springboot缓存使用 springboot-cache、整合Redis
JSR-107
Java Caching定义了五个接口,分别是CachingProvider、CacheManager、Cache、Entry、Expiry。
- CachingProvider:定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可
以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。 - CacheManager:定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache
存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。 - Cache:是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个
CacheManager所拥有。 - Entry:存储在Cache中的key-value对。
- Expiry: 每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期
的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
注:应用程序先访问缓存提供者CachingProvider,CachingProvider管理了多个缓存管理器CachingManager,而CachingManage里面才管理了多个真正的缓存Cache组件,跟系统进行缓存的CRUD操作用到的是Cache组件。
JSR107中定义了很多简化缓存开发的注解,但并不是所有的缓存组件都提供了JSR107的实现,需要自己编写JSR107的实现,难度也较大,所以JSR107用的比较少。为了简化开发,Spring提供了自己的缓存抽象,也定义了类似JSR107的注解。
Spring缓存抽象
1、简介
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术;并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发;
Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
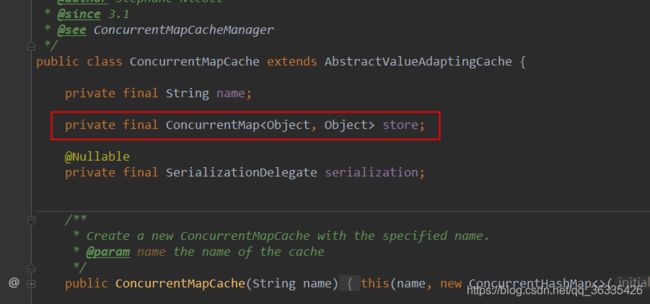
Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache , ConcurrentMapCache等;
2、常用缓存注解和参数
注解
| 注解 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| @Cacheable | 先查找缓存 , 有就返回 ,没有就执行方法 ,并将结果缓存起来 |
| @Cacheput | 先执行方法 , 再将结果缓存起来 |
| @CacheEvict | 删除缓存数据 |
| @EnableCaching | 开启基于注解的缓存 |
| @CacheConfig | 作用在类上,抽取缓存的公共配置 |
参数
| 参数 | 备注 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|
| keyGenerator | 缓存数据时key生成策略 | |
| serialize | 缓存数据时value序列化策略 | |
| value | 缓存的名称,至少一个 | @Cacheable(value=”mycache”) |
| key | 缓存的key,默认是方法的参数 | @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
| condition | 指定符合条件的情况下才缓存 | @Cacheable(condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
| unless | 当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会被缓存 | @Cacheable(unless=”#result == null”) |
| allEntries | 是否清空所有缓存,默认false | @CachEvict(allEntries=true) |
| beforeInvocation | 是否在执行方法区就清空缓存,默认false | @CachEvict(beforeInvocation=true) |
| sync | 是否使用异步模式,默认false,使用了sync就不能使用unless |
SpringBoot缓存实战
1、引入pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cacheartifactId>
dependency>
2、SpringCacheApplication启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching //开启注解缓存
public class SpringCacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
3、CacheService 缓存实现类
package com.cao.service;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author:秋一叶
* @date:2020-12-02 9:23
*/
//抽取缓存的公共配置-缓存key
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = CacheService.CACHE_KEY)
@Service
public class CacheService {
//缓存key
public static final String CACHE_KEY = "test-cache";
/**
* 获取缓存:没有缓存就执行方法并将结果缓存起来;
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = CACHE_KEY)
public String getCache(String id){
return getString(id);
}
/**
* 更新缓存:先执行方法,再将结果缓存起来;
*/
@CachePut(cacheNames = CACHE_KEY)
public String updateCache(String id){
return getString(id);
}
/**
* 清除缓存:删除缓存数据
*/
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = CACHE_KEY)
public void removeCache(String id){
System.out.println("删除缓存" + id);
}
/**
* 获取String,模拟调用方法
* @param id
* @return
*/
public String getString(String id){
return id;
}
}
缓存原理
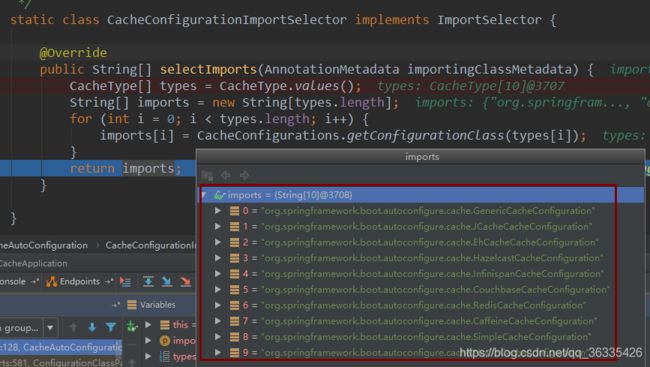
引入了缓存相关的依赖,缓存的自动配置类CacheAutoConfiguration就会生效,CacheAutoConfiguration自动导入了CacheConfigurationImportSelector;
1、缓存的自动配置类;CacheAutoConfiguration
- CacheAutoConfiguration配置列中导入了缓存配置类CacheConfigurationImportSelector,返回了10个缓存配置类;
2、缓存的配置类
3、哪个配置类生效
- 配置文件中开启自动配置报告可以在控制台查看哪个配置类生效了。
application.properties:
#开启自动配置报告
debug=true
-
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration【默认使用这个】
-
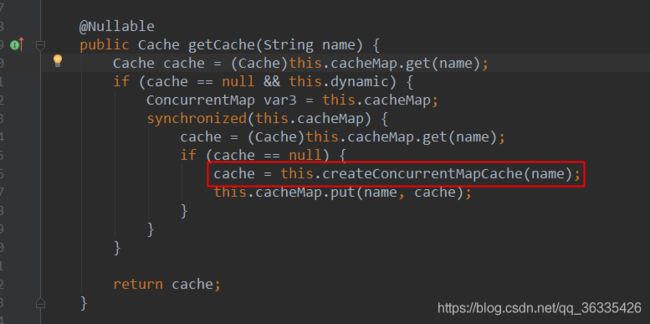
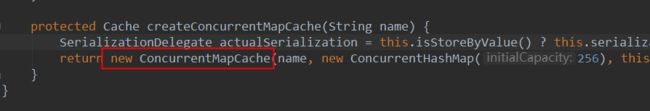
默认是SimpleCacheConfiguration,给容器中注册了一个缓存管理器ConcurrentMapCacheManager,可以获取和创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的缓存组件,ConcurrentMapCache的作用可以将数据保存在ConcurrentMap中。
SpringBoot整合redis实现缓存
1、添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
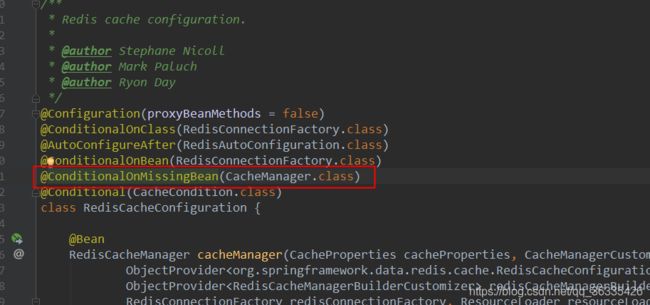
引入了redis相关的场景,RedisCacheConfiguration自动配置类就起作用了;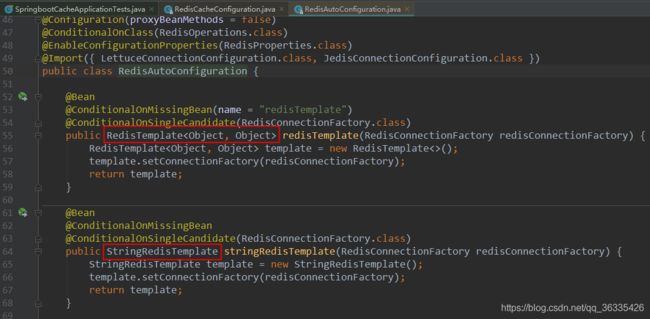
2、application.properties中添加redis配置
#开启自动配置报告
#debug=true
#配置redis
spring.redis.host=192.168.6.21
3、测试类
package com.cao;
import com.cao.spring_guava.springboot_cache.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootCacheApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; //操作k-v都是字符串的
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; //操作k-v都是对象的
@Test
public void redisCacheTest() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("秋一叶");
user.setAge(18);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("用户", user);
}
}
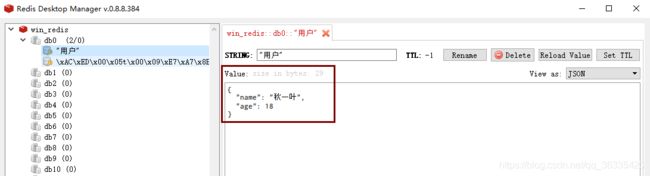
4、结果
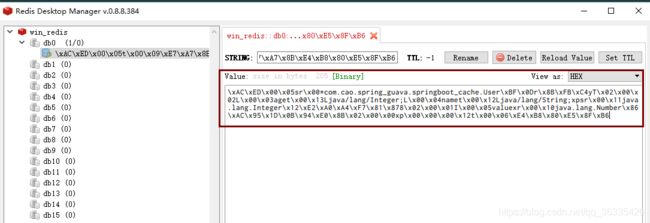
- 用redis客户端连接redis服务器,里面可以看到存的对象形式不是我们想要的。因为如果保存对象,默认使用jdk序列化机制,序列化后的数据保存到redis;
- 如果需要将数据以json的形式保存到redis,改变redisTemplate默认的序列化规则,自己定义;
5、自定义序列化规则
- MyRedisConfig类
package com.cao.spring_guava.springboot_cache.config;
import com.cao.spring_guava.springboot_cache.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
/**
* @Author 秋一叶
* @Date 2020/12/16 - 21:35
*/
@Configuration
public class MyRedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, User> userRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, User> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<User> userJackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<User>(User.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(userJackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}
}
- 测试类
package com.cao;
import com.cao.spring_guava.springboot_cache.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootCacheApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<Object, User> userRedisTemplate; //使用自定义的redisTemplate
@Test
public void redisCacheTest() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("秋一叶");
user.setAge(18);
userRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("用户", user);
}
}
6、自定义缓存管理器 RedisCacheManager
package com.cao.spring_guava.springboot_cache.config;
import com.cao.spring_guava.springboot_cache.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
/**
* @Author 秋一叶
* @Date 2020/12/16 - 21:35
*/
@Configuration
public class MyRedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, User> userRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, User> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<User> userJackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<User>(User.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(userJackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}
//自定义缓存管理器
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager deptCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, User> userRedisTemplate){
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(userRedisTemplate);
return cacheManager;
}
}