C++进阶(二)四种类型转换(static_cast, const_cast, dynamic_cast, reinterpret_cast)
C++进阶(二)四种类型转换(static_cast, const_cast, dynamic_cast, reinterpret_cast)
-
- static_cast 类型转换
- const_cast 类型转换
- reinterpret_cast 类型转换
- dynamic_cast 类型转换
- 巨人的肩膀
在 C 语言中,如果要对类型进行转换,直接使用强制类型转换。这种转换使得表达式的精度有所损失,会出现一些未定义错误。这种强制转换方式有如下缺点:
- 任何类型都能进行强制转换,编译器很难判断其正确性
- 在源码中,无法定位所有强制类型转换的语句
(Type) (expression);
Type(expression);
C++中提出4种安全可靠的类型转换方式:static_cast,const_cast,dynamic_cast,reinterpret_cast 。下面来分别介绍每种类型转换的应用场景及用法。
static_cast 类型转换
static_cast 是一种静态类型转换,用于基本类型转换,但不能用于基本类型指针之间的转换。也可用于继承关系的类对象的转换和类指针之间的转换。
示例1:基本类型之间的转换
#include 示例2:static_cast 不能用于指针之间的类型转换
#include 编译出错,无法将 int* 转换为 char* 类型。
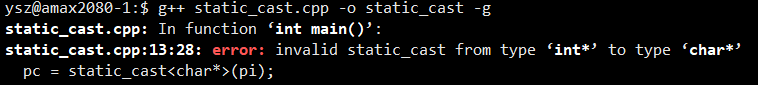
注释掉指针类型后,编译执行即可通过,下面再看下从int 类型强制转换为 char 类型,编译器如何转换。

示例3:类中定义类型转换函数(operator Type())
#include 编译运行,输出如下:
Conversion Ctor called
Conversion Operator
Conversion Ctor called
Conversion Operator
Conversion Ctor called
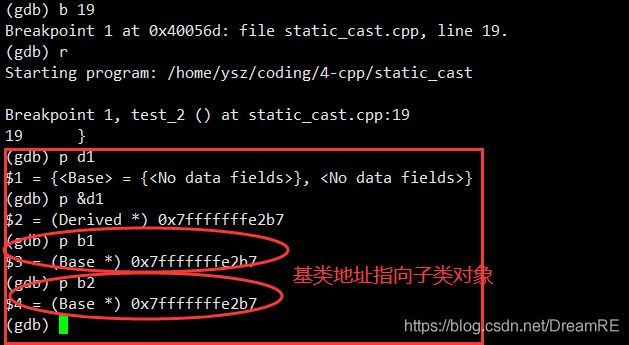
示例4:继承关系的类对象之间的转换,基类指针指向父类对象
#include 编译指向,可以看到使用 static_cast 类型转换符将基类指针指向子类对象。
const_cast 类型转换
const_cast 用于去除变量的只读属性,强制转换的目标类型是指针或引用。
示例一:在 const 成员函数中修改类中 non-const 成员变量。
#include 编译运行结果如下:
Old roll number: 3
New roll number: 5
在const 成员函数中,将this 指针修改为 const Student* const ,使用 const_cast 强制类型转换,使得const Student* const 修改为 Student* const ,所以可以修改 Student对象。
示例2:将常量指针强制转换为普通指针
int fun(int* ptr)
{
return (*ptr + 10);
}
int main(void)
{
const int val = 10;
const int *ptr = &val;
int *ptr1 = const_cast <int *>(ptr); // 转换为普通指针,作为参数传递
cout << fun(ptr1);
return 0;
}
示例3:const_cast 将指向const对象的指针进行强制类型转换,会产生未定义行为。
#include 程序可以编译运行,但是会输出10。因为在指向常量值,常量值无法改变。
示例4:const_cast 类型安全,无法在不同的类型之间进行转换
#include 示例5:const_cast 可以将 volatile 类型转化为非 volatitle 类型
#include 编译输出
typeid of b1 PVKi // Pointer to a volatile and constant integer
typeid of c1 Pi // Pointer to integer
reinterpret_cast 类型转换
reinterpret_cast 用于指针类型之间的类型转换,也用于整数与指针之间的类型转换。用法如下
data_type *var_name =
reinterpret_cast <data_type *>(pointer_variable);
示例1:指针类型转换(将int* 强制转换为 char*)
// CPP program to demonstrate working of
// reinterpret_cast
#include 编译输出,将int* 转换为 char* ,输出字符A
65 // 原始数值
A // 将int* 转换为 char*,65 --> A
0xf31c90 // 输出地址
A // 输出字符
示例2:类之间的强制类型转换
// CPP code to illustrate the pointer reinterpret
#include 编译输出,得到
In class A
dynamic_cast 类型转换
dynamic_cast 只能虚函数的类使用,用于具有继承关系的类之间的类型转换;也用于有交叉关系的类指针的类型转换。dynamic_cast 可以进行类型检查。
巨人的肩膀
- C++中
static_cast类型转换 - C++中
const_cast类型转换 - C++中
reinterpret_cast类型转换
一键三连是对我的最大支持与鼓励。欢迎关注编程小镇,每天涨一点新姿势。
