【SSM进阶篇】SSM整合实现商品模块操作
SSM整合实现商品模块
- 版权声明
- 序
-
- 1.原型设计
- 2.需求分析
- 3.业务描述
- 4.业务分析
- 一、创建
-
- 1.项目环境初始化
-
- 1.准备操作
- 2.初始化数据库
- 2.创建Modole
- 3.项目Module基础配置初始化
- 二、商品品牌API设计
- 三、品牌数据的查询及实现
-
- 1.业务描述
- 2.领域对象(POJO)设计及实现
- 3.数据逻辑对象(DAO)查询方法设计及实现
- 4.业务逻辑对象(Service)查询方法设计及实现
- 5.控制逻辑对象(Controller)查询方法设计及实现
- 三、客户端品牌列表页面设计及实现
- 总结
版权声明
本文原创作者:风骨桀骜
作者博客地址:https://windbonely.blog.csdn.net/
该项目已上传Gitee仓库:https://gitee.com/windbone/ssm_shooping/blob/master/LICENSE
提示:项目可下载研究,但是建议读者从头到尾操作一遍,加深知识点。以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
序
1.原型设计
基于品牌业务描述,对品牌模块的业务原型进行分析和设计。
2.需求分析
在品牌管理中就是实现对商品品牌信息的添加,修改,查询,删除等业务
3.业务描述
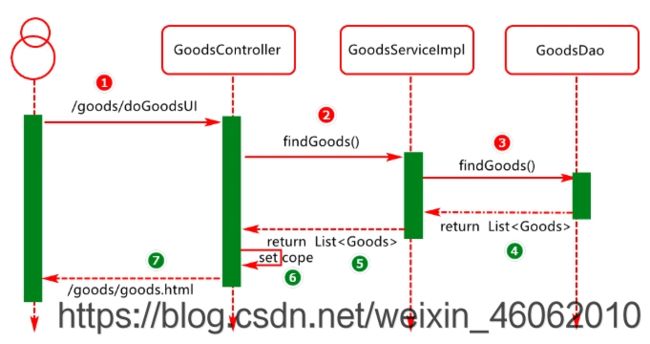
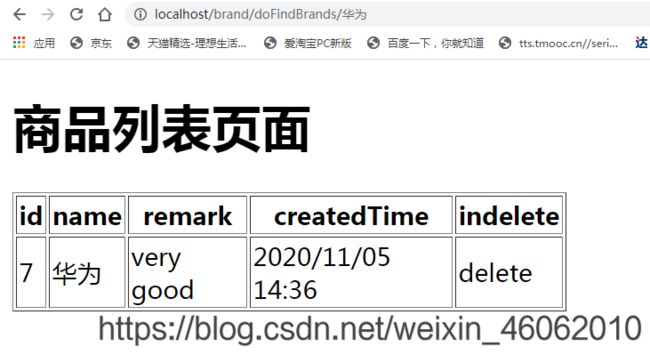
从商品库查询商品信息,转化为商品信息呈现在页面上,如下所示:
4.业务分析
一、创建
1.项目环境初始化
1.准备操作
1)JDK1.8
2)Maven 3.6.3
3)IDEA 2020.2
4)MySQL 5.7+
2.初始化数据库
登录:
mysql -uroot -proot;
设置utf8编码
set name utf8;
执行sql脚本
source d:/brand.sql
brand.sql
drop database if exists dbbrand;
create database dbbrand default character set utf8;
use dbbrand;
create table tb_brand(
id bigint primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(100) not null,
remark text,
createdTime datetime not null
)engine=InnoDB;
insert into tb_brand values (null,'联想','very good',now());
insert into tb_brand values (null,'小米','very good',now());
insert into tb_brand values (null,'美的','very good',now());
insert into tb_brand values (null,'九阳','very good',now());
insert into tb_brand values (null,'TCL','very good',now());
insert into tb_brand values (null,'创维','very good',now());
insert into tb_brand values (null,'华为','very good',now());
2.创建Modole
3.项目Module基础配置初始化
在项目文件中找到:src->main->resources->application.properties中填入:
spring.main.banner-mode=off
#server
server.port=80
#server.servlet.context-path=/
#spring datasource
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql:///dbbrand?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=utf8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
#spring mybatis
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:/mapper/*/*.xml
#spring logging
logging.level.com.cy=debug
#spring thymeleaf
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
二、商品品牌API设计
示例:pandas 是基于NumPy 的一种工具,该工具是为了解决数据分析任务而创建的。
三、品牌数据的查询及实现
1.业务描述
代码如下(示例):
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
import ssl
ssl._create_default_https_context = ssl._create_unverified_context
2.领域对象(POJO)设计及实现
设置Brand对象,基于此对象封装从数据库查询到的品牌信息,代码如下:
package com.cy.brand.pojo;
import java.util.Date;
public class Brand {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String logo;
private String remark;
private Date createdTime;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getLogo() {
return logo;
}
public void setLogo(String logo) {
this.logo = logo;
}
public String getRemark() {
return remark;
}
public void setRemark(String remark) {
this.remark = remark;
}
public Date getCreatedTime() {
return createdTime;
}
public void setCreatedTime(Date createdTime) {
this.createdTime = createdTime;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Brand{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", logo='" + logo + '\'' +
", remark='" + remark + '\'' +
", createdTime=" + createdTime +
'}';
}
}
3.数据逻辑对象(DAO)查询方法设计及实现
第一步:定义BrandDao接口,代码如下:
package com.cy.band.dao;
import com.cy.brand.pojo.Brand;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface BrandDao {
}
第二步:在BrandDao定义品牌查询方法,代码如下:
List<Brand> findBrands(String name);
第三步:基于查询方法定义SQL映射(本次sql映射基于注解方式定义)代码如下:
@Select("select * from tb_bread where name like concat('%',#{name},'%')")
List<Brand> findBrands(String name);
有时候相比之下,过于复杂的sql不建议已注解方式进行定义
//@Select("")
List<Brand> findBrands(String name);
建议在配置文件resources下创建
文件夹:mapper.brand
重点:创建的时候IDEA会把“ / “ 自动转换" . "
文件:BrandMapper.xml映射sql语句(复杂sql语句推荐用这Mybatis映射)
<mapper namespace="com.cy.band.dao.BrandDao">
<select id="findBrands" resultType="com.cy.brand.pojo.Brand">
select * from tb_brand
<if test="name!=null and name!=''">
where name like concat("%",#{name},"%")
if>
select>
mapper>
第四步:对数据层的查询方法进行单元测试。代码如下:
package com.cy.brand.dao;
import com.cy.band.dao.BrandDao;
import com.cy.brand.pojo.Brand;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class BrandDaoTest {
@Autowired
private BrandDao brandDao;
@Test
void testBrandDao(){
List<Brand> list= brandDao.findBrands("c");
for(Brand brand:list){
System.out.println(brand);
}
}
}
4.业务逻辑对象(Service)查询方法设计及实现
业务逻辑对象负责模块的具体业务处理,例如参数校验,事物控制,权限控制,日志记录等。
第一步:定义业务接口
package com.cy.band.Service;
import com.cy.brand.pojo.Brand;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface BrandService {
}
第二步:在BrandSevice接口中添加品牌查询方法
List<Brand> findBrands(String name);
第三部:定义BrandService接口实现BrandServiceImpl
package com.cy.band.Service.Impl;
import com.cy.band.Service.BrandService ;
import com.cy.band.dao.BrandDao;
import com.cy.brand.pojo.Brand;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class BrandServiceImpl implements BrandService {
private static final Logger log=//这里的实现在springboot中默认选择的是logger
LoggerFactory.getLogger(BrandServiceImpl.class);
@Autowired
private BrandDao brandDao;
@Override
public List<Brand> findBrands(String name){
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
List<Brand> list=brandDao.findBrands(name);
long t2=System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("findBrands->time->{}",(t2-t1));
return list;
}
}
5.控制逻辑对象(Controller)查询方法设计及实现
在控制逻辑对象中主要是负责请求和响应逻辑控制,例如请求url映射,参数映射,请求方式,结果集的封装,结果集的解析
package com.cy.brand.controller;
import com.cy.band.Service.BrandService;
import com.cy.brand.pojo.Brand;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class BrandController {
@Autowired
private BrandService brandService;
//http://localhost/brand/doFindBrands/?name=tcl 传统
//http://localhost/brand/doFindBrands/tcl 风格
//rest风格(一种软件架构编码风格)的URL定义
//@PathVariable 注解用于修饰方法参数,目的是告诉springmvc ,参数的值来自url
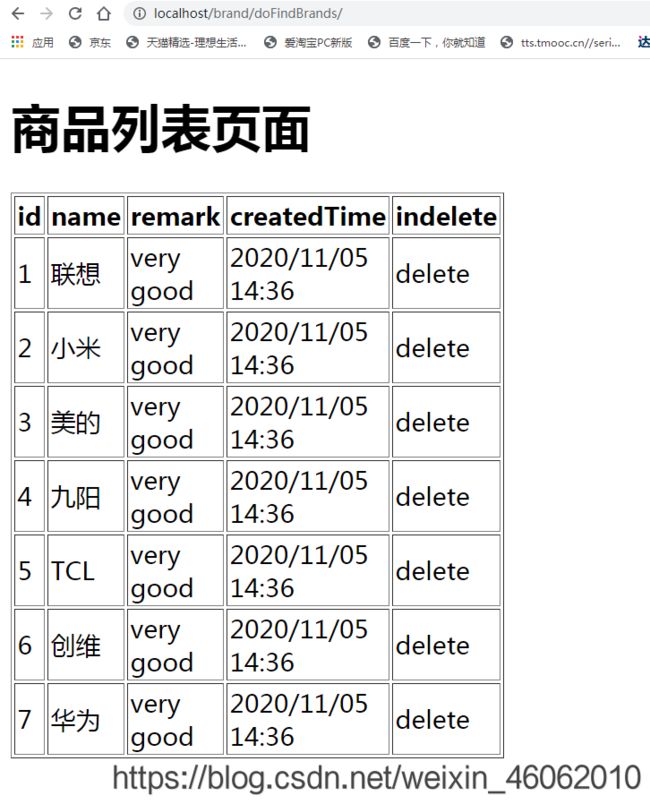
@GetMapping("/brand/doFindBrands/{name}")//rest风格
public String doFindBrands(@PathVariable String name, Model model){
List<Brand> list=brandService.findBrands(name);
model.addAttribute("list",list);
return "brand/brand";//第一个brand目录,第二个brand为view name
}
@GetMapping("/brand/doFindBrands")//显示所有商品
public String doFindBrands1(Model model){
List<Brand> list=brandService.findBrands("");
model.addAttribute("list",list);
return "brand/brand";//第一个brand目录,第二个brand为view name
}
}
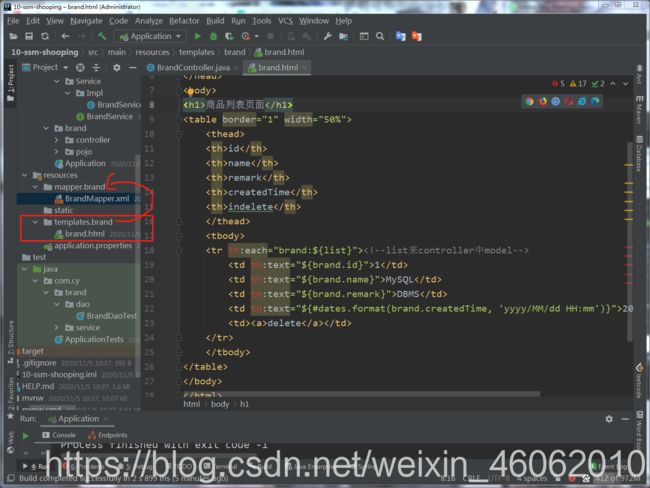
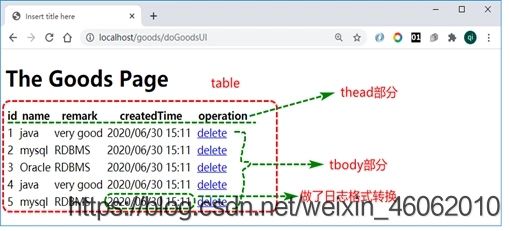
三、客户端品牌列表页面设计及实现
并在body内填入表格
<table border="1" width="50%">
<thead>
<th>idth>
<th>nameth>
<th>remarkth>
<th>createdTimeth>
<th>indeleteth>
thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="brand:${list}">
<td th:text="${brand.id}">1td>
<td th:text="${brand.name}">MySQLtd>
<td th:text="${brand.remark}">DBMStd>
<td th:text="${#dates.format(brand.createdTime, 'yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm')}">2020/07/03td>
<td><a>deletea>td>
tr>
tbody>
table>
总结
这里对文章进行总结:
以上就是今天巩固了SSM整合实现商品模块,仅仅是介绍了SSM的实战商品模块操作,让我觉得心有余而力不足。