配置 Spring.NET
作为一个容器,当然首先要存在一个容器对象了。Spring.NET 中的容器定义在程序集
Spring.Core 中,直接添加这个程序集的引用就可以开始使用了。这个程序集位于
Spring.NET-1.3.1\Spring.NET\bin\net\4.0\release 中。
一、编程方式的容器
在 Spring.NET 中,对于通过编程方式使用容器的环境,提供了
Spring.Context.Support.StaticApplicationContext,我们可以直接创建这个容器,并加入一些配置。
在下面的例子中,我们定义了基类 Person,然后定义了 Person 的派生类 Student,
public class Person
{
public string Name { set; get; }
public override string ToString()
{
return "This is Person.";
}
}
public class Student
:Person
{
public string School { set; get; }
public override string ToString()
{
return "This is Student.";
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建容器
Spring.Context.Support.StaticApplicationContext context
= new Spring.Context.Support.StaticApplicationContext();
// 注册
context.RegisterPrototype("Person", typeof(Student), null);
// 注册一个单例类型
context.RegisterSingleton("Alice", typeof(Person), null);
Person person = context.GetObject("Person") as Person;
Console.WriteLine(person);
}
}
二、Xml 方式容器
在开发中,我们通常通过 XML 配置文件来完成配置。Spring.NET 提供了
Spring.Context.Support.XmlApplicationContext,此时,对象的配置信息写在一个 xml 的配置文件中,当然了,这个配置文件有特定的格式,这些规定以 Xml Schema 的形式保存在
Spring.NET\doc\schema 文件夹的
spring-objects-1.3.xsd 中。
对于上面的例子,我们可以编写如下的配置文件 objects.xml。
<?
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"
?>
<
objects
xmlns
="http://www.springframework.net"
>
<
object
id
="Person"
type
="Student"
></
object
>
<
object
id
="Alice"
type
="Person"
></
object
>
</
objects
>
然后,在代码中,就可以直接使用容器了。
Spring.Context.Support.XmlApplicationContext context
= new Spring.Context.Support.XmlApplicationContext("objects.xml");
Person person = context.GetObject("Person") as Person;
Console.WriteLine(person);
如果你觉得这还是比较麻烦的话,还可以在程序启动的时候直接加载配置信息。
三、通过应用程序配置文件来自动加载 Spring.NET 配置
Spring.NET 提供了
Spring.Context.Support.ContextHandler,帮助我们直接在启动程序的时候加载配置信息。
实际的配置文件通过 spring 元素中 context 元素下的 resource 指定,文件的话使用
file:// 协议描述,还可以使用其它的协议。例如嵌入在程序集中的配置文件可以使用
assembly:// , 直接写在配置文件中则为 config://。
<?
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"
?>
<
configuration
>
<
configSections
>
<
sectionGroup
name
="spring"
>
<
section
name
="context"
type
="Spring.Context.Support.ContextHandler, Spring.Core"
/>
</
sectionGroup
>
</
configSections
>
<
spring
>
<
context
>
<
resource
uri
="file://objects.xml"
/>
</
context
>
</
spring
>
</
configuration
>
在程序中就可以直接使用了。
Spring.Context.IApplicationContext context
= Spring.Context.Support.ContextRegistry.GetContext();
Person person = context.GetObject("Person") as Person;
Console.WriteLine(person);
四、将所有的配置信息都保存在应用程序配置文件中
还可以不再使用另外的 Spring 配置文件,而是将所有的配置信息都保存在应用程序配置文件中。
这需要使用一个新的配置处理器
Spring.Context.Support.DefaultSectionHandler,它可以帮助我们解析 spring 配置信息。
此时的配置文件成为如下的形式,注意,现在的 resource 中使用
config:// 表示使用配置文件中的信息。
<?
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"
?>
<
configuration
>
<
configSections
>
<
sectionGroup
name
="spring"
>
<
section
name
="context"
type
="Spring.Context.Support.ContextHandler, Spring.Core"
/>
<
section
name
="objects"
type
="Spring.Context.Support.DefaultSectionHandler, Spring.Core"
/>
</
sectionGroup
>
</
configSections
>
<
spring
>
<
context
>
<
resource
uri
="config://spring/objects"
/>
</
context
>
<
objects
>
<
object
id
="Person"
type
="Student"
></
object
>
<
object
id
="Alice"
type
="Person"
></
object
>
</
objects
>
</
spring
>
</
configuration
>
主程序与第三种情况是一样的。
五、混合使用外部配置文件和嵌入的配置
甚至还可以混合使用外部配置文件和嵌入的配置信息。
<?
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"
?>
<
configuration
>
<
configSections
>
<
sectionGroup
name
="spring"
>
<
section
name
="context"
type
="Spring.Context.Support.ContextHandler, Spring.Core"
/>
<
section
name
="objects"
type
="Spring.Context.Support.DefaultSectionHandler, Spring.Core"
/>
</
sectionGroup
>
</
configSections
>
<
spring
>
<
context
>
<
resource
uri
="file://objects.xml"
/>
<
resource
uri
="config://spring/objects"
/>
</
context
>
<
objects
>
<
object
id
="Alice"
type
="Person"
></
object
>
</
objects
>
</
spring
>
</
configuration
>
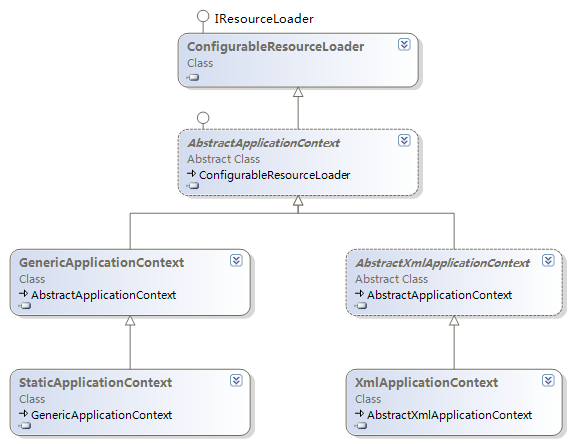
下面是两种常用容器的类图。