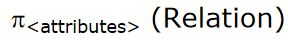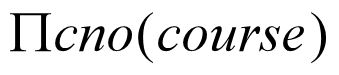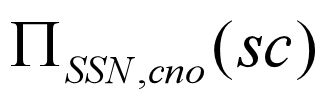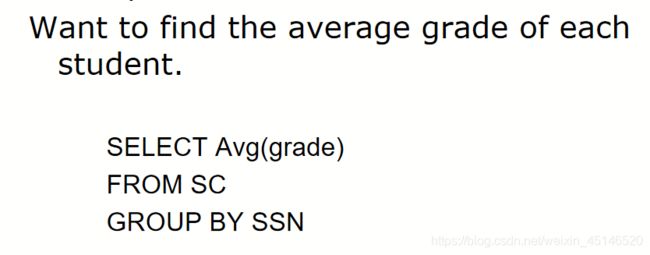数据库笔记
数据库系统概论
- 关系代数(Relational Aigebra):
-
- Union
- difference
- insersection
- cartesian product (卡迪尔积)(cross product)
- select operation
- projection operation
- RA's join
-
- Join
-
- Theta Join(θ Join)
- equi join(=)
- natural join(*)
-
-
- example (?)
-
- Outer Joins (Special Case of EquiJoin)
-
- left outer join
- right outer join
- full outer join
- Division
- View
- Specifying constraints
-
- not null constraint
- unique constraint
- primary key constraint
- Foreign key constraint
- check constraint
- default constraint
- alter table add constraint
- index
- select statement
-
- alias
- distinct
- between or not between (range search)
- in or not in (set membership search)
- like or not like (pattern match search)
-
- escape character
- is NULL or is not NULL
- ordered by
- aggregate function (聚合函数)
- group by clouse
- having clouse
- Multiple table (sql多表)
-
- inner join
- outer join
-
- Left outer join
- Right outer join
- Full outer join
- Alias
-
- date format
- trunc
- last_day and next_day
- set operation
-
- union
- intersect
- Minus
- sub queries
- comparison-operator
- exists and not exists
- insert
- update
- delete
- scalar function(标量函数)
- Trivial FD (平凡函数依赖):
- 数据库函数依赖和范式:
-
- attribute clouse (computing F+)
-
- super key and primary
- chase判断无损连接性算法
- ER图
- 锁
关系代数(Relational Aigebra):
链接一
链接二
Union
Duplicate tuples will not appear in the output as (D-3) both in R and S.
R and S must satisfy the following rules:
- Rule 1: have the same degree
- Rule 2:domain of the ith attribute both of R and S must be same
difference
- semantics: R-S is the relation containing all tuples in R that do not appear in S.
insersection
R intersection S returns all tuples that appears both in R and S
![]()

cartesian product (卡迪尔积)(cross product)
- Assuming R has n attributes and S has m attributes respectively,the cartesian product can be written as:
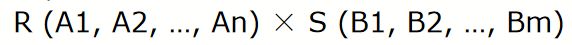
result of the above set operation is:

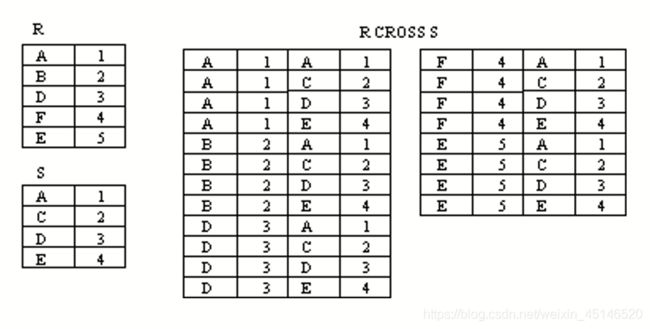
Duplicate tuples contain in ouput !!!
select operation
- This operation retrieves a subset of tuples in a relation that satisfy a select condition.

such as : - AGE=19 is a condition and student is a relation.

- And two and more condition :

- The selection operation is commutative. The below are equivalent.

projection operation
RA’s join
链接一
Join
Theta Join(θ Join)
equi join(=)
- A join is called an equijoin if only equality operator is used in all join conditions.
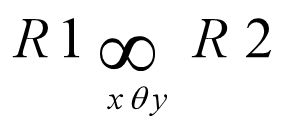
- < join condition> must always have = operation


natural join(*)
- if an attribute is common both in two relation,we can remove one in the join
- natural join omit the condition

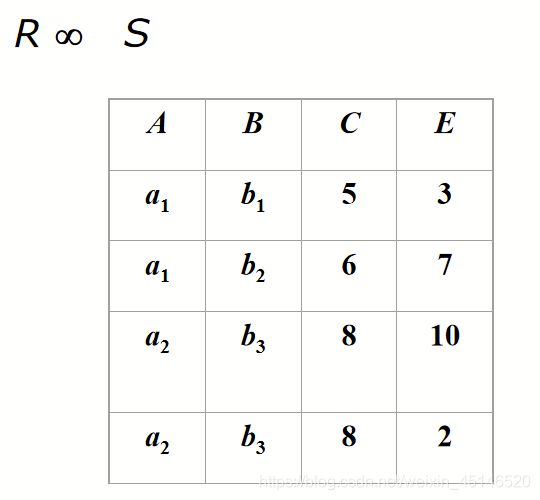
example (?)
Outer Joins (Special Case of EquiJoin)
How to keep dangling tuples in the result of a join?
left outer join

is similar to a natural join but keep all dangling tuples of R1.
right outer join

is similar to a natural join but keep all dangling tuples of R2.
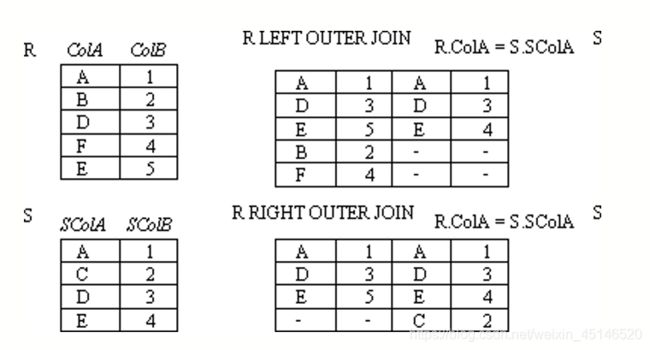
full outer join

is similar to a natural join but keep all dangling tuples of both R1 and R2.

The advantages of outer join is to take the union of tuples from two relations that are not union compatible.
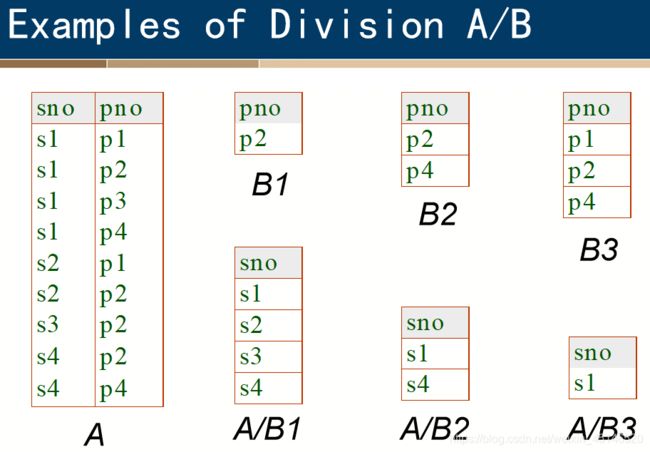
Division
Precondition: in A/B, the attributes in B must be included in the schema for A. Also, the result has attributes A-B
Another example is: Suppose we want to find all the students who have selected all courses (See Figure 3.19 Course Table ) provided by the school.
We can think of it as three steps:
1.We can obtain the NO. of all courses provided by the school by:
2.We can also find all SSN, cno pairs for which the student has selected courses by:
3.Now we need to find all students who selected all the courses. The divide operation provides exactly those students:
View
an interesting example
create table table1 (bm float )
insert into table1 values(5000)
create view TestViewCheckOption AS
select * from Table1 where Bm < 5003
with check option
update TestViewCheckOption set Bm = 5005
go
- update error because 5005 can not appear in view with check option.
And a view can be changed by alter statement.
ALTER VIEW view_name [(column_list)] [WITH ENCRYPTION]
AS select_statement
[WITH CHECK OPTION]
Specifying constraints
not null constraint
For item must contain a not null value
unique constraint
can not have same value.
Note that you can have many UNIQUE constraints per table, but only one PRIMARY KEY constraint per table.
primary key constraint
Foreign key constraint
- two tables, one is referencing table, another is referenced table
- columns in referencing table must primary key or other candicate key in referenced table

check constraint
default constraint
alter table add constraint
index
- A database index enables the database application to find data quickly without having to scan the whole table.

select statement
- The SELECT clause lists what columns to return.
- The FROM clause which indicates the table(s) from which data is to be retrieved.
- The WHERE clause specifies which rows to retrieve.
- The GROUP BY clause groups rows sharing a property so that an aggregate function can be applied to each group. The WHERE clause is applied before the GROUP BY clause.
- The HAVING clause selects among the groups defined by the GROUP BY clause. Because it acts on the results of the GROUP BY clause, aggregation functions can be used in the HAVING clause predicate.
- The ORDER BY clause specifies an order in which to return the rows. Without an ORDER BY clause, the order of rows returned by an SQL query is undefined.
alias
distinct
between or not between (range search)
in or not in (set membership search)
like or not like (pattern match search)
use for inexact condition search
- The % wildcard matches zero or more characters of any type.
- The _ wildcard matches exactly one character of any type.


To match strings that there are at least one character between ‘a’ and ‘c’ .
SELECT SNAME
FROM STUDENT
WHERE SNAME LIKE ‘a_%c’;
escape character
If the search strings can include the wildcards(%,_) itself, we can use an escape character to represent the wildcards.
For example, to match the string ‘20%’, we can use :
Like ‘20#%’ ESCAPE ‘#’
is NULL or is not NULL
ordered by
aggregate function (聚合函数)
distinct is not an argument in the function,it use before function is
applied.
group by clouse
having clouse
- The HAVING clause was added to SQL because the WHERE keyword could not be used with aggregate functions.



Multiple table (sql多表)
SQL allows us to query multiple tables in one SELECT-FROM-WHERE statement.
- The SELECT and WHERE can refer to the attributes of any of the tables once we list each table in the FROM clause.
- ANSI standard SQL specifies four types of JOINs: INNER, OUTER, LEFT, and RIGHT.
- a table (base table, view, or joined table) can JOIN to itself in a self-join.
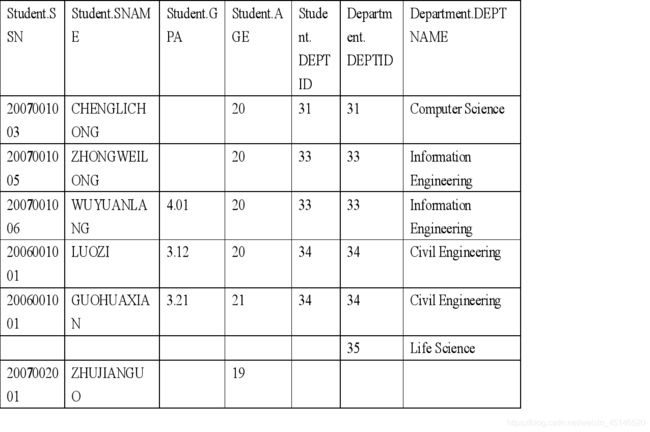
table student
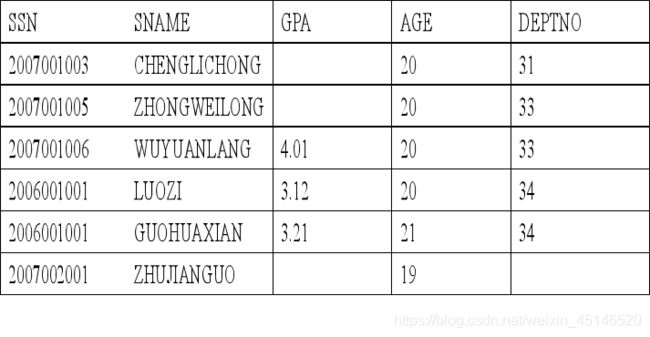
table department

inner join
outer join
- Rows are returned even when there are no matches through the JOIN critieria.
Left outer join
Right outer join
Although 35 have no students we should list it too.

Full outer join
Alias
date format
date ------- to_char
select the name,job and date of hire of the employees in department 20(format the hiredate column using a picture MM/DD/YY).
Select ename “employee”,job, to_char(hiredate,’MM/DD/YY’) “HireDate”
From emp
Where deptno=20
Use a picture to format hiredate as DAY(day of the week),MONTH(name of the month),DD(day of the month) and YYYY(year).
Select to_char(hiredate,’DAY,MONTH,DD,YYYY’ ) “HireDate”
From EMP
Which employees were hired in March?
Select ename “Employee”,hiredate
From emp
Where to_char(hiredate,’MON’)=‘3月’
Show the weekday of the first day of the month in which each employee was hired.
Select ename “employee”,hiredate,to_char(trunc(hiredate,’month’),’day’)
From emp
trunc
1 trunc用于对值的截断。用法有两种:sysdate=2010-10-20
- trunc(NUMBER)截断数字:trunc(n1,n2),n2表示要截断到哪一位。也可为负数,如:
trunc(19.85)——>19; trunc(19.85,1)——>19.8; - trunc(DATE)截断日期
截取今天:trunc(sysdate,‘dd’)或trunc(sysdate)——》2012-03-24
截取本周第一天:trunc(sysdate,‘d’)——》2012-3-18
截取本月第一天:trunc(sysdate,‘mm’)——》2012-3-1
截取本年第一天:trunc(sysdate,‘y’)——》2012-1-1
last_day and next_day
last_day求一个日期所在月的最后一天
next_day(日期,‘sun|mon|…|fri|sat’)从日期后的下一天开始找,如果与相应的星期满足,则返回满足条件的日期。
求一个月的最后一天
SQL> select last_day(sysdate) from dual;
下一个星期一的日期
SQL> select next_day(sysdate,‘mon’) from dual;
下个月的第一个星期五
SQL> select next_day(last_day(sysdate),‘fri’) from dual
set operation
链接一
union
- union removes duplicate rows.
- union all keeps duplicate rows.
intersect
Minus
sub queries
comparison-operator
链接一
ALL – the comparison must be true for all returned values.
ANY – The comparison need only be true for one returned value.
IN may be used in place of = ANY.
NOT IN may be used in place of != ALL.



exists and not exists
insert
update
delete
scalar function(标量函数)
链接一
Trivial FD (平凡函数依赖):
such as {stu,num,id}
{stu,num} -> { stu } is a Trivial FD
{stu,num} -> { id } is not a Trivial FD
数据库函数依赖和范式:
函数依赖及范式
1NF、2NF、3NF、BCNF
范式
范式练习题
attribute clouse (computing F+)
super key and primary
- AB is a superkey of R since (AB)+ = ABCDE.
- Since A+ = A, B+ = BD, neither A nor B is a superkey.
- Hence ,AB is a candidate key.
one
for each pair AiAj, i != j
if Ai or Aj is a candidate key
then AiAj is not a candidate key;
else compute (Ai Aj)+;
if (AiAj)+ = A1 A2 ... An
then (Ai Aj) is a candidate key;
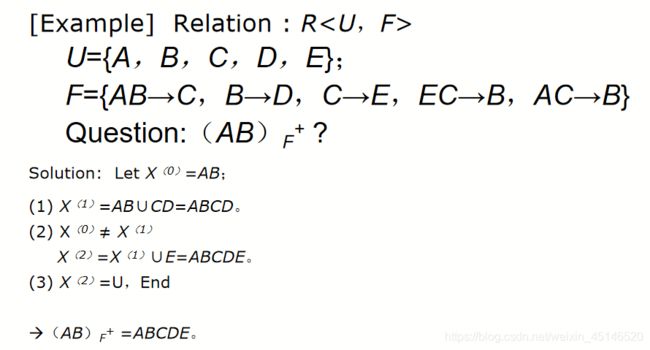
Relation schema: R = (A, B, C, D, E)
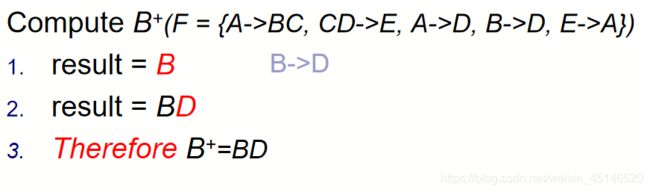
F = {A->BC, CD->E, A->D, B->D, E->A}
(1)Find A+, B+, BC+
(2)Find Candidate keys of R
hence candicate keys are ?
A?B?D?E? BC? CD?
Candidate keys : A 、E、 BC、 CD
chase判断无损连接性算法
已知R
F={A→C,B→C,C→D,DE→C,CE→A},R的一个分解为R1(AD),R2(AB),R3(BE),R4(CDE),R5(AE),判断这个分解是否具有无损连接性。

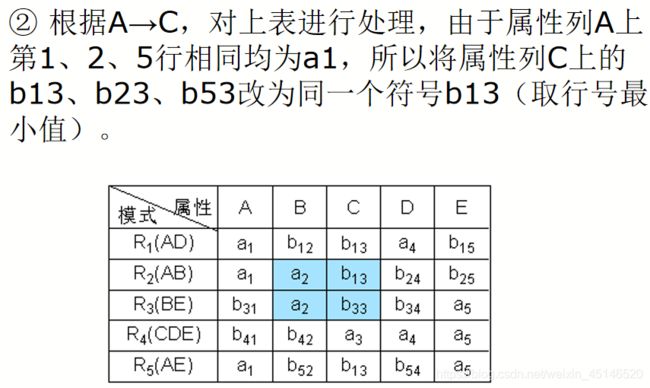
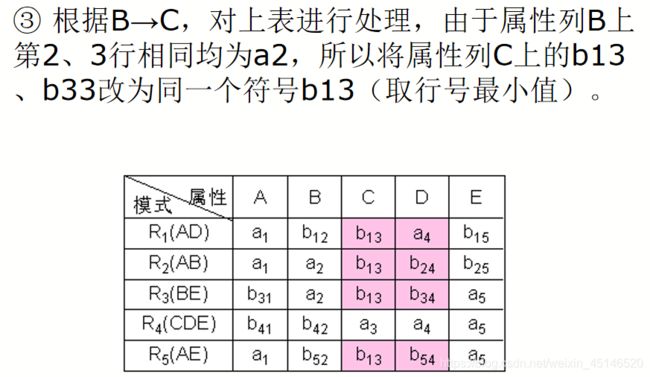



超键,候选键,主键,外键:链接地址
一对一、一对多、多对多等关系: 链接地址
ER图
ER图解析
锁
锁一
锁二