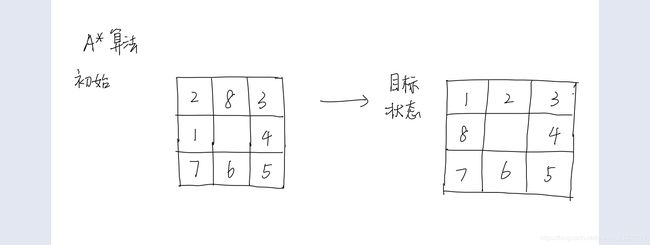
人工智能 八数码
八数码问题代码实现
1.原理:
对于八数码问题的解决,首先要考虑是否有答案。每一个状态可认为是一个1×9的矩阵,问题即通过矩阵的变换,是否可以变换为目标状态对应的矩阵?由数学知识可知,可计算这两个有序数列的逆序值,如果两者都是偶数或奇数,则可通过变换到达,否则,这两个状态不可达。这样,就可以在具体解决问题之前判断出问题是否可解,从而可以避免不必要的搜索。
如果初始状态可以到达目标状态,那么采取什么样的方法呢?
常用的状态空间搜索有深度优先和广度优先。广度优先是从初始状态一层一层向下找,直到找到目标为止。深度优先是按照一定的顺序前查找完一个分支,再查找另一个分支,以至找到目标为止。广度和深度优先搜索有一个很大的缺陷就是他们都是在一个给定的状态空间中穷举。这在状态空间不大的情况下是很合适的算法,可是当状态空间十分大,且不预测的情况下就不可取了。他的效率实在太低,甚至不可完成。由于八数码问题状态空间共有9!个状态,对于八数码问题如果选定了初始状态和目标状态,有9!/2个状态要搜索,考虑到时间和空间的限制,在这里采用A*算法作为搜索策略。在这里就要用到启发式搜索
启发式搜索就是在状态空间中的搜索对每一个搜索的位置进行评估,得到最好的位置,再从这个位置进行搜索直到目标。这样可以省略大量无畏的搜索路径,提到了效率。在启发式搜索中,对位置的估价是十分重要的。采用了不同的估价可以有不同的效果。
启发中的估价是用估价函数表示的,如:f(n) = g(n) +h(n)其中f(n) 是节点n的估价函数,g(n)是在状态空间中从初始节点到n节点的实际代价,h(n)是从n到目标节点最佳路径的估计代价。 在此八数码问题中,显然g(n)就是从初始状态变换到当前状态所移动的步数,估计函数f(n)我们就可采用当前状态各个数字牌不在目标状态未知的个数,即错位数。
使用宽度优先搜索方法解决该问题
问题状态的表示建立数据结构:
(1)3×3的一个矩阵,矩阵元素S ij∈{0,1,…,8};其中1≤i,j≤3,
(2)数字0指示空格,
(3)数字1 - 8指示相应棋牌。
(4)制定操作算子集:
直观方法——为每个棋牌制定一套可能的走步:左、上、右、下四种移动。这样就需32个操作算子。
简易方法——仅为空格制定这4种走步,因为只有紧靠空格的棋牌才能移动。
空格移动的唯一约束是不能移出棋盘。
2.例子:
3.步骤:
初始状态为S(3),其中d(n)等于当前状态位于搜索树的深度0,h(n)等于当前状态不位于目的状态数码的个数3,故0+3=3。
第一次循环
1、从Open表中取出第一个代价最小的状态S(3),如果该状态是目的状态,则搜索结束并返回Closed表;如果没有,则继续循环。
2、空白区域可以往上下左右四个方向移动,通过上述的计算方法可以得到A(4)、B(4)、C(5)和D(5)四个状态。
3、将A(4)、B(4)、C(5)和D(5)四个状态归入Open表中按每一个状态的代价升序排列,并将上一步状态S(3)归入Closed表中。
第二次循环:
1、从Open表中取出第一个代价最小的状态A(4),如果该状态是目的状态,则搜索结束并返回Closed表;如果没有,则继续循环。
2、空白区域可以往左右移动,由于往下移动后得到的状态已经在Closed表中出现,故不考虑。
3、将得到的E(4)和F(6)归入Open表中,并对Open表重新排序,将上一步状态A(4)归入Cloesd表中。
第三次循环:
1、从Open表中取出第一个代价最小的状态B(4),如果该状态是目的状态,则搜索结束并返回Closed表;如果没有,则继续循环。
2、空白区域可以往上下移动,由于往右移动后得到的状态已经在Closed表中出现,故不考虑。
3、将得到的G(5)和H(6)归入Open表中,并对Open表重新排序,将上一步状态B(4)归入Cloesd表中。
第四次循环:
1、从Open表中取出第一个代价最小的状态E(4),如果该状态是目的状态,则搜索结束并返回Closed表;如果没有,则继续循环。
2、空白区域可以往下移动,由于往右移动后得到的状态已经在Closed表中出现,故不考虑。
3、将得到的I(4)归入Open表中,并对Open表重新排序,将上一步状态E(4)归入Cloesd表中。
第五次循环:
1、从Open表中取出第一个代价最小的状态I(4),如果该状态是目的状态,则搜索结束并返回Closed表;如果没有,则继续循环。
2、空白区域可以往下、右移动,由于往上移动后得到的状态已经在Closed表中出现,故不考虑。
3、将得到的J(4)和K(6)归入Open表中,并对Open表重新排序,将上一步状态I(4)归入Cloesd表中。
第六次循环:
从Open表中取出第一个代价最小的状态J(4),该状态就是目的状态,停止搜索并返回Close表。
三种方法解决八数码问题:
宽度优先:
import numpy as np
class State:
def __init__(self, state, directionFlag=None, parent=None):
self.state = state
# state is a ndarray with a shape(3,3) to storage the state
self.direction = ['up', 'down', 'right', 'left']
if directionFlag:
self.direction.remove(directionFlag)
# record the possible directions to generate the sub-states
self.parent = parent
self.symbol = ' '
def getDirection(self):
return self.direction
def showInfo(self):
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
print(self.state[i, j], end=' ')
print("\n")
print('->')
return
def getEmptyPos(self):
postion = np.where(self.state == self.symbol)
return postion
def generateSubStates(self):
if not self.direction:
return []
subStates = []
boarder = len(self.state) - 1
# the maximum of the x,y
row, col = self.getEmptyPos()
if 'left' in self.direction and col > 0:
#it can move to left
s = self.state.copy()
temp = s.copy()
s[row, col] = s[row, col-1]
s[row, col-1] = temp[row, col]
news = State(s, directionFlag='right', parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
if 'up' in self.direction and row > 0:
#it can move to upper place
s = self.state.copy()
temp = s.copy()
s[row, col] = s[row-1, col]
s[row-1, col] = temp[row, col]
news = State(s, directionFlag='down', parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
if 'down' in self.direction and row < boarder: #it can move to down place
s = self.state.copy()
temp = s.copy()
s[row, col] = s[row+1, col]
s[row+1, col] = temp[row, col]
news = State(s, directionFlag='up', parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
if self.direction.count('right') and col < boarder: #it can move to right place
s = self.state.copy()
temp = s.copy()
s[row, col] = s[row, col+1]
s[row, col+1] = temp[row, col]
news = State(s, directionFlag='left', parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
return subStates
def solve(self):
# generate a empty openTable
openTable = []
# generate a empty closeTable
closeTable = []
# append the origin state to the openTable
openTable.append(self)
steps = 1
# start the loop
while len(openTable) > 0:
n = openTable.pop(0)
closeTable.append(n)
subStates = n.generateSubStates()
path = []
for s in subStates:
if (s.state == s.answer).all():
while s.parent and s.parent != originState:
path.append(s.parent)
s = s.parent
path.reverse()
return path, steps+1
openTable.extend(subStates)
steps += 1
else:
return None, None
if __name__ == '__main__':
# the symbol representing the empty place
# you can change the symbol at here
symbolOfEmpty = ' '
State.symbol = symbolOfEmpty
# set the origin state of the puzzle
originState = State(np.array([[2, 8, 3], [1, 6 , 4], [7, symbolOfEmpty, 5]]))
# and set the right answer in terms of the origin
State.answer = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [8, State.symbol, 4], [7, 6, 5]])
s1 = State(state=originState.state)
path, steps = s1.solve()
if path: # if find the solution
for node in path:
# print the path from the origin to final state
node.showInfo()
print(State.answer)
print("Total steps is %d" % steps)
A*算法
import numpy as np
import operator
O=int(input(("请输入方阵的行/列数:")))
A=list(input("请输入初始状态:"))
B=list(input("请输入目标状态:"))
z=0
M=np.zeros((O,O))
N=np.zeros((O,O))
for i in range(O):
for j in range(O):
M[i][j]=A[z]
N[i][j]=B[z]
z=z+1
openlist=[]#open表
class State:
def __init__(self,m):
self.node=m#节点代表的状态
self.f=0#f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
self.g=0#g(n)
self.h=0#h(n)
self.father=None#节点的父亲节点
init = State(M)#初始状态
goal=State(N)#目标状态
#启发函数
def h(s):
a=0
for i in range(len(s.node)):
for j in range(len(s.node[i])):
if s.node[i][j]!=goal.node[i][j]:
a=a+1
return a
#对节点列表按照估价函数的值的规则排序
def list_sort(l):
cmp=operator.attrgetter('f')
l.sort(key=cmp)
#A*算法
def A_star(s):
global openlist#全局变量可以让open表进行时时更新
openlist=[s]
while(openlist):#当open表不为空
get=openlist[0] #取出open表的首节点
if (get.node==goal.node).all():#判断是否与目标节点一致
return get
openlist.remove(get)#将get移出open表
#判断此时状态的空格位置
for a in range(len(get.node)):
for b in range(len(get.node[a])):
if get.node[a][b]==0:
break
if get.node[a][b]==0:
break
#开始移动
for i in range(len(get.node)):
for j in range(len(get.node[i])):
c=get.node.copy()
if (i+j-a-b)**2==1:
c[a][b]=c[i][j]
c[i][j]=0
new=State(c)
new.father=get#此时取出的get节点成为新节点的父亲节点
new.g=get.g+1#新节点与父亲节点的距离
new.h=h(new)#新节点的启发函数值
new.f=new.g+new.h#新节点的估价函数值
openlist.append(new)#加入open表中
list_sort(openlist)#排序
def printpath(f):
if f is None:
return
#注意print()语句放在递归调用前和递归调用后的区别。放在后实现了倒叙输出
printpath(f.father)
print(f.node)
final=A_star(init)
if final:
print("有解,解为:")
printpath(final)
else:
print("无解")
参考代码:blog