从koa-session中间件学习cookie与session
原文链接
关于cookie和session是什么网上有很多介绍,但是具体的用法自己事实上一直不是很清楚,通过koa-session中间件的源码自己也算是对cookie和session大致搞明白了。
在我了解cookie的时候,大多数教程讲的是这些:
function setCookie(name,value)
{
var Days = 30;
var exp = new Date();
exp.setTime(exp.getTime() + Days*24*60*60*1000);
document.cookie = name + "="+ escape (value) + ";expires=" + exp.toGMTString();
} 它给我一个错觉:cookie只能在客户端利用js设置读取删除等,但事实上很多的cookie是由服务端在response的headers里面写进去的:
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use((ctx) => {
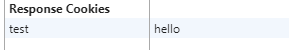
ctx.cookies.set('test', 'hello', {httpOnly: false});
ctx.body = 'hello world';
})
app.listen(3000);访问localhost:3000,打开控制台可以看到:
那么下次浏览器再访问localhost:3000的时候就会把这些cookie信息通过request的headers带给服务器。
了解http协议的话可以经常看到这么一句话:http是无状态的协议。什么意思呢?大致这么理解一下,就是你请求一个网站的时候,服务器不知道你是谁,比如你第一次访问了www.google.com,过了三秒钟你又访问了www.google.com,虽然这两次都是你操作的但是服务器事实上是不知道的。不过根据我们的生活经验,你登录了一个网站后,过了三秒你刷新一下,你还是在登录态的,这好像与无状态的http矛盾,其实这是因为有session。
按照上面的说法,session是用来保存用户信息的,那他与cookie有什么关系,事实上按照我的理解session只是一个信息保存的解决方法,实现这个方法可以有多种途径。既然cookie可以保存信息,那么我们可以直接利用cookie来实现session。对应于koa-session中间件,当我们没有写store的时候,默认即利用cookie实现session。
看一个官方例子:
const session = require('koa-session');
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.keys = ['some secret hurr'];
const CONFIG = {
key: 'koa:sess', /** (string) cookie key (default is koa:sess) */
/** (number || 'session') maxAge in ms (default is 1 days) */
/** 'session' will result in a cookie that expires when session/browser is closed */
/** Warning: If a session cookie is stolen, this cookie will never expire */
maxAge: 86400000,
overwrite: true, /** (boolean) can overwrite or not (default true) */
httpOnly: true, /** (boolean) httpOnly or not (default true) */
signed: true, /** (boolean) signed or not (default true) */
rolling: false, /** (boolean) Force a session identifier cookie to be set on every response. The expiration is reset to the original maxAge, resetting the expiration countdown. default is false **/
};
app.use(session(CONFIG, app));
// or if you prefer all default config, just use => app.use(session(app));
app.use(ctx => {
// ignore favicon
if (ctx.path === '/favicon.ico') return;
let n = ctx.session.views || 0;
ctx.session.views = ++n;
ctx.body = n + ' views';
});
app.listen(3000);
console.log('listening on port 3000');每次我们访问views都会+1。
看一下koa-session是怎么实现的:
module.exports = function(opts, app) {
// session(app[, opts])
if (opts && typeof opts.use === 'function') {
[ app, opts ] = [ opts, app ];
}
// app required
if (!app || typeof app.use !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('app instance required: `session(opts, app)`');
}
opts = formatOpts(opts);
extendContext(app.context, opts);
return async function session(ctx, next) {
const sess = ctx[CONTEXT_SESSION];
if (sess.store) await sess.initFromExternal();
try {
await next();
} catch (err) {
throw err;
} finally {
await sess.commit();
}
};
};一步一步的来看,formatOpts是用来做一些默认参数处理,extendContext的主要任务是对ctx做一个拦截器,如下:
function extendContext(context, opts) {
Object.defineProperties(context, {
[CONTEXT_SESSION]: {
get() {
if (this[_CONTEXT_SESSION]) return this[_CONTEXT_SESSION];
this[_CONTEXT_SESSION] = new ContextSession(this, opts);
return this[_CONTEXT_SESSION];
},
},
session: {
get() {
return this[CONTEXT_SESSION].get();
},
set(val) {
this[CONTEXT_SESSION].set(val);
},
configurable: true,
},
sessionOptions: {
get() {
return this[CONTEXT_SESSION].opts;
},
},
});
}
所以走到下面这个代码时,事实上是新建了一个ContextSession对象sess。这个对象有个属性为session(要保存的session对象),有一些方法用来初始化session(如initFromExternal、initFromCookie),具体是什么下面用到再看。
const sess = ctx[CONTEXT_SESSION]接着看是执行了如下代码,也即执行我们的业务逻辑
await next();然后就是下面这个了,看样子应该是类似保存cookie的操作。
await sess.commit();至此全部流程结束,好像并没有看到有什么初始化session的操作。其实在执行我们的业务逻辑时,假入我们操作了session,如例子:
let n = ctx.session.views || 0;就会触发ctx的session属性拦截器,ctx.session实际上是sess的get方法返回值(返回值其实是一个Session对象),代码如下:
get() {
const session = this.session;
// already retrieved
if (session) return session;
// unset
if (session === false) return null;
// cookie session store
if (!this.store) this.initFromCookie();
return this.session;
}在get里面执行了session的初始化操作,我们考虑没有store的情况即执行initFromCookie();
initFromCookie() {
debug('init from cookie');
const ctx = this.ctx;
const opts = this.opts;
const cookie = ctx.cookies.get(opts.key, opts);
if (!cookie) {
this.create();
return;
}
let json;
debug('parse %s', cookie);
try {
json = opts.decode(cookie);
} catch (err) {
// backwards compatibility:
// create a new session if parsing fails.
// new Buffer(string, 'base64') does not seem to crash
// when `string` is not base64-encoded.
// but `JSON.parse(string)` will crash.
debug('decode %j error: %s', cookie, err);
if (!(err instanceof SyntaxError)) {
// clean this cookie to ensure next request won't throw again
ctx.cookies.set(opts.key, '', opts);
// ctx.onerror will unset all headers, and set those specified in err
err.headers = {
'set-cookie': ctx.response.get('set-cookie'),
};
throw err;
}
this.create();
return;
}
debug('parsed %j', json);
if (!this.valid(json)) {
this.create();
return;
}
// support access `ctx.session` before session middleware
this.create(json);
this.prevHash = util.hash(this.session.toJSON());
}class Session {
/**
* Session constructor
* @param {Context} ctx
* @param {Object} obj
* @api private
*/
constructor(ctx, obj) {
this._ctx = ctx;
if (!obj) {
this.isNew = true;
} else {
for (const k in obj) {
// restore maxAge from store
if (k === '_maxAge') this._ctx.sessionOptions.maxAge = obj._maxAge;
else this[k] = obj[k];
}
}
}很明了的可以看出来其主要逻辑就是新建一个session,第一次访问服务器时session.isNew为true。
当我们执行完业务逻辑时,最后执行sess.commit()
async commit() {
const session = this.session;
const prevHash = this.prevHash;
const opts = this.opts;
const ctx = this.ctx;
// not accessed
if (undefined === session) return;
// removed
if (session === false) {
await this.remove();
return;
}
// force save session when `session._requireSave` set
let changed = true;
if (!session._requireSave) {
const json = session.toJSON();
// do nothing if new and not populated
if (!prevHash && !Object.keys(json).length) return;
changed = prevHash !== util.hash(json);
// do nothing if not changed and not in rolling mode
if (!this.opts.rolling && !changed) return;
}
if (typeof opts.beforeSave === 'function') {
debug('before save');
opts.beforeSave(ctx, session);
}
await this.save(changed);
}commit事保存session前的准备工作,比如在我们没有强制保存session的时候它会判断时候保存session
let changed = true;
if (!session._requireSave) {
const json = session.toJSON();
// do nothing if new and not populated
if (!prevHash && !Object.keys(json).length) return;
changed = prevHash !== util.hash(json);
// do nothing if not changed and not in rolling mode
if (!this.opts.rolling && !changed) return;
}还提供了hook给我们使用
if (typeof opts.beforeSave === 'function') {
debug('before save');
opts.beforeSave(ctx, session);
}到此开始真正的save session
async save(changed) {
const opts = this.opts;
const key = opts.key;
const externalKey = this.externalKey;
let json = this.session.toJSON();
// set expire for check
const maxAge = opts.maxAge ? opts.maxAge : ONE_DAY;
if (maxAge === 'session') {
// do not set _expire in json if maxAge is set to 'session'
// also delete maxAge from options
opts.maxAge = undefined;
} else {
// set expire for check
json._expire = maxAge + Date.now();
json._maxAge = maxAge;
}
// save to external store
if (externalKey) {
debug('save %j to external key %s', json, externalKey);
await this.store.set(externalKey, json, maxAge, {
changed,
rolling: opts.rolling,
});
this.ctx.cookies.set(key, externalKey, opts);
return;
}
// save to cookie
debug('save %j to cookie', json);
json = opts.encode(json);
debug('save %s', json);
this.ctx.cookies.set(key, json, opts);
}对于我们讨论的这种情况,可以看到就是将信息encode之后写入了cookie,并且包含了两个字段_expire和_maxAge。
简单验证一下,CONFIG添加encode和decode
const CONFIG = {
key: 'koa:sess', /** (string) cookie key (default is koa:sess) */
/** (number || 'session') maxAge in ms (default is 1 days) */
/** 'session' will result in a cookie that expires when session/browser is closed */
/** Warning: If a session cookie is stolen, this cookie will never expire */
maxAge: 86400000,
overwrite: true, /** (boolean) can overwrite or not (default true) */
httpOnly: true, /** (boolean) httpOnly or not (default true) */
signed: true, /** (boolean) signed or not (default true) */
rolling: false, /** (boolean) Force a session identifier cookie to be set on every response. The expiration is reset to the original maxAge, resetting the expiration countdown. default is false **/
encode: json => JSON.stringify(json),
decode: str => JSON.parse(str)
};
第一次访问时![]()
再次访问
_expire用来下次访问服务器时判断session是否已过期
valid(json) {
if (!json) return false;
if (json._expire && json._expire < Date.now()) {
debug('expired session');
return false;
}
const valid = this.opts.valid;
if (typeof valid === 'function' && !valid(this.ctx, json)) {
// valid session value fail, ignore this session
debug('invalid session');
return false;
}
return true;
}_maxAge用来保存过期时间,ctx.sessionOptions经过拦截器指向的其实是sess.opts
class Session {
/**
* Session constructor
* @param {Context} ctx
* @param {Object} obj
* @api private
*/
constructor(ctx, obj) {
this._ctx = ctx;
if (!obj) {
this.isNew = true;
} else {
for (const k in obj) {
// restore maxAge from store
if (k === '_maxAge') this._ctx.sessionOptions.maxAge = obj._maxAge;
else this[k] = obj[k];
}
}
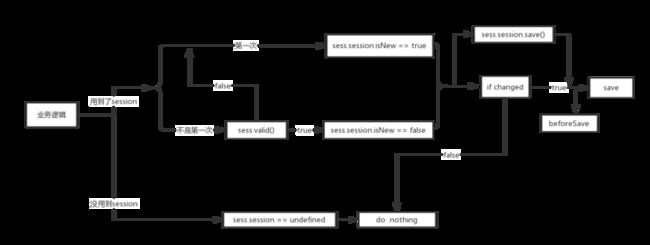
}画一个简单的流程图看一下这整个逻辑时怎样的
通常情况下,把session保存在cookie有下面两个缺点:
- Session is stored on client side unencrypted
- Browser cookies always have length limits
所以可以把session保存在数据库中等,在koa-session中,可以设置store并提供三个方法:get、set、destroy。
当设置了store的时候,初始化操作是在initFromExternal完成的
async initFromExternal() {
debug('init from external');
const ctx = this.ctx;
const opts = this.opts;
const externalKey = ctx.cookies.get(opts.key, opts);
debug('get external key from cookie %s', externalKey);
if (!externalKey) {
// create a new `externalKey`
this.create();
return;
}
const json = await this.store.get(externalKey, opts.maxAge, { rolling: opts.rolling });
if (!this.valid(json)) {
// create a new `externalKey`
this.create();
return;
}
// create with original `externalKey`
this.create(json, externalKey);
this.prevHash = util.hash(this.session.toJSON());
}externalKey事实上是session数据的索引,此时相比于直接把session存在cookie来说多了一层,cookie里面存的不是session而是找到session的钥匙。当然我们保存的时候就要做两个工作,一是将session存入数据库,另一个是将session对应的key即(externalKey)写入到cookie,如下:
// save to external store
if (externalKey) {
debug('save %j to external key %s', json, externalKey);
await this.store.set(externalKey, json, maxAge, {
changed,
rolling: opts.rolling,
});
this.ctx.cookies.set(key, externalKey, opts);
return;
}我们可以测试一下,事实上我们可以把session存在任意的媒介,不一定非要是数据库(主要是电脑没装数据库),只要store提供了三个接口即可:
const session = require('koa-session');
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const path = require('path');
const fs = require('fs');
app.keys = ['some secret hurr'];
const store = {
get(key) {
const sessionDir = path.resolve(__dirname, './session');
const files = fs.readdirSync(sessionDir);
for (let i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
if (files[i].startsWith(key)) {
const filepath = path.resolve(sessionDir, files[i]);
delete require.cache[require.resolve(filepath)];
const result = require(filepath);
return result;
}
}
},
set(key, session) {
const filePath = path.resolve(__dirname, './session', `${key}.js`);
const content = `module.exports = ${JSON.stringify(session)};`;
fs.writeFileSync(filePath, content);
},
destroy(key){
const filePath = path.resolve(__dirname, './session', `${key}.js`);
fs.unlinkSync(filePath);
}
}
const CONFIG = {
key: 'koa:sess', /** (string) cookie key (default is koa:sess) */
/** (number || 'session') maxAge in ms (default is 1 days) */
/** 'session' will result in a cookie that expires when session/browser is closed */
/** Warning: If a session cookie is stolen, this cookie will never expire */
maxAge: 86400000,
overwrite: true, /** (boolean) can overwrite or not (default true) */
httpOnly: true, /** (boolean) httpOnly or not (default true) */
signed: true, /** (boolean) signed or not (default true) */
rolling: false, /** (boolean) Force a session identifier cookie to be set on every response. The expiration is reset to the original maxAge, resetting the expiration countdown. default is false **/
store
};
app.use(session(CONFIG, app));
// or if you prefer all default config, just use => app.use(session(app));
app.use(ctx => {
// ignore favicon
if (ctx.path === '/favicon.ico') return;
let n = ctx.session.views || 0;
ctx.session.views = ++n;
if (n >=5 ) ctx.session = null;
ctx.body = n + ' views';
});
app.listen(3000);
console.log('listening on port 3000');浏览器输入localhost:3000,刷新五次则views重新开始计数。
全文完。