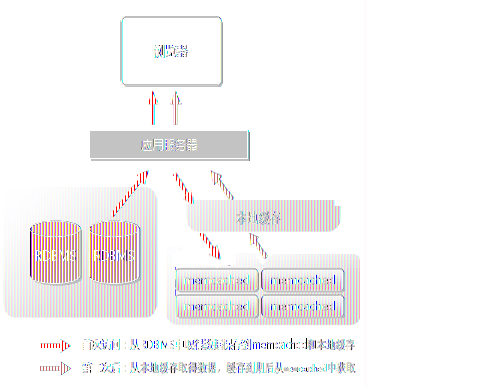
在Discuz!NT中进行缓存分层(本地缓存+memcached)
在以前的两篇文章(Discuz!NT 缓存设计简析, Discuz!NT中集成Memcached分布式缓存)中,介绍了Discuz!NT中的缓存设计思路以及如何引入Memcached,当然前者是IIS进程的缓存(本地缓存),后者是分布式内存对象缓存系统。
两者通过Discuz!NT中的memcached.config文件中的ApplyMemCached结点的值来决定使用哪一种缓存方式。不过在之后,有朋友反映当使用Memcached时,特别是在大并发来时,效率会打折扣,甚至有很多时间会消耗在socket套接字(创建和传输方面)上。而事实上也的确如此,尽管Memcached在使用池化的方式初始化一定数量的套接字资源(之前测试时实始化为128个链接),在小并发(100左右)时,可能问题不大,但并发上了1000-2000时,其效率要比本地化缓存机制低1/3(loadrunner测试场景),比如loadrunner测试1000并发时,如果showtopic(显示主题),本地缓存处理时间为15秒,而使用memcached可能会达到25-35秒。
显然这是用户所不能忍受的,所以要想解决方案。也就有了今天的文章。
其实要解决这个问题的原理很简单,就是将之前的两种缓存方案(本地缓存和memcached)进行整合,原理如下:
首先在iis进程中会将要缓存的数据缓存一份,同时也将该数据放入memcached一份,当然本地缓存的数据生命周期要比memcached少。这就造成本地缓存数据到期后,当再次访问其则将memcached中的数据加载到本地缓存中并返回给应用程序。当缓存的数据更新时,则要更新memcached中的数据和本地缓存的数据(当然如果你要将应用程序布署的到多个站点时,因为不同的站点运行在不同的web园或主机上,这时你就不可以用最简单的方式来更新其它进程和主机上的应用程序了,因为当前缓存的数据只保存在当前web园进程中),这也就是为什么要给本地缓存数据设置到期时间这个值,让其在到期后来自动从memcached获取数据。
原理解释完了之后,我们来看看如何实现这个方案.
首先,我们要看一下默认的本地缓存策略文件,其功能也就是两年前所说的那个本地缓存策略功能,如下:
/// 默认缓存管理类
/// </summary>
public class DefaultCacheStrategy : ICacheStrategy
{
private static readonly DefaultCacheStrategy instance = new DefaultCacheStrategy();
protected static volatile System.Web.Caching.Cache webCache = System.Web.HttpRuntime.Cache;
/// <summary>
/// 默认缓存存活期为3600秒(1小时)
/// </summary>
protected int _timeOut = 3600 ;
private static object syncObj = new object ();
/// <summary>
/// 构造函数
/// </summary>
static DefaultCacheStrategy()
{}
/// <summary>
/// 设置到期相对时间[单位: 秒]
/// </summary>
public virtual int TimeOut
{
set { _timeOut = value > 0 ? value : 3600 ; }
get { return _timeOut > 0 ? _timeOut : 3600 ; }
}
public static System.Web.Caching.Cache GetWebCacheObj
{
get { return webCache; }
}
/// <summary>
/// 加入当前对象到缓存中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="objId"> 对象的键值 </param>
/// <param name="o"> 缓存的对象 </param>
public virtual void AddObject( string objId, object o)
{
if (objId == null || objId.Length == 0 || o == null )
{
return ;
}
CacheItemRemovedCallback callBack = new CacheItemRemovedCallback(onRemove);
if (TimeOut == 7200 )
{
webCache.Insert(objId, o, null , DateTime.MaxValue, TimeSpan.Zero, System.Web.Caching.CacheItemPriority.High, callBack);
}
else
{
webCache.Insert(objId, o, null , DateTime.Now.AddSeconds(TimeOut), System.Web.Caching.Cache.NoSlidingExpiration, System.Web.Caching.CacheItemPriority.High, callBack);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 加入当前对象到缓存中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="objId"> 对象的键值 </param>
/// <param name="o"> 缓存的对象 </param>
public virtual void AddObjectWith( string objId, object o)
{
if (objId == null || objId.Length == 0 || o == null )
{
return ;
}
CacheItemRemovedCallback callBack = new CacheItemRemovedCallback(onRemove);
webCache.Insert(objId, o, null , System.DateTime.Now.AddSeconds(TimeOut), System.Web.Caching.Cache.NoSlidingExpiration, System.Web.Caching.CacheItemPriority.High, callBack);
}
/// <summary>
/// 加入当前对象到缓存中,并对相关文件建立依赖
/// </summary>
/// <param name="objId"> 对象的键值 </param>
/// <param name="o"> 缓存的对象 </param>
/// <param name="files"> 监视的路径文件 </param>
public virtual void AddObjectWithFileChange( string objId, object o, string [] files)
{
if (objId == null || objId.Length == 0 || o == null )
{
return ;
}
CacheItemRemovedCallback callBack = new CacheItemRemovedCallback(onRemove);
CacheDependency dep = new CacheDependency(files, DateTime.Now);
webCache.Insert(objId, o, dep, System.DateTime.Now.AddSeconds(TimeOut), System.Web.Caching.Cache.NoSlidingExpiration, System.Web.Caching.CacheItemPriority.High, callBack);
}
/// <summary>
/// 加入当前对象到缓存中,并使用依赖键
/// </summary>
/// <param name="objId"> 对象的键值 </param>
/// <param name="o"> 缓存的对象 </param>
/// <param name="dependKey"> 依赖关联的键值 </param>
public virtual void AddObjectWithDepend( string objId, object o, string [] dependKey)
{
if (objId == null || objId.Length == 0 || o == null )
{
return ;
}
CacheItemRemovedCallback callBack = new CacheItemRemovedCallback(onRemove);
CacheDependency dep = new CacheDependency( null , dependKey, DateTime.Now);
webCache.Insert(objId, o, dep, System.DateTime.Now.AddSeconds(TimeOut), System.Web.Caching.Cache.NoSlidingExpiration, System.Web.Caching.CacheItemPriority.High, callBack);
}
/// <summary>
/// 建立回调委托的一个实例
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key"></param>
/// <param name="val"></param>
/// <param name="reason"></param>
public void onRemove( string key, object val, CacheItemRemovedReason reason)
{
switch (reason)
{
case CacheItemRemovedReason.DependencyChanged:
break ;
case CacheItemRemovedReason.Expired:
{
// CacheItemRemovedCallback callBack = new CacheItemRemovedCallback(this.onRemove);
// webCache.Insert(key, val, null, System.DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(TimeOut),
// System.Web.Caching.Cache.NoSlidingExpiration,
// System.Web.Caching.CacheItemPriority.High,
// callBack);
break ;
}
case CacheItemRemovedReason.Removed:
{
break ;
}
case CacheItemRemovedReason.Underused:
{
break ;
}
default : break ;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 删除缓存对象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="objId"> 对象的关键字 </param>
public virtual void RemoveObject( string objId)
{
if (objId == null || objId.Length == 0 )
{
return ;
}
webCache.Remove(objId);
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回一个指定的对象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="objId"> 对象的关键字 </param>
/// <returns> 对象 </returns>
public virtual object RetrieveObject( string objId)
{
if (objId == null || objId.Length == 0 )
{
return null ;
}
return webCache.Get(objId);
}
}
因为在一开始设计Discuz!NT缓存方案时,就使用了Strategy(策略)模式,所以这里我们只要将上面所说的改动方案以继承的方式继承自上面的
DefaultCacheStrategy 之后,就可以在DNTCache中使用它了。因为之前我已经将memcached引入到了discuznt产品中,所以这里只要改动一下已有的那个MemCachedStrategy,使其支持上面所说的缓存分布方案即可,请看下面的代码:
/// 企业级MemCache缓存策略类,只能使用一个web园程序
/// </summary>
public class MemCachedStrategy : DefaultCacheStrategy
{
/// <summary>
/// 添加指定ID的对象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="objId"></param>
/// <param name="o"></param>
public override void AddObject( string objId, object o)
{
// 先向本地cached加入,然后再加到memcached
RemoveObject(objId);
base .AddObject(objId, o);
MemCachedManager.CacheClient.Set(objId, o);
}
/// <summary>
/// 添加指定ID的对象(关联指定文件组)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="objId"></param>
/// <param name="o"></param>
/// <param name="files"></param>
public override void AddObjectWithFileChange( string objId, object o, string [] files)
{
;
}
/// <summary>
/// 添加指定ID的对象(关联指定键值组)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="objId"></param>
/// <param name="o"></param>
/// <param name="dependKey"></param>
public override void AddObjectWithDepend( string objId, object o, string [] dependKey)
{
;
}
/// <summary>
/// 移除指定ID的对象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="objId"></param>
public override void RemoveObject( string objId)
{
// 先移除本地cached,然后再移除memcached中的相应数据
if ( base .RetrieveObject(objId) != null )
base .RemoveObject(objId);
if (MemCachedManager.CacheClient.KeyExists(objId))
MemCachedManager.CacheClient.Delete(objId);
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回指定ID的对象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="objId"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public override object RetrieveObject( string objId)
{
object obj = base .RetrieveObject(objId);
if (obj == null )
{
obj = MemCachedManager.CacheClient.Get(objId);
if (obj != null )
base .AddObject(objId, obj);
}
return obj;
}
/// <summary>
/// 到期时间
/// </summary>
public override int TimeOut
{
get
{
return MemCachedConfigs.GetConfig().LocalCacheTime;
}
}
}
注:MemCachedStrategy 原来已实现了ICacheStrategy接口,参见这篇文章。
这样,我们还是可以通过memcached.config中的ApplyMemCached来判断是否使用本地缓存方案还是当前的缓存分层方案。当然原有的memcache.config中还有添加一下属性用于记录当使用缓存分层方案之后的本地缓存的缓存数据时间,以向上面的类属性TimeOut注入相应参数信息。
这样memcached.config的内容就会变成这个样子(本地测试配置):
< MemCachedConfigInfo xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance%22 xmlns:xsd=" http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema%22 >
< ApplyMemCached > true </ ApplyMemCached >
< ServerList > 10.0.2.137:11211 </ ServerList >
< PoolName > DiscuzNT_MemCache </ PoolName >
< IntConnections > 128 </ IntConnections >
< MinConnections > 128 </ MinConnections >
< MaxConnections > 512 </ MaxConnections >
< SocketConnectTimeout > 1000 </ SocketConnectTimeout >
< SocketTimeout > 3000 </ SocketTimeout >
< MaintenanceSleep > 30 </ MaintenanceSleep >
< FailOver > true </ FailOver >
< Nagle > true </ Nagle >
< LocalCacheTime > 60 </ LocalCacheTime >
</ MemCachedConfigInfo >
这样,当使用Lr测试时,其在并发1000的情况下与使用本地缓存方案的响应时间基本稳定在15秒左右,想一下大家就会明白了,因为在数据首次加载并进行缓存时(本地和memcached都会缓存一份,参见上面的实现代码)。当再次访问时,如在60秒的数据有效期内,仅访问本地缓存,只有在数据过期时间,才会运行再次加载数据的工作,而这种加载也只是从memcached中获得数据,这里我们可以暂时将memcached中的数据想像是永不过期,这样就可以减少对database的访问压力,因为这时相对于本地缓存而言,memcached已经变成了一个‘缓存数据库’了:
{
object obj = base .RetrieveObject(objId);
if (obj == null )
{
obj = MemCachedManager.CacheClient.Get(objId);
if (obj != null )
base .AddObject(objId, obj);
}
return obj;
}
现在用两张图再对比说明之前的memcached与现在的缓存分层方案:
改进后:
总结:其实在大网站的数据缓存方案中,往往会将大量的数据(不经常变化或对时效性要求不强,但却需频繁访问的数据)放入到缓存中,以此来降低数据库的负载。本地缓存数据的时效性和稳定性受制于IIS进程中线程的运行情况,资源的占用等因素影响,可以说数据的稳定性(不易丢失)远不如memcached,所以这种分层方案可以有效的解决这个问题,当然这种做法还有一些其它方面的好处,就不一一说明了。
原文链接: http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2009/11/17/1604436.html
作者: daizhj, 代震军
Tags: discuz!nt,memcached,分层
网址: http://daizhj.cnblogs.com/