JAVA-高频面试题汇总:二叉树(一)
前言
为了让小伙伴们更好地刷题,我将所有leetcode常考题按照知识点进行了归纳.
已完成:
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:动态规划
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:二叉树(二)
接下来我对树这一知识点进行归纳总结,树的内容总结了二十多道,将分为几篇文章讲解,归纳基于JAVA语言,是我一边复习一边整理的,如有疑惑欢迎交流!
小编微信: Apollo___quan
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:树(一)
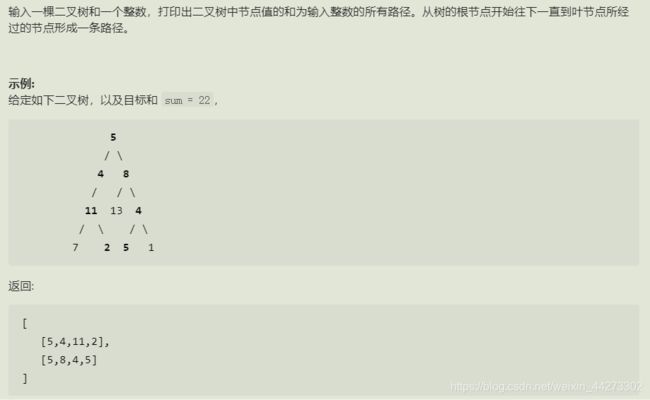
1.二叉树中和为某一值的路径
思路
1.创建path记录路径,用tar记录路径和(tar = tar - root.val)
2.前序遍历,添加当前节点到path,当tar == 0 且无左右子树时将path加到res
3.遍历左子树与右子树,最后一步删除当前节点表示前两步结束后进行回溯
注意的点:
1.ArrayList与LinkedList的remove方法
2.res.add(new ArrayList(path))时传入的应是新的对象而不能时path对象,否则后续path发生变化会影响结果
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); //List是接口 需要ArrayList或LinkedList实现
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
recur(root, sum);
return res;
}
void recur(TreeNode root, int tar){
if(root==null) return;
path.add(root.val);
tar = tar - root.val; //值传递,若回溯不改变上一层的tar值,与path相区别
if(tar == 0 && root.left ==null && root.right ==null){
res.add(new ArrayList(path));//如果直接传入path,传的是path对象,后续对path的改动都会有影响
}
recur(root.left, tar);
recur(root.right, tar);
path.remove(path.size()-1); //注意path是全局变量,如果回溯需要删除该节点
}
}
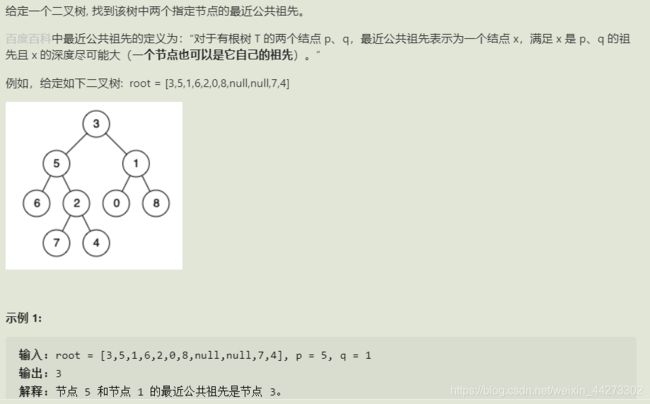
2.二叉树的最近公共祖先
思路
1.递归,可能出现的情况为 ①目标点在root异侧 ②root点为其中一点 ③两侧都没有目标点
2.设置Left与Right遍历左右子树,根据Left与Right讨论上面三种情况,先假设Left与Right的递归合理,否则容易绕晕
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q) return root; //为空树或节点为其中一点,直接返回
TreeNode Left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode Right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(Left == null && Right == null) return null; //左右都无目标点,返回null
else if(Left == null) return Right; //左子树没有,都在右子树,返回右子树遍历结果
else if(Right == null) return Left; //右子树没有,都在左子树,返回左子树遍历结果
else return root; //左右都不为null,说明在两边,该点即为最近公共点
}
}
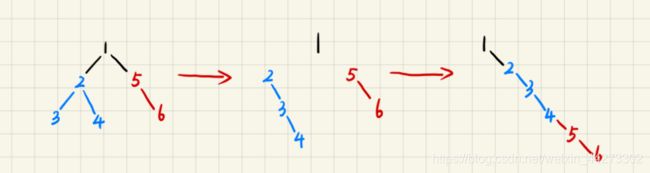
3.二叉树展开为链表
思路
推荐leetcode大佬的解答,思路很清晰
其实是分为三步:
1.首先将根节点的左子树变成链表
2.其次将根节点的右子树变成链表
3.最后将变成链表的右子树放在变成链表的左子树的最右边
这就是一个递归的过程,递归的一个非常重要的点就是:
不去管函数的内部细节是如何处理的,我们只看其函数作用以及输入与输出。
对于函数flatten来说:
1.函数作用:将一个二叉树,原地将它展开为链表
2.输入:树的根节点
3.输出:无
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return ;
}
//将根节点的左子树变成链表
flatten(root.left);
//将根节点的右子树变成链表
flatten(root.right);
TreeNode temp = root.right;
//把树的右边换成左边的链表
root.right = root.left;
//记得要将左边置空
root.left = null;
//找到树的最右边的节点
while(root.right != null) root = root.right;
//把右边的链表接到刚才树的最右边的节点
root.right = temp;
}
}
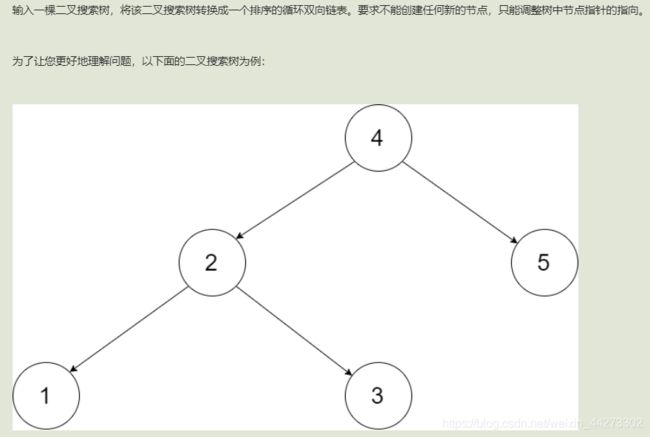
4.二叉搜索树与双向链表
这题与第三题乍一看很像,其实差别很大
思路
1.中序遍历,一边利用pre指针不断记录节点关系
2.注意最后头尾节点的连接,因为是循环双向链表
class Solution {
Node pre = null;
Node head; //head为了记录头节点
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root == null) return pre;
dfs(root);
head.left = pre;
pre.right = head;
return head;
}
public void dfs(Node node){
if(node == null) return;
dfs(node.left);
if(pre != null) pre.right = node;
else head = node; //head记录头节点
node.left = pre; //如果是头节点则node = head,最终head.left都要覆盖为pre,所以这一步没影响
pre = node; //pre指针后移到node
dfs(node.right);
}
}
5.二叉树的右视图
思路
其实就是层序遍历只记录每层最后一点
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int count = 0;
int size = queue.size(); //记录长度
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
count++;
if(count == size ){
//只添加最后一个数据,与层序遍历区别
list.add(node.val);
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
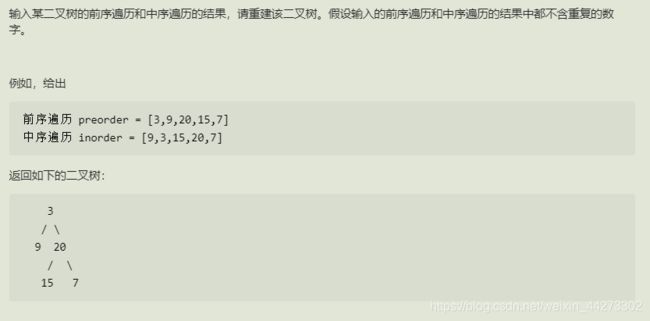
6.重建二叉树
思路
1.利用前序遍历与中序遍历的特性将树分为左子树与右子树
2.化为子问题进行递归,每一代求解root.left与root.right,并返回root
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] in) {
if(pre.length==0) return null;
TreeNode root =new TreeNode(0);
root.val=pre[0]; //前序遍历的第一个节点即根节点,后面跟着左子树,然后右子树
int index=0;
for(int i=0;i<in.length;i++){
if(in[i]==root.val) {
//中序遍历中找根节点,右边的为右子树,左边的为左子树
index=i;
break;
}
}
//将左子树看成一棵二叉树调用该方法,可以得到左子树根结点,即上面根结点的左子结点
root.left=reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,1,index+1),Arrays.copyOfRange(in,0,index));
//将右子树看成一棵二叉树调用该方法,可以得到右子树根结点,即上面根结点的右子结点
root.right=reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,index+1,pre.length),Arrays.copyOfRange(in,index+1,in.length));
return root;
}
}
第二部分已完成
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:二叉树(二)