为什么使用Java框架Spring Boot部署深度学习模型
稍早前训练了一些深度学习模型后,遇到了模型部署的一些问题,首先现有的很多业务都是java实现的,例如预算控制,用户限额等,图片识别直接和这些系统交互会造成一定的代码侵入,以及多个系统出现冗余,所以考虑使用Spring Boot将图片侦测服务包装起来,以独立的领域,搭建一个的服务,对外提供图片侦测的功能。其次Spring框架在服务管理、负载等方面有成熟的方案,也方便日后的扩展升级。
本文记录了使用Java部署深度学习模型的过程,注意模型核心还是运行在Pytorch框架上的,这里只是一个提供外围访问或域内调用的API。
可直接参见完整Java项目:https://github.com/anylots/detection
python模型项目的DetectNet:https://github.com/anylots/DetectNet,提供http接口;based on Yet-Another-EfficientDet-Pytorch
框架组成
管理时应用架构为Spring Boot+Thymeleaf+Bootstrap组合,运行时为Pytorch+Flask组合。
Java 管理时部分
第一步,使用接收到的imageLink或上传的文件调用图片识别服务,返回数据为图片的BASE64编码。
第二步,组装Spring的ModelAndView对象 。
第三步,返回ModelAndView对象 ,Thymeleaf引擎会将识别结果返回给前端。
`@Controller
public class ImageDetectController {
/**
* service of imageDetect
*/
@Autowired
private ImageDetectService imageDetectService;
/**
* detect
*
* @return detect.html
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/detect", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String detect() {
return "detect";
}
/**
* detect out
*
* @param imageLink
* @return detectOut.html
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/detectImage", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ModelAndView detectOut(String imageLink) {
// step 1. detect image by imageUrl
String detectFrame = imageDetectService.detect(imageLink);
// step 2. assemble modelAndView
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("detectOut");
modelAndView.addObject("img", detectFrame);
// step 3. return detect result page
return modelAndView;
}`
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
* 35
* 36
* 37
* 38
* 39
* 40
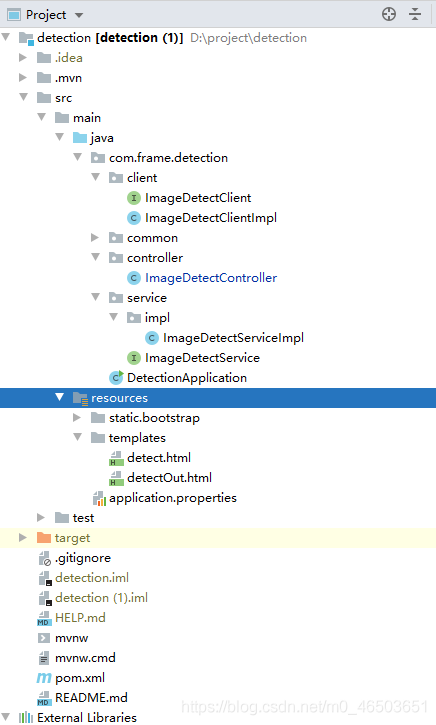
spring boot 项目结构
Python 运行时部分
使用flask提供http接口
这里先根据传入的url获取图片,然后调用service层得到识别后的图片信息,最后通过http接口返回给spring boot管理时(现在对python的rpc框架还不了解,后续再研究研究)。
图片数据格式就参考了旷视公司的图片识别接口,采用BASE64编码传输图片信息,
`@app.route('/detect/imageDetect', methods=['post'])
def process():
# step 1. receive image url
image_link = request.form.get("imageLink")
if not image_link.strip():
return "error" # check request
response = req.get(image_link)
image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content))
# step 2. detect image
image_array = service.detect(image)
# step 3. convert image_array to byte_array
img = Image.fromarray(image_array, 'RGB')
img_byte_array = io.BytesIO()
img.save(img_byte_array, format='JPEG')
# step 4. return image_info to page
image_info = base64.b64encode(img_byte_array.getvalue()).decode('ascii')
return image_info
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.jinja_env.auto_reload = True
app.config['TEMPLATES_AUTO_RELOAD'] = True
app.run(debug=False, port=8081)`
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
Pytorch部署EfficientDet
这里使用里一个service层来包装EfficientDet模型,将transforms 、CLASS分类信息、识别器定义为全局变量,避免每次请求都去初始化这些信息,降低耗时。
`import random
import time
import cv2 as opencv
import numpy as np
import torchvision
from PIL import Image
from detector import *
# image detector,return output of detection data
detector = Detector()
# data transforms
transforms = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()
])
# set of names and colors
names = cfg.COCO_CLASS
# draw identification frame based on detection data
class ImgDetectService:
# return a image with boxes based on detection data
def detect(self, img):
start_time = time.time()
# convert image to array
frame = np.array(img)
# convert to cv format
frames = frame[:, :, ::-1]
# convert to model format
image = Image.fromarray(frames, 'RGB')
width, high = image.size
x_w = width / 416
y_h = high / 416
normal_img = image.resize((416, 416))
img_data = transforms(normal_img)
img_data = torch.FloatTensor(img_data).view(-1, 3, 416, 416).to(cfg.DEVICE)
# detect image
y = detector(img_data, 0.7, cfg.ANCHORS_GROUP)[0]
tl = round(0.002 * (width + high) / 2) + 1 # line thickness
tf = 1
for i in y:
# plots one bounding box on image img
x1 = int((i[0]) * x_w)
y1 = int((i[1]) * y_h)
x2 = int((i[2]) * x_w)
y2 = int((i[3]) * y_h)
cls = i[5]
color = [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
opencv.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, thickness=2)
# plots label
label = names[int(cls)]
label_size = opencv.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
opencv.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x1 + label_size[0], y1 - label_size[1] - 3), color, -1)
opencv.putText(frame, label, (x1, y1 - 8), 0, tl / 3, [225, 255, 255], thickness=tf,
lineType=opencv.LINE_AA)
end_time = time.time()
print(end_time - start_time)
return frame`
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
* 35
* 36
* 37
* 38
* 39
* 40
* 41
* 42
* 43
* 44
* 45
* 46
* 47
* 48
* 49
* 50
* 51
* 52
* 53
* 54
* 55
* 56
* 57
* 58
* 59
* 60
* 61
* 62
* 63
* 64
* 65
* 66
* 67
* 68
* 69
* 70
效果演示:
分别启动detection和DetectNet项目
填入需要识别的图片url或者上传图片文件,点击提交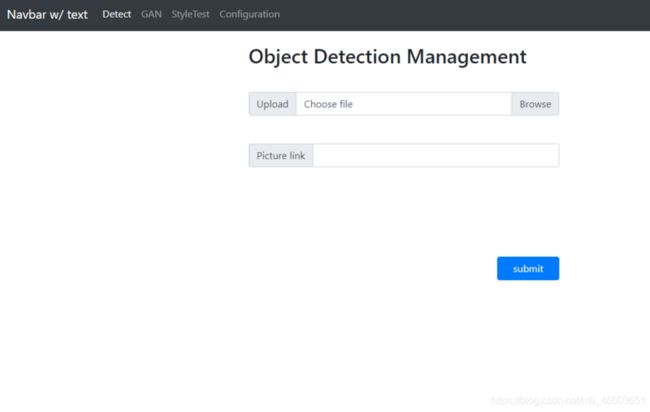
识别结果
请求总耗时150ms左右,其中pytorch运行时耗时在90ms(device=CUDA,GTX1050Ti),管理时耗时60ms(i5 8400 8GRAM)。耗时较大,这个估计和http接口有关,后续研究下python的rpc调用,以及数据压缩传输。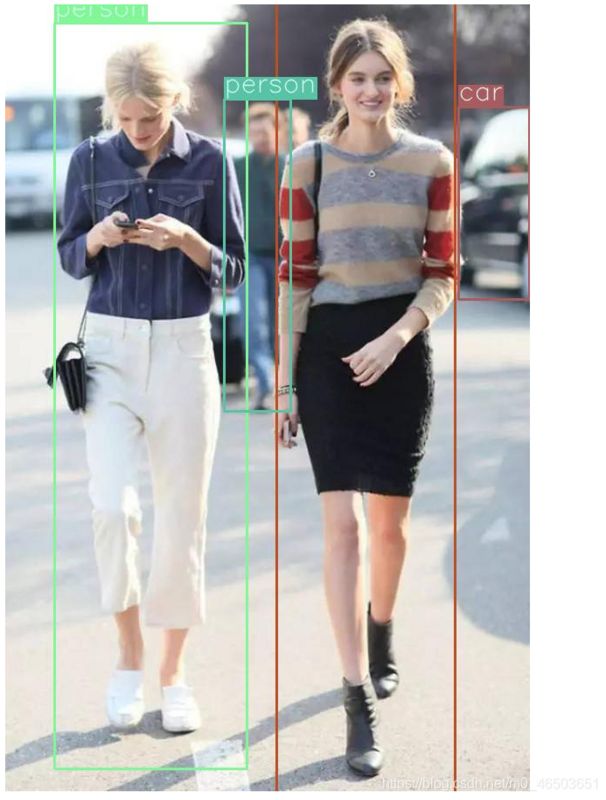
模型权重:链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1SyIa... 提取码: 3pif
说明:本文记录细节和逻辑还有很多未完善的地方,对图片识别服务搭建、部署还将继续研究,然后继续更新
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_4650...