POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors (LCA,dfs+ST在线算法)
Nearest Common Ancestors
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 14902 | Accepted: 7963 |
Description
A rooted tree is a well-known data structure in computer science and engineering. An example is shown below:
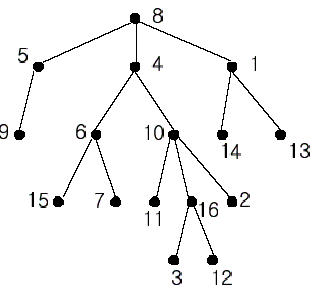
In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.

In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T) is given in the first line of the input file. Each test case starts with a line containing an integer N , the number of nodes in a tree, 2<=N<=10,000. The nodes are labeled with integers 1, 2,..., N. Each of the next N -1 lines contains a pair of integers that represent an edge --the first integer is the parent node of the second integer. Note that a tree with N nodes has exactly N - 1 edges. The last line of each test case contains two distinct integers whose nearest common ancestor is to be computed.
Output
Print exactly one line for each test case. The line should contain the integer that is the nearest common ancestor.
Sample Input
2 16 1 14 8 5 10 16 5 9 4 6 8 4 4 10 1 13 6 15 10 11 6 7 10 2 16 3 8 1 16 12 16 7 5 2 3 3 4 3 1 1 5 3 5
Sample Output
4 3
1 /* *********************************************** 2 Author :kuangbin 3 Created Time :2013-9-5 0:09:55 4 File Name :F:\2013ACM练习\专题学习\LCA\POJ1330.cpp 5 ************************************************ */ 6 7 #include <stdio.h> 8 #include <string.h> 9 #include <iostream> 10 #include <algorithm> 11 #include <vector> 12 #include <queue> 13 #include <set> 14 #include <map> 15 #include <string> 16 #include <math.h> 17 #include <stdlib.h> 18 #include <time.h> 19 using namespace std; 20 /* 21 * LCA (POJ 1330) 22 * 在线算法 DFS + ST 23 */ 24 const int MAXN = 10010; 25 int rmq[2*MAXN];//rmq数组,就是欧拉序列对应的深度序列 26 struct ST 27 { 28 int mm[2*MAXN]; 29 int dp[2*MAXN][20];//最小值对应的下标 30 void init(int n) 31 { 32 mm[0] = -1; 33 for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) 34 { 35 mm[i] = ((i&(i-1)) == 0)?mm[i-1]+1:mm[i-1]; 36 dp[i][0] = i; 37 } 38 for(int j = 1; j <= mm[n];j++) 39 for(int i = 1; i + (1<<j) - 1 <= n; i++) 40 dp[i][j] = rmq[dp[i][j-1]] < rmq[dp[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]]?dp[i][j-1]:dp[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]; 41 } 42 int query(int a,int b)//查询[a,b]之间最小值的下标 43 { 44 if(a > b)swap(a,b); 45 int k = mm[b-a+1]; 46 return rmq[dp[a][k]] <= rmq[dp[b-(1<<k)+1][k]]?dp[a][k]:dp[b-(1<<k)+1][k]; 47 } 48 }; 49 //边的结构体定义 50 struct Edge 51 { 52 int to,next; 53 }; 54 Edge edge[MAXN*2]; 55 int tot,head[MAXN]; 56 57 int F[MAXN*2];//欧拉序列,就是dfs遍历的顺序,长度为2*n-1,下标从1开始 58 int P[MAXN];//P[i]表示点i在F中第一次出现的位置 59 int cnt; 60 61 ST st; 62 void init() 63 { 64 tot = 0; 65 memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); 66 } 67 void addedge(int u,int v)//加边,无向边需要加两次 68 { 69 edge[tot].to = v; 70 edge[tot].next = head[u]; 71 head[u] = tot++; 72 } 73 void dfs(int u,int pre,int dep) 74 { 75 F[++cnt] = u; 76 rmq[cnt] = dep; 77 P[u] = cnt; 78 for(int i = head[u];i != -1;i = edge[i].next) 79 { 80 int v = edge[i].to; 81 if(v == pre)continue; 82 dfs(v,u,dep+1); 83 F[++cnt] = u; 84 rmq[cnt] = dep; 85 } 86 } 87 void LCA_init(int root,int node_num)//查询LCA前的初始化 88 { 89 cnt = 0; 90 dfs(root,root,0); 91 st.init(2*node_num-1); 92 } 93 int query_lca(int u,int v)//查询u,v的lca编号 94 { 95 return F[st.query(P[u],P[v])]; 96 } 97 bool flag[MAXN]; 98 int main() 99 { 100 //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); 101 //freopen("out.txt","w",stdout); 102 int T; 103 int N; 104 int u,v; 105 scanf("%d",&T); 106 while(T--) 107 { 108 scanf("%d",&N); 109 init(); 110 memset(flag,false,sizeof(flag)); 111 for(int i = 1; i < N;i++) 112 { 113 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); 114 addedge(u,v); 115 addedge(v,u); 116 flag[v] = true; 117 } 118 int root; 119 for(int i = 1; i <= N;i++) 120 if(!flag[i]) 121 { 122 root = i; 123 break; 124 } 125 LCA_init(root,N); 126 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); 127 printf("%d\n",query_lca(u,v)); 128 } 129 return 0; 130 }