常用模块
系统调用os模块
得到当前工作目录,即当前Python脚本工作的目录路径: os.getcwd()
返回指定目录下的所有文件和目录名:os.listdir()
函数用来删除一个文件:os.remove()
删除多个目录:os.removedirs(r“c:\python”)
检验给出的路径是否是一个文件:os.path.isfile()
检验给出的路径是否是一个目录:os.path.isdir()
判断是否是绝对路径:os.path.isabs()
检验给出的路径是否真地存:os.path.exists()
返回一个路径的目录名和文件名:os.path.split() e.g os.path.split(’/home/swaroop/byte/code/poem.txt’) 结果:(’/home/swaroop/byte/code’, ‘poem.txt’)
分离扩展名:os.path.splitext() e.g os.path.splitext(’/usr/local/test.py’) 结果:(’/usr/local/test’, ‘.py’)
获取路径名:os.path.dirname()
获得绝对路径: os.path.abspath()
获取文件名:os.path.basename()
运行shell命令: os.system()
读取操作系统环境变量HOME的值:os.getenv(“HOME”)
返回操作系统所有的环境变量: os.environ
设置系统环境变量,仅程序运行时有效:os.environ.setdefault(‘HOME’,’/home/alex’)
给出当前平台使用的行终止符:os.linesep Windows使用’\r\n’,Linux and MAC使用’\n’
指示你正在使用的平台:os.name 对于Windows,它是’nt’,而对于Linux/Unix用户,它是’posix’
重命名:os.rename(old, new)
创建多级目录:os.makedirs(r“c:\python\test”)
创建单个目录:os.mkdir(“test”)
获取文件属性:os.stat(file)
修改文件权限与时间戳:os.chmod(file)
获取文件大小:os.path.getsize(filename)
结合目录名与文件名:os.path.join(dir,filename)
改变工作目录到dirname: os.chdir(dirname)
获取当前终端的大小: os.get_terminal_size()
杀死进程: os.kill(10884,signal.SIGKILL)
系统调用sys模块
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径
sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0)
sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息
sys.maxint 最大的Int值
sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值
sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称
sys.stdout.write(‘please:’) #标准输出 , 引出进度条的例子, 注,在py3上不行,可以用print代替
val = sys.stdin.readline()[:-1] #标准输入
sys.getrecursionlimit() #获取最大递归层数
sys.setrecursionlimit(1200) #设置最大递归层数
sys.getdefaultencoding() #获取解释器默认编码
sys.getfilesystemencoding #获取内存数据存到文件里的默认编码
time模块
在Python中,通常有这几种方式来表示时间:
1.时间戳(timestamp), 表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏移量。例子:1554864776.161901
2.格式化的时间字符串,比如“2020-10-03 17:54”
3.元组(struct_time)共九个元素。由于Python的time模块实现主要调用C库,所以各个平台可能有所不同,mac上:time.struct_time(tm_year=2020, tm_mon=4, tm_mday=10, tm_hour=2, tm_min=53, tm_sec=15, tm_wday=2, tm_yday=100, tm_isdst=0)
time模块方法
1.time.localtime([secs]):将一个时间戳转换为当前时区的struct_time。若secs参数未提供,则以当前时间为准。
2.time.gmtime([secs]):和localtime()方法类似,gmtime()方法是将一个时间戳转换为UTC时区(0时区)的struct_time。
3.time.time():返回当前时间的时间戳。
4.time.mktime(t):将一个struct_time转化为时间戳。
5.time.sleep(secs):线程推迟指定的时间运行,单位为秒。
6.time.asctime([t]):把一个表示时间的元组或者struct_time表示为这种形式:’Sun Oct 1 12:04:38 2019’。如果没有参数,将会将time.localtime()作为参数传入。
7.time.ctime([secs]):把一个时间戳(按秒计算的浮点数)转化为time.asctime()的形式。如果参数未给或者为None的时候,将会默认time.time()为参数。它的作用相当于time.asctime(time.localtime(secs))。
8.time.strftime(format[, t]):把一个代表时间的元组或者struct_time(如由time.localtime()和time.gmtime()返回)转化为格式化的时间字符串。如果t未指定,将传入time.localtime()。
举例:time.strftime(“%Y-%m-%d %X”, time.localtime()) #输出’2017-10-01 12:14:23’
9.time.strptime(string[, format]):把一个格式化时间字符串转化为struct_time。实际上它和strftime()是逆操作。
举例:time.strptime(‘2017-10-3 17:54’,”%Y-%m-%d %H:%M”) #输出 time.struct_time(tm_year=2017, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=3, tm_hour=17, tm_min=54, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=1, tm_yday=276, tm_isdst=-1)
字符串转时间格式对应表
%a Locale’s abbreviated weekday name.
%A Locale’s full weekday name.
%b Locale’s abbreviated month name.
%B Locale’s full month name.
%c Locale’s appropriate date and time representation.
%d Day of the month as a decimal number [01,31].
%H Hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number [00,23].
%I Hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number [01,12].
%j Day of the year as a decimal number [001,366].
%m Month as a decimal number [01,12].
%M Minute as a decimal number [00,59].
%p Locale’s equivalent of either AM or PM. (1)
%S Second as a decimal number [00,61]. (2)
%U Week number of the year (Sunday as the first day of the week) as a decimal number [00,53]. All days in a new year preceding the first Sunday are considered to be in week 0. (3)
%w Weekday as a decimal number [0(Sunday),6].
%W Week number of the year (Monday as the first day of the week) as a decimal number [00,53]. All days in a new year preceding the first Monday are considered to be in week 0. (3)
%x Locale’s appropriate date representation.
%X Locale’s appropriate time representation.
%y Year without century as a decimal number [00,99].
%Y Year with century as a decimal number.
%z Time zone offset indicating a positive or negative time difference from UTC/GMT of the form +HHMM or -HHMM, where H represents decimal hour digits and M represents decimal minute digits [-23:59, +23:59].
%Z Time zone name (no characters if no time zone exists).
时间转换图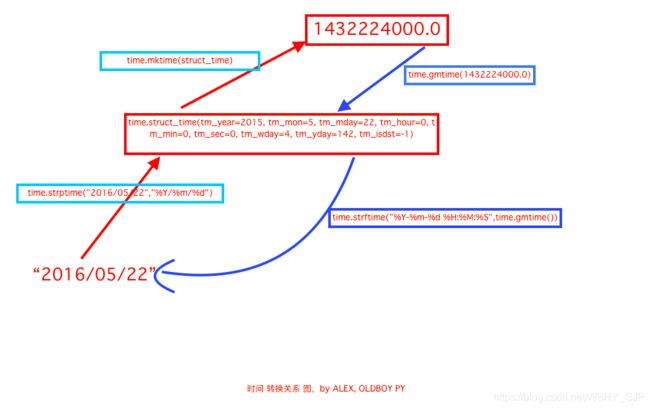
datetime模块
datetime模块常见方法:
datetime.date:表示日期的类。常用的属性有year, month, day;
datetime.time:表示时间的类。常用的属性有hour, minute, second, microsecond;
datetime.datetime:表示日期时间。
datetime.timedelta:表示时间间隔,即两个时间点之间的长度。
datetime.tzinfo:与时区有关的相关信息。(这里不详细充分讨论该类,感兴趣的童鞋可以参考python手册)
需要记住的几个方法:
1.d=datetime.datetime.now() 返回当前的datetime日期类型
d.timestamp(),d.today(), d.year,d.timetuple()等方法可以调用
2.datetime.date.fromtimestamp(322222) 把一个时间戳转为datetime日期类型
3.时间运算
datetime.datetime.now()
datetime.datetime(2017, 10, 1, 12, 53, 11, 821218)
datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(4) #当前时间 +4天
datetime.datetime(2017, 10, 5, 12, 53, 35, 276589)
datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(hours=4) #当前时间+4小时
datetime.datetime(2017, 10, 1, 16, 53, 42, 876275)
4.时间替换
d.replace(year=2999,month=11,day=30)
datetime.date(2999, 11,