Directx教程(28) 简单的光照模型(7)
现实生活中的点光源都是随着距离衰减的,比如一个电灯泡在近处会照的很亮,远处光线就很弱。本节中我们在前面光公式的基础上,再给漫反射和高光加上一个衰减因子。
光源随着距离衰减并不是纯线性的,常用的公式是:
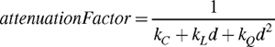
- d 是光源到着色点的距离。
- kC, kL, 和 kQ 分别是常量、线性以及二次衰减系数。
现在在light.ps中,计算光照的代码变成了:
for ( i = 0; i < NUM_LIGHTS; i++)
{
//自发射颜色
emissive = Ke[i];
//计算环境光
ambient = Ka[i] * globalAmbient[i];
//计算漫反射光
//用LightDirection就是纯平行光
//光源位置减顶点位置
L = normalize(lightPosition[i].xyz - P);
d = distance(lightPosition[i].xyz, P);
//衰减系数
atte = 1 / (attenuation[i].x + attenuation[i].y * d +attenuation[i].z * d * d);
diffuseLight = max(dot(N, L), 0);
diffuse = Kd[i] * lightColor[i] * diffuseLight * atte ;
//计算高光
V = normalize(cameraPosition.xyz - P);
H = normalize(L + V);
specularLight = pow(max(dot(N, H), 0), shininess[i]);
if (diffuseLight <= 0)
specularLight = 0;
specular = Ks[i] * lightColor[i] * specularLight * atte;
finalcolor += emissive + ambient + diffuse + specular;
}
相应的,在lightShaderClass.h中的struct LightMaterialBufferType,也要做一些变化,增加一个D3DXVECTOR4分量attenuation,它的x,y,z分别表示常量、线性以及二次衰减系数。之所以用D3DVECTOR4,是因为const buffer要求是4的倍数,我曾尝试用3个float,结果程序竟然有编译错误。
…
D3DXVECTOR4 attenuation[NUM_LIGHTS]; //衰减系数,x,y,z对应常量,线性和二次系数
…
在light.ps中,const buffer LightMaterialBuffer,也要增加衰减因子,它和LightMaterialBufferType中的attenuation是相对应的。
float4 attenuation[NUM_LIGHTS]; //衰减系数
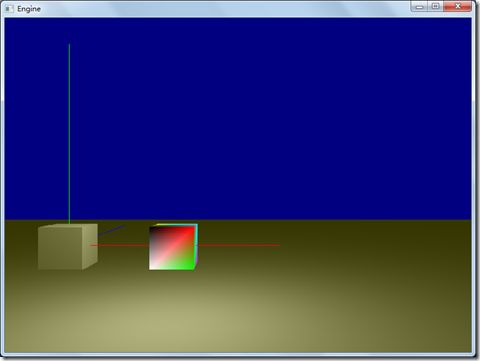
程序执行后的效果如下:
完整的代码请参考:
工程文件myTutorialD3D11_21
代码下载:
http://files.cnblogs.com/mikewolf2002/myTutorialD3D11.zip
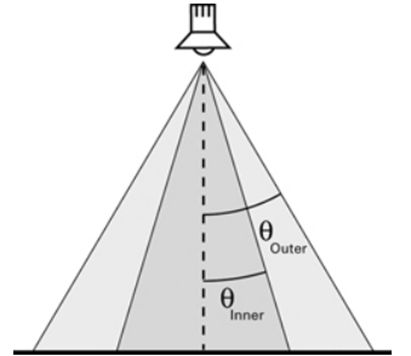
接下来我们再实现一个探照灯(spotlight)的效果,如下图所示,只有在圆锥内角(inner)的范围才是光照能够达到的范围。但是只考虑内角的话,我们的光照会比较生硬,内角圆锥内,有光,内角圆锥外,一片漆黑,所以我们又加了一个外角(outer),对于内角和外角之间的空间,我们使用hlsl的差值函数smoothstep来计算得到一个0-1之间的数值。
light.ps的主要代码:
下面的函数通过smoothstep计算出spotlight的因子。其中cosInnerCone是内角的余弦值,cosOuterCone是外角的余弦值。如果计算出的cosDirection值大于内角余弦值,则smoothstep值为1,如果cosDirection值小于外角余弦值,则其值为0,对于在这两者之间的值,smoothstep会用多项式差值得到一个0-1之间的值。
//一个计算spot light系数的函数
float dualConeSpotlight(float3 P, float3 lightpos, float3 lightdir, float cosInnerCone, float cosOuterCone)
{
float3 V = normalize(P - lightpos);
float cosDirection = dot(V, normalize(lightdir));
return smoothstep(cosOuterCone, cosInnerCone, cosDirection);
}
for ( i = 0; i < NUM_LIGHTS; i++)
{
//自发射颜色
emissive = Ke[i];
//计算环境光
ambient = Ka[i] * globalAmbient[i];
//计算漫反射光
//用LightDirection就是纯平行光,在spotlight情况下代表光的方向
spotEffect = dualConeSpotlight(P, lightPosition[i].xyz, lightDirection[i],spotattenuation[i].x, spotattenuation[i].y);
//光源位置减顶点位置
L = normalize(lightPosition[i].xyz - P);
d = distance(lightPosition[i].xyz, P);
//衰减系数
atte = 1 / (attenuation[i].x + attenuation[i].y * d +attenuation[i].z * d * d);
diffuseLight = max(dot(N, L), 0);
diffuse = Kd[i] * lightColor[i] * diffuseLight * atte * spotEffect;
//计算高光
V = normalize(cameraPosition.xyz - P);
H = normalize(L + V);
specularLight = pow(max(dot(N, H), 0), shininess[i]);
if (diffuseLight <= 0)
specularLight = 0;
specular = Ks[i] * lightColor[i] * specularLight * spotEffect;
finalcolor += emissive + ambient + diffuse + specular;
}
同样的,我们的const buffer LightMaterialBuffer中,增加了
float4 spotattenuation[NUM_LIGHTS];
它的x,y分别表示内角和外角余弦值。
lightShaderClass.h中的材质光照结构中也增加了
D3DXVECTOR4 spotattenuation[NUM_LIGHTS]; //对于spotlight,x,y分别存储内和外角cos值
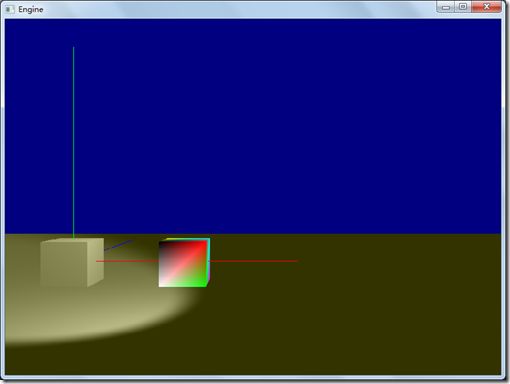
程序最终执行效果如下:
完整的代码请参考:
工程文件myTutorialD3D11_22
代码下载: