthor = book.getElementsByTagName("author").item(0)
.getFirstChild().getNodeValue();
String strYear = book.getElementsByTagName("year").item(0)
.getFirstChild().getNodeValue();
String strPrice = book.getElementsByTagName("price").item(0)
.getFirstChild().getNodeValue();
System.out.println("标题:" + strTitle);
System.out.println("标题ID:" + strTid);
System.out.println("作者:" + strAuthor);
System.out.println("出版日期:" + strYear);
System.out.println("价格:" + strPrice);
}
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
二.Json数据解析
Example 1:
我们要解析一下一段键值对。
/***
* {
* "weatherinfo":
*
* {"city":"北京",
* "cityid":"101010100",
* ,
* "WD":"西南风",
* "WS":"1级","SD":"93%",
* "WSE":"1","time":"08:45",
* "isRadar":"1",
* "Radar":"JC_RADAR_AZ9010_JB"}
* }
*
*/
注意:我们要用到一个org.json.jar包:
解析的过程是:
public static String setInit() throws JSONException {
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
JSONObject js = new JSONObject();
js.put("city", "北京");
js.put("temp", "26");
js.put("WD", "西南风");
json.put("weatherinfo", js);
return json.toString();
}
public static void getInit(String str) throws JSONException {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(str);
JSONObject js = jsonObject.getJSONObject("weatherinfo");
String a = js.getString("city");
int b = js.getInt("temp");
String c = js.getString("WD");
System.out.println(a + b + c);
}
测试代码:北京26西南风
Example 2:
升华一下:看看我们如何动态获取天气文本信息:
String urlstr = "http://www.weather.com.cn/data/sk/101010100.html";
try {
URL url = new URL(urlstr); //URL 统一资源定位符
HttpURLConnection huc = (HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();
huc.setRequestMethod("GET");
InputStreamReader is = new InputStreamReader(huc.getInputStream(),"UTF-8");
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(is);
String mString = "";
String m = "";
while ((m = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null) {
mString+=m;
}
System.out.println(mString);
getInit(mString);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}