最小生成树与二分图
最小生成树与二分图
- 最小生成树
-
- Prim算法
- Kruskal算法
- 二分图
-
- 染色法
-
- dfs
- bfs
- 匈牙利法
最小生成树
Prim算法
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/860/
算法思想
维护一个集合,每次找到一条集合中点可以到达的最小的边,然后把这条边的终点记录在集合中,继续重复迭代,直到所有的点都选择完毕。
时间复杂度:因为是两层循环,所以说时间复杂度还是O(n2)。
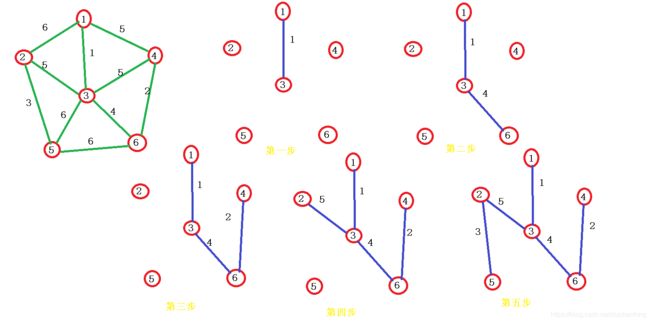
算法流程
源代码
#include Kruskal算法
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/861/
算法思想
首先先对所有的边从小到大排序,然后在保证没有回路的前提下选出权重较小的 n − 1 n-1 n−1条边,如果 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)是所有集合中没有选择的边中权重最小的,并且 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)不会和已选的边构成回路。如果 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)的两个 点 i i i 和 j j j 同属于一个连通分支,那么选择 i i i 和 j j j会构成回路,反之则不会。
连通分支
对于一个无向图而言,它的一个极大连通子图即为一连通支。比如说,一个图由三部分构成,其中每一部分都是连通的,但三个部分之间互相不连通,那么每一部分即为无向图的一个连通分支。此图的连通分支数为3。
时间复杂度:给每个边排序的时间复杂度为 O ( n ∗ l o g n ) O(n * logn) O(n∗logn),选择边的时候时间复杂度是 O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn),所以说总的时间复杂度是 O ( n ∗ l o g n ) O(n * logn) O(n∗logn)。

算法流程
#include 二分图
二分图,就是在一个图中,一定不含有奇数个节点的环;(不构成环的连通分支,是特殊的二分图)
二分图不一定要求是连通的,可以是几个连通图构成的
染色法
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/862/
算法思路
将所有点分成两个集合,使得所有边只出现在集合之间
dfs
流程
- 染色可以使用1和2区分不同颜色,用0表示未染色
- 遍历所有点,每次将未染色的点进行
dfs, 默认染成1或者2,算法中可以使用 3 − c 3-c 3−c - 由于某个点染色成功不代表整个图就是二分图,因此只有某个点染色失败才能立刻
break/return,染色失败相当于至少存在2个点染了相同的颜色
#include bfs
算法流程
bool bfs(int u) {
color[u] = 1; // 当前节点染色为 c 颜色,那么他的下一个节点应该为 3-c 颜色 1,2
queue<int> que;
que.push(u);
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
while(size --) {
int f = que.front();
que.pop();
for(int i = h[f]; ~i ; i = ne[i]) {
int v = e[i];
if(!color[v]) {
color[v] = 3 - color[f];
que.push(v);
} else if ( color[f] == color[v] ){
// 与下一个节点的染色出现矛盾
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
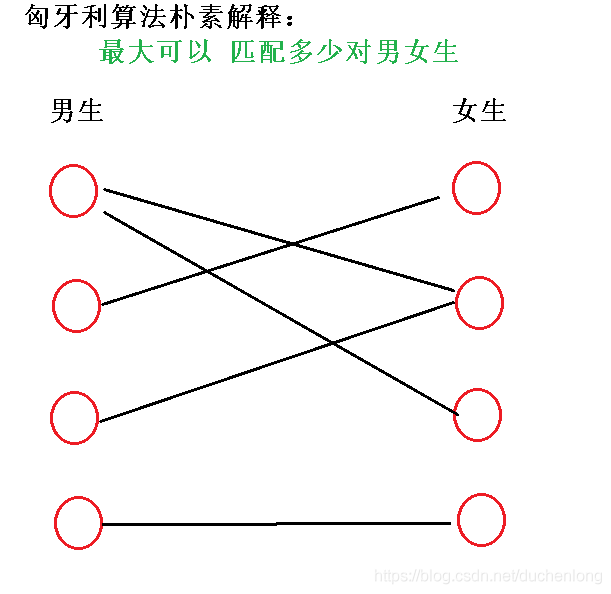
匈牙利法
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/863/
算法描述
就是在一个二分图中,每个集合中的点只能用一次,问可以连多少条边
yxz人生导师的描述
两个集合,一个男生,一个女生。
已知每个男生钟意的女生编号,为尽量多的男生进行分配,hha
如果男生钟意的妹子已经有了男朋友,
你就去问问她男朋友,
你有没有备胎,
把这个让给我好吧
#include