WebCast听课录(5)
课程名:Windows应用程序开发入门到精通六:如何使用.NET开发Windows应用程序
程序的托管执行
程序集
名称空间
委托
线程
应用程序域
特性
数据类型
反射
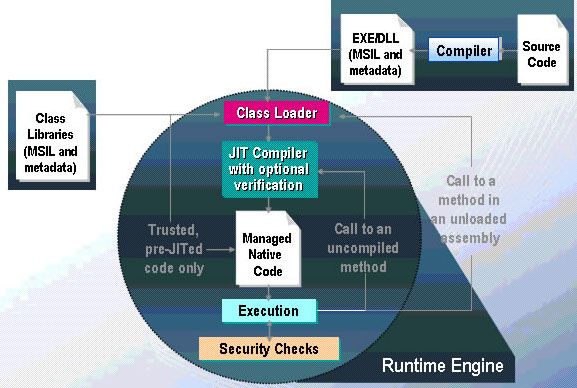
1,托管代码指第一次编译形成中间代码(MSIL),执行时需要再编译成本地代码(二进制代码).类加载器会加载中间语言代码,或dll中的类库,再调用JIT来编译为托管的本地代码,最后被托管地执行,在执行时会不断地进行安全性策略检查。在加载dll类库时,不是全部装载,而只是装载Main()方法所在的class,在执行时会检查所要调用的类是否已经在内存中,若没有则实时装载进来。
2,IDisposable 接口 定义一种释放分配的非托管资源的方法。当托管对象不再使用时,垃圾回收器会自动释放分配给该对象的内存,不过,进行垃圾回收的时间不可预知。另外,垃圾回收器对窗口句柄、打开的文件和流等非托管资源一无所知。将此接口的 Dispose 方法与垃圾回收器一起使用来显式释放非托管资源。当不再需要对象时,对象的使用者可以调用此方法。
 using
System;
using
System; using
System.ComponentModel;
using
System.ComponentModel;
 //
The following example demonstrates how to create
//
The following example demonstrates how to create //
a resource class that implements the IDisposable interface
//
a resource class that implements the IDisposable interface //
and the IDisposable.Dispose method.
//
and the IDisposable.Dispose method.

 public
class
DisposeExample
public
class
DisposeExample

 {
{
 //实现IDisposable的基类,通过实现此接口,就表明此类型的实例会分配非托管资源
//实现IDisposable的基类,通过实现此接口,就表明此类型的实例会分配非托管资源 public class MyResource: IDisposable
public class MyResource: IDisposable

 {
{
 private IntPtr handle;//指向一个内部非托管资源的指针
private IntPtr handle;//指向一个内部非托管资源的指针
 private Component component = new Component();//类中使用的其他托管资源
private Component component = new Component();//类中使用的其他托管资源
 private bool disposed = false;//跟踪Dispose是否已经被调用
private bool disposed = false;//跟踪Dispose是否已经被调用

 public MyResource(IntPtr handle)
public MyResource(IntPtr handle)

 {
{ this.handle = handle;
this.handle = handle; }
}

 //实现IDisposable接口,不要让此方法virtual。派生类应该不允许override这个方法
//实现IDisposable接口,不要让此方法virtual。派生类应该不允许override这个方法 public void Dispose()
public void Dispose()

 {
{ Dispose(true);
Dispose(true); //此对象将被Dispose方法清理掉,因此,你需要调用GC.SuppressFinalize方法来
//此对象将被Dispose方法清理掉,因此,你需要调用GC.SuppressFinalize方法来 //将此对象从需要终止的对象队列中移除,并且防止这个对象执行两次终止代码
//将此对象从需要终止的对象队列中移除,并且防止这个对象执行两次终止代码 GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
GC.SuppressFinalize(this); }
}

 //若disposing为true,则方法被用户代码直接或间接调用。托管资源和非
//若disposing为true,则方法被用户代码直接或间接调用。托管资源和非 //托管资源可以被释放。
//托管资源可以被释放。 //若disposing为false,则方法被运行时从解析器内部调用并且你不应该再应用其他对象,
//若disposing为false,则方法被运行时从解析器内部调用并且你不应该再应用其他对象, //只有非托管资源能被释放。
//只有非托管资源能被释放。 private void Dispose(bool disposing)
private void Dispose(bool disposing)

 {
{ // Check to see if Dispose has already been called.
// Check to see if Dispose has already been called. if(!this.disposed)
if(!this.disposed)

 {//检查Dispose是否已经被调用过了
{//检查Dispose是否已经被调用过了
 if(disposing)
if(disposing)

 {//若disposing为true,释放所有托管和非托管资源
{//若disposing为true,释放所有托管和非托管资源
 component.Dispose(); // 在此处释放托管资源
component.Dispose(); // 在此处释放托管资源
 }
}
 // 在这调用适当的方法来清理非托管资源,
// 在这调用适当的方法来清理非托管资源, // 若disposing为false,则只有下面的代码会执行
// 若disposing为false,则只有下面的代码会执行  CloseHandle(handle);
CloseHandle(handle); handle = IntPtr.Zero;
handle = IntPtr.Zero;  }
} disposed = true;
disposed = true;  }
}
 // Use interop to call the method necessary
// Use interop to call the method necessary  // to clean up the unmanaged resource.
// to clean up the unmanaged resource. [System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImport("Kernel32")]
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImport("Kernel32")] private extern static Boolean CloseHandle(IntPtr handle);
private extern static Boolean CloseHandle(IntPtr handle);
 //这个解析器只在Dispose方法没有被调用时才运行,它为你的基类提供了解析的
//这个解析器只在Dispose方法没有被调用时才运行,它为你的基类提供了解析的 //机会。在其派生类中不要提供解析器。
//机会。在其派生类中不要提供解析器。 ~MyResource()
~MyResource() 

 {
{ Dispose(false);//解析器内部调用,只释放非托管资源,托管资源由垃圾回收器负责
Dispose(false);//解析器内部调用,只释放非托管资源,托管资源由垃圾回收器负责 }
} }
} public static void Main()
public static void Main()

 {
{ // Insert code here to create
// Insert code here to create // and use the MyResource object.
// and use the MyResource object.  }
} }
}


3,COM Marshaller用于与COM进行互操作,CLR会把 COM组件包装成一个应用程序集,在此应用程序集中会把方法中使用的参数类型都映射为CLR的数据类型,CLR就会和COM Marshaller进行交互,而后者与真正的COM组件进行交互。
4,.NET Framework 允许您异步调用任何方法。定义与您需要调用的方法具有相同签名的委托;公共语言运行库将自动为该委托定义具有适当签名的 BeginInvoke 和 EndInvoke 方法。
BeginInvoke 方法用于启动异步调用。它与您需要异步执行的方法具有相同的参数,只不过还有两个额外的参数。BeginInvoke 立即返回,不等待异步调用完成。BeginInvoke 返回 IasyncResult,可用于监视调用进度。EndInvoke 方法用于检索异步调用结果。调用 BeginInvoke 后可随时调用 EndInvoke 方法;如果异步调用未完成,EndInvoke 将一直阻塞到异步调用完成。EndInvoke 的参数包括您需要异步执行的方法的 out 和 ref 参数以及由 BeginInvoke 返回的 IAsyncResult。
调用了 BeginInvoke 后,可以:
1,进行某些操作,然后调用 EndInvoke 一直阻塞到调用完成。
2,使用 IAsyncResult.AsyncWaitHandle 获取 WaitHandle,使用它的 WaitOne 方法将执行一直阻塞到发出WaitHandle 信号,然后调用 EndInvoke。
3,轮询由 BeginInvoke 返回的 IAsyncResult,确定异步调用何时完成,然后调用 EndInvoke。
4,将用于回调方法的委托传递给 BeginInvoke。该方法在异步调用完成后在 ThreadPool 线程上执行,它可以调用 EndInvoke。
 public
delegate
bool
SimpleDelegate(
string
Message);
public
delegate
bool
SimpleDelegate(
string
Message);
 public
class
DelegateExample
public
class
DelegateExample

 {
{ public DelegateExample()
public DelegateExample()

 {
{ }
}
 public void CallMeBack(SimpleDelegate CallBack)
public void CallMeBack(SimpleDelegate CallBack)

 {
{ IAsyncResult result = CallBack.BeginInvoke("Calling you back from thread"+System.AppDomain.GetCurrentThreadId(),null,null);
IAsyncResult result = CallBack.BeginInvoke("Calling you back from thread"+System.AppDomain.GetCurrentThreadId(),null,null);
 bool callBackResult = (bool)CallBack.EndInvoke(result);
bool callBackResult = (bool)CallBack.EndInvoke(result); System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(callBackResult.ToString(),"Callback Result");
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(callBackResult.ToString(),"Callback Result");
 }
} }
}

 public
class
Test
public
class
Test

 {
{ public static void Main()
public static void Main()

 {
{ Delegates();
Delegates(); }
}
 public static bool SimpleDelegateHandler(string Message)
public static bool SimpleDelegateHandler(string Message)

 {
{ System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(Message,
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(Message, "Code Running On Thread ID"+System.AppDomain.GetCurrentThreadId().ToString());
"Code Running On Thread ID"+System.AppDomain.GetCurrentThreadId().ToString()); return true;
return true; }
} public static void Delegates()
public static void Delegates()

 {
{ DelegateExample ex = new DelegateExample();
DelegateExample ex = new DelegateExample(); ex.CallMeBack(new SimpleDelegate(SimpleDelegateHandler));
ex.CallMeBack(new SimpleDelegate(SimpleDelegateHandler));
 }
}
 }
}

5,线程应用示例:
 public
delegate
void
DoneDelegate(
bool
arg);
public
delegate
void
DoneDelegate(
bool
arg);
 private
void
DelegateHandler(
bool
Stopped)
private
void
DelegateHandler(
bool
Stopped)

 {
{ btnStart.Text = "Save";
btnStart.Text = "Save";
 if(Stopped)
if(Stopped)

 {
{ MessageBox.Show("Save Stopped","Stopped",
MessageBox.Show("Save Stopped","Stopped", MessageBoxButtons.OK,MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
MessageBoxButtons.OK,MessageBoxIcon.Warning); }
} else
else

 {
{ MessageBox.Show("Save Done");
MessageBox.Show("Save Done"); }
} }
}

 private
void
ProcessSave()
private
void
ProcessSave()

 {
{ bool Stopped = false;
bool Stopped = false; for(int i=1;i<=50;i++)
for(int i=1;i<=50;i++)

 {
{ System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(100);
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(100); if(btnStart.Text == "Stopped")
if(btnStart.Text == "Stopped")

 {//用户要求停止
{//用户要求停止 Stopped = true;
Stopped = true; break;
break; }
} }
} new DoneDelegate(DelegateHandler).BeginInvoke(Stopped,null,null);//开始异步回调
new DoneDelegate(DelegateHandler).BeginInvoke(Stopped,null,null);//开始异步回调 }
}


 private
void
btnStart_Click(
object
sender, System.EventArgs e)
private
void
btnStart_Click(
object
sender, System.EventArgs e)

 {
{ if(btnStart.Text=="start")
if(btnStart.Text=="start")

 {
{ btnStart.Text = "Stop";
btnStart.Text = "Stop"; System.Threading.Thread t = new Thread(new System.Threading.ThreadStart
System.Threading.Thread t = new Thread(new System.Threading.ThreadStart (ProcessSave));
(ProcessSave)); t.Start();//启动新线程来处理
t.Start();//启动新线程来处理 }
} else
else

 {
{ btnStart.Text = "Stopped";
btnStart.Text = "Stopped"; }
} }
}

通过delegate可以把界面元素和处理代码隔离开,并且后者可以去访问界面元素(尽管两者不是同一个类下的成员)
6,思考题:
 [assembly:CLSCompliant(
true
)]
[assembly:CLSCompliant(
true
)] //
[CLSCompliant(false)]
//
[CLSCompliant(false)]
 public
class
Class2
public
class
Class2

 {
{
 public static void Main(String[] args)
public static void Main(String[] args)

 {
{ UInt32 a1 = GetMinValue();
UInt32 a1 = GetMinValue(); UInt32 a2 = GETMINVALUE();
UInt32 a2 = GETMINVALUE(); }
}
 public static UInt32 GetMinValue()
public static UInt32 GetMinValue()

 {
{ return UInt32.MinValue;
return UInt32.MinValue;
 }
}
 public static UInt32 GETMINVALUE()
public static UInt32 GETMINVALUE()

 {
{ return UInt32.MinValue;
return UInt32.MinValue;
 }
} }
}

如果编译上面这段代码,会有什么问题?会报两种错误,因为[assembly:CLSCompliant(true)]指定了要遵从CLS性,因此由于 CLS 中没有指定 UInt32 类型,所以返回类型会报错,而且两个方法的签名除了大小写以外是一样的,因此也不符合CLS,(例如在VB.net里就区分不出大小写的差别,尽管在C#是可以区分的。)
当然,若把去掉[CLSCompliant(false)]的注释,就指明了此类是不需要符合CLS的,因此就不会报错了。