怎么实现huffman(哈夫曼编码)以及解码
【题目描述】
给定一篇用于通信的英文电文,统计该电文中每个字符出现的频率,按频率左小右大的方法为这些字符建立哈夫曼(Huffamn)树,并编出每个字符的哈夫曼树码,输出该电文的哈夫曼码译文。
【输入】
输入文件huffman.in是一篇用于通信的英文电文。
【输出】
输出文件huffman.out输出该电文的哈夫曼码译文。
【输入输出样例1】
| huffman.in |
huffman.out |
| aaccdddbacbcddddddd |
011011000011101001100010001111111 |
【数据限制】
2<=英文电文字符数<=10000000
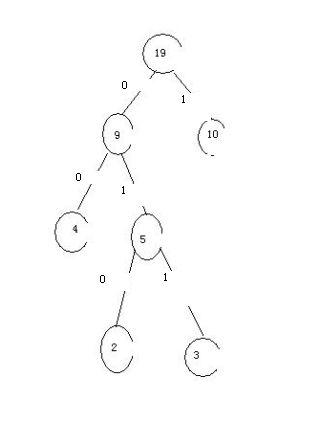
统计以上abcd出现的个数。
a:3 b:2 c:4 d:10
构造出哈夫曼树
a:011 b:010 c :00 d:1
下面主要通过两个结构体数组来实现:
struct node1
{ int w, lch, rch, parent;
}ht[2*N0-1+1];
| 数组下标 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 父节点的数组下标parent | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 左孩子节点的数组下标lch | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 右孩子节点的数组下标rch | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 权值w | 3 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
-》
| 数组下标 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 父节点的数组下标parent | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 左孩子节点的数组下标lch | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||
| 右孩子节点的数组下标rch | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 权值w | 3 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 5 |
-》.。。。。。。。。
| 数组下标 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 父节点的数组下标parent | 5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 0 |
| 左孩子节点的数组下标lch | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 6 |
| 右孩子节点的数组下标rch | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 权值w | 3 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 5 | 9 | 19 |
struct node2
{ char ch;//对应的字符abcd
int start;//编码的起始位置 注意这个编码是倒着的 所以这里用start
int code[N0];//这个是编码数组
}hc[N0+1];
大概图如下面
美工不好啊 大概将就看了啊
下面给出大家想要的程序部分
//#include "stdio.h"
//#include "string.h "
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
const int N0=10;
const int N=100;
const int INF=1000000;
struct node1
{ int w, lch, rch, parent;
}ht[2*N0-1+1];
struct node2
{ char ch;
int start;
int code[N0];
}hc[N0+1];
int n,root;//n为叶子的个数
void readData()
{ char ch;
int num[256]={ 0 };
n=0;
freopen( "huffman.in", "r", stdin);//读文本文件
while( (ch=getchar()) != EOF )
num[ch]++;
for( int i=0; i<=255; i++ )
{ if( num[i] )
{ n++;
ht[n].w=num[i];
hc[n].ch=i;
}
}
}
void select1( int t, int *s1, int *s2)//用两个数来记录没有在树上的最小的两个值,从而进一步生成树。
{ int w1,w2;
w1=w2=INF;
for( int i=1; i<=t; i++ )
if( ht[i].parent==0 )
if( ht[i].w<w1 )
{ w2=w1;
*s2=*s1;
w1=ht[i].w;
*s1=i;
}
else if( ht[i].w<w2 )
{ w2=ht[i].w;
*s2=i;
}
}
void createHufTreeHuCode()
{ int i, s1, s2;
int child, parent;
root=2*n-1;
for( i=n+1; i<=root; i++)
{ select1(i-1, &s1, &s2 );
ht[i].w=ht[s1].w+ht[s2].w;
ht[i].lch=s1;
ht[i].rch=s2;
ht[s1].parent=ht[s2].parent=i;
}
for( i=1; i<=n; i++)
{ child=i;
while( child != root )
{ parent=ht[child].parent;
if( ht[parent].lch==child )
hc[i].code[hc[i].start++]=0;
else
hc[i].code[hc[i].start++]=1;
child=parent;
}
}
}
void txt2code()
{
int i,j,m;
char ch1[N+1]={0};
freopen( "huffman.in", "r", stdin);
for (int k=1;k<N+1;k++)
{
scanf("%c",&ch1[k]);
}
for( j=1,i=1; i<=N; i++)
{ if (ch1[i]==0)
{
break;
}
while (ch1[i]!=hc[j].ch)
{
if (hc[j].ch==0)
{continue;
}
j++;
}
for( m=hc[j].start-1; m>=0; m--)
printf("%d", hc[j].code[m]);
j=1;
}
}
int main()
{
readData();
createHufTreeHuCode();
freopen("huffman.out", "w", stdout);
txt2code();
return 0;
}
二、译码
【题目描述】
给定2个输入文件,第1个输入文件是用于通信的英文电文,统计该电文中每个字符出现的频率,按频率左小右大的方法为这些字符建立哈夫曼(Huffamn)树,并编出每个字符的哈夫曼树码;第2个输入文件是已经按第1个输入文件的英文电文编好的哈夫曼码,输出该哈夫曼码的对应的英文电文。
【输入】
第1个输入文件为huffman.in是用于通信的英文电文, 第2个输入文件codeToTxt.in是已经按第1个输入文件编好的哈夫曼码。
【输出】
输出文件codeToTxt.out输出codeToTxt.in文件内容的英文电文。
【输入输出样例1】
| huffman.in |
codeToTxt.in |
codeToTxt.out |
| aaccdddbacbcddddddd |
011111011000011101001100010001111 |
adddaccdddbacbcdddd |
【数据限制】
2<=英文电文字符数<=10000000
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
const int N0=10;
const int N=100;
const int INF=1000000;
struct node1
{ int w, lch, rch, parent;
}ht[2*N0-1+1];
struct node2
{ char ch;
int start;
int code[N0];
}hc[N0+1];
int n,root,num[256];
void readData()
{ char ch;
n=0;
freopen( "huffman.in", "r", stdin);
while( (ch=getchar()) != EOF )
num[ch]++;//同时得到了两个东西,一个是字符,一个是个数
for( int i=0; i<=255; i++ )
{ if( num[i] )
{ n++;
ht[n].w=num[i];//个数
hc[n].ch=i;//字符
}
}
}
void select1( int t, int *s1, int *s2)
{ int w1,w2;
w1=w2=INF;
for( int i=1; i<=t; i++ )
if( ht[i].parent==0 )
if( ht[i].w<w1 )
{ w2=w1;
*s2=*s1;
w1=ht[i].w;
*s1=i;
}
else if( ht[i].w<w2 )
{ w2=ht[i].w;
*s2=i;
}
}
void createHufTreeHuCode()
{ int i, s1, s2;
int child, parent;
root=2*n-1;
for( i=n+1; i<=root; i++)
{ select1( i-1, &s1, &s2 );
ht[i].w=ht[s1].w+ht[s2].w;
ht[i].lch=s1;
ht[i].rch=s2;
ht[s1].parent=ht[s2].parent=i;
}
for( i=1; i<=n; i++)
{ child=i;
while( child != root )
{ parent=ht[child].parent;
if( ht[parent].lch==child )
hc[i].code[hc[i].start++]=0;
else
hc[i].code[hc[i].start++]=1;
child=parent;
}
}
}
void code2txt()
{ char ch=0;
int i=root;
freopen( "codeToTxt.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("codeToTxt.out", "w", stdout);
while( (ch=getchar()) != EOF )
{
if(ht[i].lch&&ht[i].rch)
{if(ch=='0')
i=ht[i].lch;
else
i=ht[i].rch;
}
if(ht[i].lch==0&&ht[i].rch==0)
{ printf("%c",hc[i].ch);
i=root;
}
}
}
int main()
{ readData();
createHufTreeHuCode();
code2txt();
return 0;
}