Android Studio 从外部导入数据库并显示到页面中
文章目录
- Android Studio从外部导入数据库并显示到页面中
-
- 1. 从外部导入数据库
- 2. 显示数据库内容
- 3. 踩坑记录
Android Studio从外部导入数据库并显示到页面中
最近在开发一个单词学习的App, 准备好单词的外部数据库之后突然卡在了将数据库导入项目这一步,参考了很多网上的资料,自己动手尝试了一遍,最后成功了。在这里将我的操作过程记录一下。
1. 从外部导入数据库
首先,要导入的数据库及其内容是这样的(使用的数据库工具是SQLite Expert Professional 4.2):

该数据库存储在文件1.db中。
打开Android Studio,在要导入的项目中,切换至Project视图,新建一个和Java、res同级的目录assets(这个目录的位置与开发环境有关,我看网上说使用Eclispe开发环境时它在res/下,但在AS中它必须与res目录同级),然后将1.db复制到assets目录下:

做到这里的时候,不知道大家有没有这样的疑问:为什么要将数据库文件放在assets下?
有个解释说,这个文件夹主要用于存放应用程序中使用的外部资源文件,然后程序可以通过 I/O 流(使用
AssetManager)对目录中的文件进行读写,存放在此目录下的文件都会被打包到发布包中。
接着,实现类MyDBOpenHelper.java;
这个类就是实现从assets目录读取数据库文件然后写入SD卡中,如果在SD卡中存在,就打开数据库,不存在就从assets目录下复制过去。
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyDBOpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private static String PACKAGE_NAME = "com.example.wordsofmultilanguage"; //包名
private static String DB_PATH = "/data" + Environment.getDataDirectory().getAbsolutePath() + "/" + PACKAGE_NAME + "/databases/";
private static String DB_NAME = "1";
private SQLiteDatabase db;
private final Context context;
public MyDBOpenHelper(Context context) {
super(context, DB_NAME , null, 1);
this. context = context;
}
public void createDB() throws IOException {
this.getReadableDatabase();
try {
copyDB();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new Error("Error copying database");
}
}
public void copyDB() throws IOException{
try {
InputStream ip = context.getAssets().open(DB_NAME+".db");
Log.i("Input Stream....",ip+"");
String op= DB_PATH + DB_NAME ;
OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream( op);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int length;
while ((length = ip.read(buffer))>0){
output.write(buffer, 0, length);
Log.i("Content.... ",length+"");
}
output.flush();
output.close();
ip.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
Log.v("error", e.toString());
}
}
public void openDB() throws SQLException {
String myPath = DB_PATH + DB_NAME;
db = SQLiteDatabase.openDatabase(myPath, null, SQLiteDatabase.OPEN_READWRITE);
Log.i("open DB......",db.toString());
}
@Override
public synchronized void close() {
if(db != null)
db.close();
super.close();
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
}
}
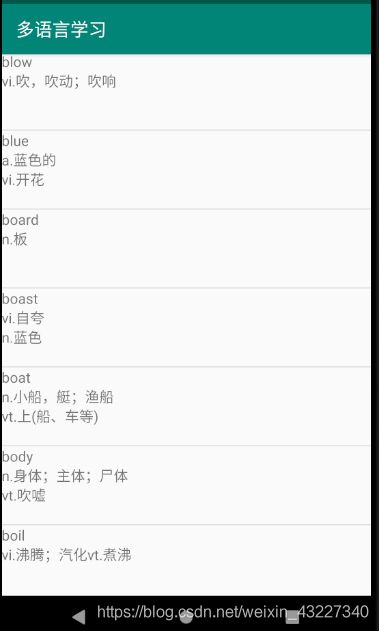
2. 显示数据库内容
在页面上显示数据库内容(即英文单词和释义)时,用到了ListView控件,新建一个 布局文件im.xml:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/word_info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
LinearLayout>
对ListView的每一条item做布局item.xml:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/word"
android:textSize="16dp"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/mean1"
android:textSize="16dp"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/mean2"
android:textSize="16dp"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/mean3"
android:textSize="16dp"
/>
LinearLayout>
完成第一步外部数据库的导入之后,定义一个类initdate.java用来实例化数据库:
public class initdate {
public String word;
public String meaning1;
public String meaning2;
public String meaning3;
public initdate(String word, String meaning1, String meaning2, String meaning3){
this.word = word;
this.meaning1 = meaning1;
this.meaning2 = meaning2;
this.meaning3 = meaning3;
}
}
然后,实现类
package com.example.wordsofmultilanguage;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import java.io.IOException;
import android.database.SQLException;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.SimpleTimeZone;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
public class test extends AppCompatActivity {
//创建一个List对象来存储数据
List<initdate>list = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.im);
ListView listView = (ListView)this.findViewById(R.id.word_info);
MyDBOpenHelper db;
db = new MyDBOpenHelper(this);
try {
db.createDB();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new Error("Database not created....");
}
try {
db.openDB();
} catch (SQLException sqle) {
throw sqle;
}
SQLiteDatabase db1;
db1 = openOrCreateDatabase("1", Context.MODE_PRIVATE, null);
Cursor c = db1.rawQuery("SELECT * FROM words1", null);
c.moveToFirst();
//获取表数据
while (!c.isAfterLast()) {
list.add(new initdate(c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("word")),c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("meaning1")),
c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("meaning2")),c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("meaning3"))));
c.moveToNext();
}
//将获取到的数据通过一个循环存放到map对象中
List<HashMap<String, Object>> data = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, Object>>();
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
HashMap<String, Object>item = new HashMap<String, Object>();
item.put("word", list.get(i).word);
item.put("meaning1", list.get(i).meaning1);
if(list.get(i).meaning2 != null){
item.put("meaning2", list.get(i).meaning2);
}
//item.put("meaning2", list.get(i).meaning2);
if(list.get(i).meaning3 != null){
item.put("meaning2", list.get(i).meaning3);
}
//item.put("meaning3", list.get(i).mmeaning3);
data.add(item);
}
//创建SimpleAdapter适配器将数据绑定到item显示控件上
SimpleAdapter adapter = new SimpleAdapter(this, data, R.layout.item,
new String[]{
"word", "meaning1", "meaning2", "meaning3"}, new int[]{
R.id.word, R.id.mean1, R.id.mean2, R.id.mean3});
//实现列表的显示
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
}
}
3. 踩坑记录
在操作过程中,导入数据库文件的时候曾经碰到以下问题:

我数据库使用的编码形式是UTF-8,这是我导入1.db文件后显示的内容,全是乱码,并且提示File was loaded in the wrong encoding: 'UTF-8',我的解决办法是啥也不做,不用管,只要原先的数据库内容没问题,继续往下做就可以。原因好像是因为AS打不开这个类型的文件,要用专门的SQLite工具打开,如果尝试打开的话就会变成一堆乱码,而且从此以后不管删除、重新导入多少次AS都很”贴心“地给你显示成乱码。(小白第一次用 AS 开发项目,啥也不懂,被这玩意儿坑死了,想了各种办法,最后发现它根本不影响……)